
Exogenous comes from the Greek word exo meaning outside and gignomai meaning to produce. It then introduces several examples using supply and demand functions to explain how some variables are endogenous while others are exogenous to the system.
A factor in a causal model or causal system whose value is independent from the states of other variables in the system.
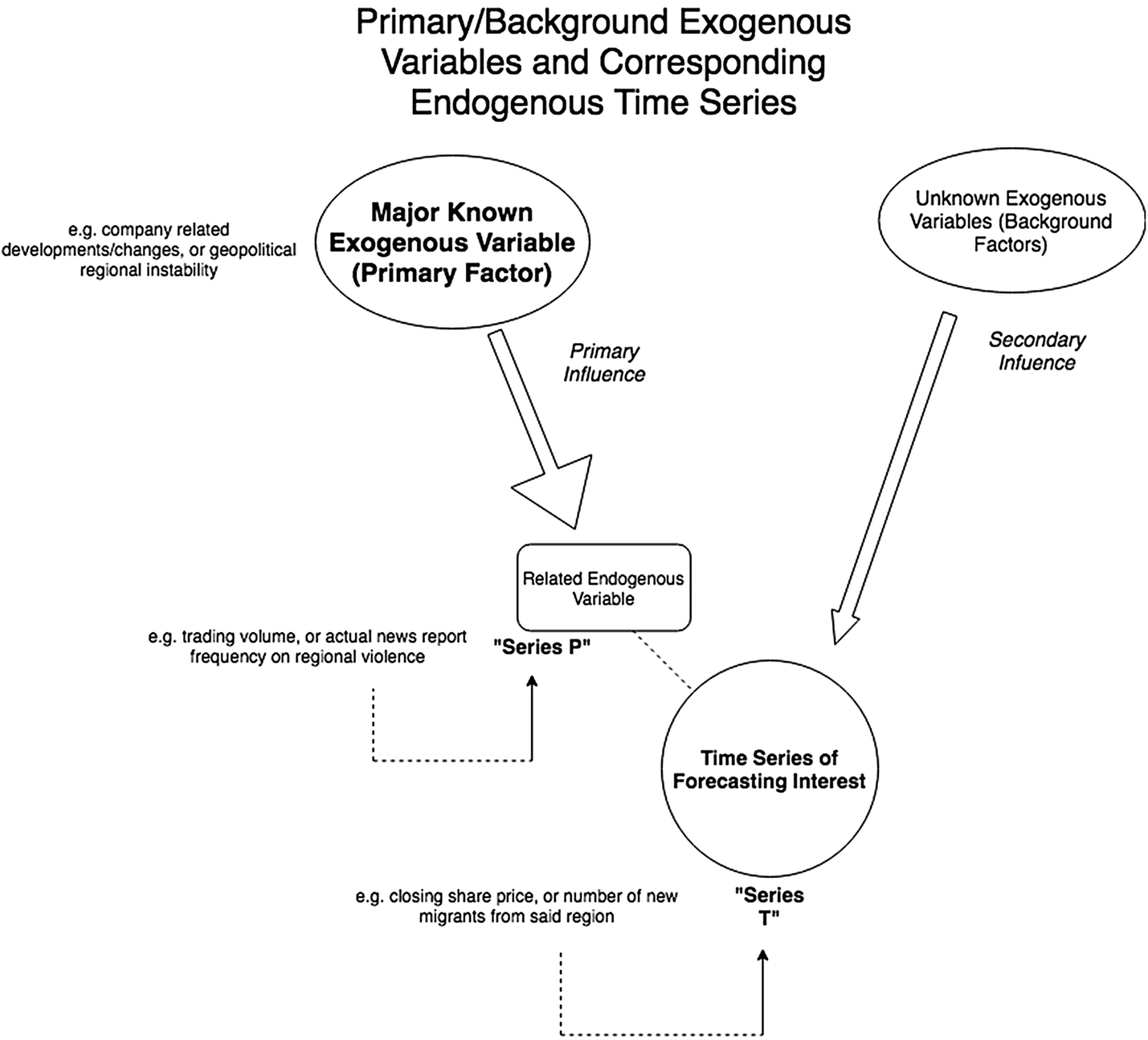
What are exogenous variables. An exogenous variable is a factor that is outside of a given economic model. It often has an impact on the outcome of the model or how certain situations turn out but it isnt usually determinative in its own right and changes in the model dont usually impact it. Exogenous variables are variables whose cause is external to the model and whose role is to explain other variables or outcomes in the model.
1 for example the model does not explain the variability in maternal educational level and parental income. Exogenous variables are variables whose cause is external to the model and whose role is to explain other variables or outcomes in the model. An exogenous variable is a variable that is not affected by other variables in the system.
For example take a simple causal system like farming. Variables like weather farmer skill pests and availability of seed are all exogenous to crop production. With respect to economics an exogenous variable is a variable that is independent or determined outside of the model.
This means that an exogenous variable has a one way relationship with the model in question it influences or impacts that model AND is not affected by the model. Two variables that can occur in regression models are. Variables that are explained by other variables within a model.
Variables that are not explained by other variables within a model. When using regression models researchers are often interested in understanding the relationship between one or more explanatory variables and a response variable. Exogenous variables are those variables that are independent from income Y and the interest rate i.
These are variables such as autonomous consumption. In contrast to endogenous variables exogenous variables are considered independent. In other words one variable within the formula doesnt dictate or directly correlate to a change in another.
3 Exogenous Variables of Tourism. These include demographic and social trends. Economic and financial issues.
Political legislative and regulatory trends. Even though not considered in the WTO study certain issues such as the environment and global warming cannot be ignored. Exogenous variables generated without are variables coming from outside and not explained by the model.
In a sense their role is similar to that of parameters. In the real world however exogenous variables are observed while parameters usually are not. Exogenous external growth factors include things such as the rate of technological advancement or the savings rate.
Endogenous internal growth factors meanwhile would be. Exogenous variable see also endogenous variable. A factor in a causal model or causal system whose value is independent from the states of other variables in the system.
A factor whose value is determined by factors or variables outside the causal system under study. An exogenous variable is a variable that appears in a model but whose value is determined outside of it. Its name derives from the Greek words exo meaning outside and gen meaning born.
An exogenous variable is a variable which is not affected by other variables. On the other hand a variable is said to be endogenous if its value is determined by other variables. In GMM application xtabond2 we need to classify our variables as endogenous predetermined and exogenous variables.
What is the criteria for doing so. How would we get to know which variable. An exogenous variable is a variable that is not affected by other variables but will affect other variables of the system.
Exogenous comes from the Greek word exo meaning outside and gignomai meaning to produce. For example take a simple system like vegetable farming. This post goes over the difference between endogenous and exogenous variables focusing on understanding the intuitive between these types of variables.
It then introduces several examples using supply and demand functions to explain how some variables are endogenous while others are exogenous to the system. Exogenous originated from the Greek words exo meaning outside and gen meaning born and describes something generated from outside a system. It is the opposite of endogenous which describes something generated from within the system.
Exogenous variables therefore are variables that are not caused by any other variables in a model of interest. In other words their value. We call the former endogenous variables and the latter exogenous variables.
For econometric applications the crucial difference between an endogenous and an exogenous variable is that we must assume that exogenous variables are not systematically affected by changes in the other variables of the model especially by changes in the endogenous.