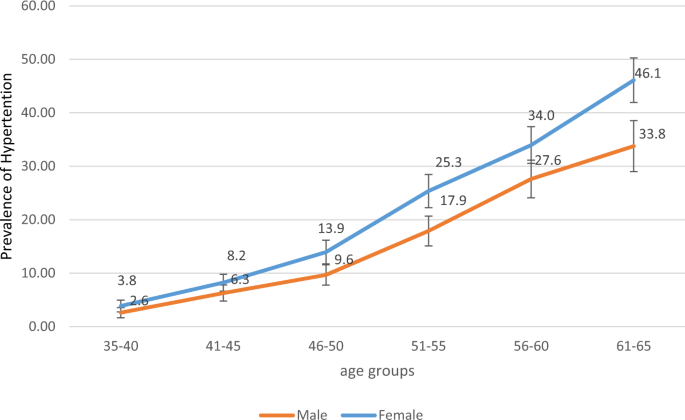
The estimated prevalence was found increased with age. It is slightly lower than 308 the reported worldwide prevalence for the general population.

42 The large disparity might be explained mainly by the different numbers of visits for BP measurements in these 2 systematic reviews.
Worldwide prevalence of hypertension a systematic review. The reported prevalence of hypertension varied around the world with the lowest prevalence in rural India 34 in men and 68 in women and the highest prevalence in Poland 689 in men and 725 in women. Data extraction All data were extracted independently by two investigators using a standardized protocol and data collection form. Results The reported prevalence of hypertension varied around the world with the lowest prevalence in rural India 34 in men and 68 in women and the highest prevalence in Poland 689 in men and 725 in women.
Awareness of hypertension was. The estimated prevalence 95 confidence interval of hypertension was 252 212 296 for the overall sample 347 274 428 for ART-experienced and 127 74 208 for ART-naïve participants. The estimated prevalence was found increased with age.
The pooled prevalence was 400 95 CI 329-478 for hypertension 967 95 CI 726-1238 for prehypertension 400 95 CI 210-648 for stage 1 hypertension and 095 95 CI 048-157 for stage 2 hypertension in children 19 years and younger. In subgroup meta-analyses the prevalence of childhood hypertension was higher when measured by aneroid. Our overall pooled prevalence of childhood hypertension was lower than that in a previous systematic review of the worldwide prevalence 40 vs 112.
42 The large disparity might be explained mainly by the different numbers of visits for BP measurements in these 2 systematic reviews. A recent systematic review and meta-analysis reported a global pooled prevalence rates of 40 95 confidence interval CI. The crude prevalence of hypertension ranged from 62 95CI.
40 to 84 to 489 95CI. 423 to 555 for men and 10 95CI. 81 to 12 to 473 95CI.
43 to 516 for women. In most studies prevalence of hypertension was higher in males than females. In addition prevalence across urban and rural ranged from 95 95CI.
136 to 214 to 516 95CI. 498 to 534 and 48 95CI. From the random-effects meta-analysis we estimated an overall hypertension prevalence of 289 251 328 with a prevalence of 295 248 343 among men and 250 202 297 among women.
We estimated a prevalence of 306 245 366 and 264 194 334 among urban and rural dwellers respectively. The pooled awareness rate of hypertension was 174 114 233. An estimated 113 billion people worldwide have hypertension most two-thirds living in low- and middle-income countries.
In 2015 1 in 4 men and 1 in 5 women had hypertension. Fewer than 1 in 5 people with hypertension have the problem under control. Hypertension is a major cause of premature death worldwide.
Globally an estimated 26 of the worlds population 972 million people has hypertension and the prevalence is expected to increase to 29 by 2025 driven largely by increases in. An estimate of the prevalence of hypertension in Nigeria. A systematic review and meta-analysis.
Adeloye D Basquill C Aderemi AV Thompson JY Obi FA. J Hypertens 332230-242 01 Feb 2015 Cited by. 53 articles PMID.
It is slightly lower than 308 the reported worldwide prevalence for the general population. 78 Applying the estimated prevalence from our analysis to the 34 million PLWH worldwide there are approximately 86 71 101 million PLWH are hypertensive. In addition to the overall study sample prevalence was also estimated for ART-experienced and ART-naïve participants for different.
A recent systematic review estimated that the overall worldwide prevalence of HTN is approximately 26 in the adult population. Hypertension is one of the 5 global leading causes of mortality in the world. Little is known about the current prevalence of hypertension in Iran however.
This systematic review aimed to investigate the current prevalence of hypertension in Iran. A systematic review of hypertension was conducted using international databases including Medline PubMed and Science Direct Scopus and Persian. This systematic review investigated the prevalence of hypertension and albuminuria markers of diabetes-related nephropathy and important predictors of kidney outcomes in pediatric type 2 diabetes.
Approximately 1 in 4 pediatric patients with type 2 diabetes had hypertension. Hypertension has become a growing public health concern particularly in developing countries with an estimated prevalence of 373 in comparison with 229 in industrialized nations. 1 Projections are that by the year of 2025 750 or 117 billion people of the people with hypertension in the world will be living in emerging nations.
The estimated prevalence 95 confidence interval of hypertension was 252 212 296 for the overall sample 347 274 428 for ART-experienced and 127 74 208 for ART-naïve participants. The estimated prevalence was found increased with age. For example a recent systematic review estimated that the pooled prevalence of hypertension in adults aged 65 years 610 in SSA was 25 times that among persons aged 1864 years 244 20.
Introduction It is unclear whether early detection of hypertension through screening leads to healthier behaviours and better control of blood pressure levels. There is a need to learn from studies that have assessed the impact of different screening approaches on patient important outcomes. This systematic review protocol outlines the methods that will be used to assess the comparative.