A neuroendocrine tumour NET is a tumour that develops from cells of the neuroendocrine system. These can occur anywhere in the body where neuroendocrine cells are present but most commonly they are seen in the intestine.

Metastatic neuroendocrine carcinoma is a heterogeneous group of tumors with variable aggressivenessDepending on the primary site different treatment options exist including liver directed treatments to liver involvement or systemic chemotherapy if the primary is pancreatic.
What is metastatic neuroendocrine carcinoma. A metastatic neuroendocrine tumor is the one which has spread from the place of its origin to other different parts in the body. Usually the cancer cells break off and separate from the main tumor or the site of cancer and then travel through the bloodstream to different parts of the body. The same is the case with the neuroendocrine tumors.
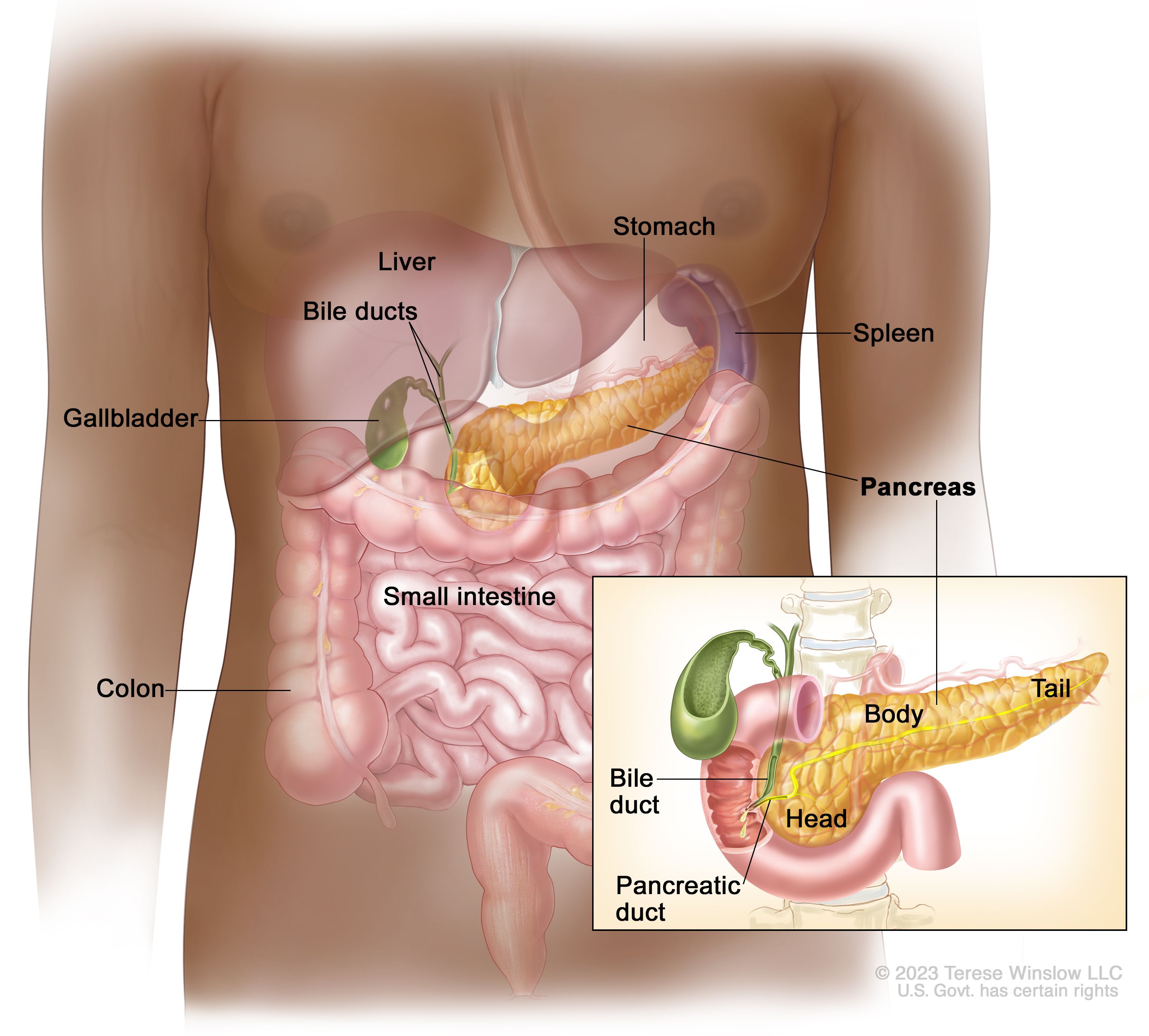
Secondary or Metastatic Cancer is a term used to describe cancer cells that have spread from the place where they started primary site to another part of the body secondary site. If these cells form a single secondary tumour that tumour is called a metastasis if they form more than one tumour at one or more secondary sites these secondary tumours are called metastases. Classification of Gastroenteropancreatic Neuroendocrine Tumors Most neuroendocrine metastases to the liver are of GI or pancreatic origin so-called gastroenteropancreatic GEP tumors Rindi et al 1998.
