
It is not able to detect less than 30. The survivor curve construction is performed by counting microbiologic survivors in terms of colony-forming units recovered after exposing the microbiologic population to sublethal sterilizing cycles of graded exposures of EO with all other parameters except time remaining constant.
The death curve for organisms exhibiting substantial resistance will have a shallow slope and those with low resistance to the sterilization process will have a much steeper slope see Figure 2.
Survivor curve of sterilization. Sterilization Criteria. Survivor curve Death Curve D Value Z Value F Value Sensitivity. The data indicate that the survival curves for liquid chemical sterilants may not exhibit log-linear kinetics and the shape of the survivor curve may vary depending of the formulation chemical nature and stability of the liquid chemical sterilant.
The graphic representation of inactivation against increasing exposure to stated conditions AAMI 2006c. Extent of exposure to a sterilization. A straight line survivor curve such as the one shown in Figure 1 is typical.
The D-value time to reduce the microbial population by 90 for Bst should be 15 to 30 minutes at 1211C 250F. 1 For the purpose of this discussion a D121 value of 20 minutes and a sterilization temperature of 121C 250F is used. A straight line survivor curve such as the one shown in Figure 1 is typical.
The D-value time to reduce the microbial population by. Slightly below the chamber sterilization temperature to avoid superheating of the steam as it enters the chamber. The linearity of the curve implies that the value of the exponent n is 1 or very close to 1.
Based on these findings if the number of survivors is N the appropriate kinetic model for the rate of inactivation is represented by the following equation. Using this model the response equation when EtO concentration and temperature are kept. The SurvivalKill calculations were initially used when the survivor curve method was the primary means of calculating the D-value.
The survivor curve D-value method measures the number of surviving spores after a sterilization insult. It is not able to detect less than 30. Survivor Curve Construction Method.
The survivor curve construction method involves the direct enumeration of survivors in terms of colony forming units CFUs recovered after exposure to graded amounts of the sterilization cycle. A CFU is defined as a visible outgrowth of a population of organisms arising from a single or multiple cells. Spore population which produces parabolic survivor curves.
Sterilization cycle is not to make sterile every object as. The slope of this line represents the resistance of the microorganism to the sterilization process. The death curve for organisms exhibiting substantial resistance will have a shallow slope and those with low resistance to the sterilization process will have a much steeper slope see Figure 2.
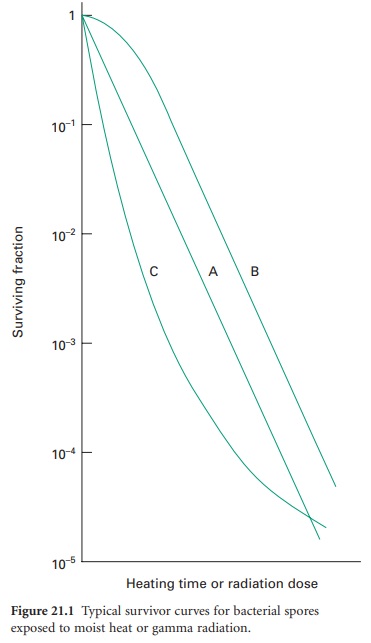
Is known precisely only during the survivor. Survivor curves have been employed principally in the examination of heat sterilization methods but can equally well be applied to any biocidal process. Figure 211 Typical survivor curves for bacterial spores exposed to moist heat or gamma radiation.
22 Expressions of resistance 221 D-value. Based Sterilization BBS method and the Overkill Sterilization OS method. The BBS method is defined as a sterilization process with.
D-values can be calculated by using one of two methods survivor curve or fraction negative analysis. A survivor curve plots the surviving microorganisms against a critical process parameter usually time. The logarithmic nature of the survivor or destruction curve indicates that complete destruction of the microbial population is not a theoretical possibility since a decimal fraction of the population should remain even after an infinite number of D values.
Direct enumeration is the process of determining the lethality of the sterilization process by construction of a survivor curve using direct enumeration physical counts through serial dilutions of surviving organisms. Utilize the semi-log survivor curve equation in support of the development and ongoing control of the sterilization program Assess risk associated with the cycle phases and identification of key and critical process parameters in the development of the sterilization process for liquid and poroushard goods load types. The survivor curve construction is performed by counting microbiologic survivors in terms of colony-forming units recovered after exposing the microbiologic population to sublethal sterilizing cycles of graded exposures of EO with all other parameters except time remaining constant.
Sterilization of health care productsgeneral. Death rates or survivor curve It is determined by assessing the reduction in the number of viable microorganisms resulting from contact with a given destructive force. Sterility indicators Changing appearances in colour or pattern the sterilization indicators visually show if cleaning conditions are passing or procedures have been.
The severe heat treatment during sterilization produces substantial changes in nutritional and sensory qualities of foods. A death rate curve or survivor curve. A typical relationship for a.