If a NET spreads to another part in the body from where it started doctors call it metastatic cancer. If this happens it is a good idea to talk with doctors who have experience in treating it. Doctors can have different opinions about the best standard treatment plan.
Clinical trials might also be an option. Learn more about getting a. A neuroendocrine tumour is a rare tumour that can develop in many different organs of the body.
It affects the cells that release hormones into the bloodstream neuroendocrine cells. It affects the cells that release hormones into the bloodstream neuroendocrine cells. Grade 3 high-grade tumor.
These cells divide at a fast rate and therefore grow quickly. For many types of cancer the grade also describes how much cancer cells look like healthy cells when viewed under a microscope called degree of differentiation. How different the tumour cells are from normal cells is described as differentiation.
The level of differentiation is an important prognostic factor for NETs. Well-differentiated NETs have a better prognosis than poorly differentiated neuroendocrine carcinomas. Grade is a description of how fast NET cells are growing.
The grade may be determined by counting the cells that are dividing called mitotic. Neuroendocrine cancertumor starts in the neuroendocrine cells in your body. These cells have features of both the type of cells- endocrine cells and nerve cells.
Most of these tumors are benign while some are malignant. These can occur anywhere in the body where neuroendocrine cells are present but most commonly they are seen in the intestine. A neuroendocrine tumour NET is a tumour that develops from cells of the neuroendocrine system.
Cells that are similar to nerve cells make up the neuroendocrine system. They make chemical messengers called hormones. Hormones control how different organs in the body work.
Amrubicin in patients with platinum-refractory metastatic neuroendocrine carcinoma and mixed adenoneuroendocrine carcinoma of the gastrointestinal tract. Araki T Takashima A Hamaguchi T Honma Y Iwasa S Okita N Kato K Yamada Y Hashimoto H Taniguchi H Kushima R Nakao K Boku N Shimada Y Anticancer Drugs 2016 Sep278794-9. Neuroendocrine Cancer Symptoms Neuroendocrine systems are mainly concerned with releasing hormones based on neurotic impulses.
Hence the main parts affected by the aggressive varieties of the Neuroendocrine Tumour NET include hormonal abnormalities like low blood sugar or. Cholecystectomy is also a routine part of liver resection for metastatic neuroendocrine tumor. Resecting as much as metastatic liver tumors from neuroendocrine carcinoma is called tumor surgical debulking.
This is often performed in combination with radiofrequency ablation to preserve as much non-affected liver parenchyma as possible. Tricky to answer. Metastatic neuroendocrine carcinoma is a heterogeneous group of tumors with variable aggressivenessDepending on the primary site different treatment options exist including liver directed treatments to liver involvement or systemic chemotherapy if the primary is pancreatic.
The prognosis is based on location pattern of spread and grade. Brain metastases BM are rarely reported in patients with neuroendocrine carcinoma NEC of non-lung origin and neuroendocrine tumors NET of the gastroenteropancreatic GEP or bronchopulmonary system. However symptomatic brain metastases are associated with dismal prognosis so early detection and treatment could be advisable.
Neuroendocrine prostate cancer NEPC is an aggressive variant of prostate cancer that may arise de novo or in patients previously treated with hormonal therapies for prostate adenocarcinoma as a mechanism of resistance. Despite being important to recognise the clinical features of NEPC are poorly defined and could help guide when to perform a biopsy to look for NEPC histologic transformation. Metastatic neuroendocrine carcinoma often presents as carcinoma of unknown primary.
Although most cases display immunohistochemical positivity for neuroendocrine markers subsets of cases display reduced or negative expression for some of these proteins.