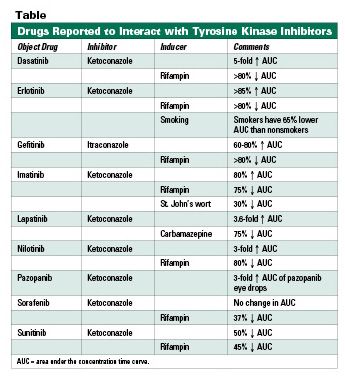
The Effect of Enzyme Inducers on TKIs Rifampin is an inducer of most CYP450 enzymes and has been shown to reduce the AUC of most TKIs. Rash with EGFR TKIs Skin adverse effects with EGFR inhibitors are very common and we must be aware of them to improve the care of our patients.
A tyrosine kinase inhibitor is a pharmaceutical drug that inhibits tyrosine kinases.
Tyrosine kinase inhibitor drugs side effects. Most common side effects are skin changes weakness diarrhoea and hepatotoxicity. The majority of the side effects are observed in a mild or moderate grade and are reversible. A rare but potentially fatal side effect of TKI therapy is interstitial lung disease ILD.
Side effects of the five drugs reviewed here highlight the differences between cardiovascular pulmonary gastrointestinal and endocrine toxicities as well as possible second malignancies. There is increasing evidence that patients whose disease is controlled by TKIs will have greater impact on their quality of life from comorbidities or drug adverse events than from the disease itself. However understanding the tyrosine kinase inhibition pathways has not yet translated into understanding the side effects of the BCR-ABL1 inhibitors.
While imatinib has been considered well tolerated it is clear that it has had side effects including gastrointestinal cardiovascular dermatologic and hepatic toxicities that a minority of patients cannot tolerate. Besides the haematological side effects of most of TKIs like anemia thrombopenia and neutropenia the most common extra-heamatologic adverse effects are edema nausea hypothyroidism vomiting and diarrhea. Other common side effects of afatinib were.
Diarrhoea 95 of patients stomatitis 72 paronychia 57 and dry skin 29. Rash with EGFR TKIs Skin adverse effects with EGFR inhibitors are very common and we must be aware of them to improve the care of our patients. These inhibitors usually show scarce binding selectivity which is particularly evident in type I over type II providing inhibition or other kinases with consequently off-target side effects.
The side effects of TKIs are usually mild and treatable. Side effects are often more noticeable when you first start treatment and they may improve with time. If you have severe side effects your doctor may ask you to stop taking the drug for a few days.
After a short break you may be able to start taking it again without having the same problems. Occasionally people need to stop treatment with the TKI they are taking because their side effects. A tyrosine kinase inhibitor is a pharmaceutical drug that inhibits tyrosine kinases.
Tyrosine kinases are enzymes responsible for the activation of many proteins by signal transduction cascades. The proteins are activated by adding a phosphate group to the protein a step that TKIs inhibit. TKIs are typically used as anticancer drugs but also for other diseases such as idiopathic pulmonary.
Approved kinase inhibitors were well optimized for their target kinases. This profiling also implicates activity at particular off-target kinases in drug side effects. Thus large-scale kinase profiling at both Km and physiological ATP concentrations could be useful in characterizing the targets and off-targets of kinase inhibitors.
Our findings that chemically different TKI which share kinase inhibition as the common mechanism of action are active strongly indicates that it is a tyrosine kinase target-based activity and not off-target arbitrary effect. We propose that TKI approved for human use and widely available can be rapidly deployed as specific target-based therapy for COVID-19. Competing Interest Statement.
Cutaneous Adverse Effects of Small-Molecule Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors. Biologic therapies such as tyrosine kinase inhibitors TKIs have revolutionized medicine and offer targeted therapy for an increasing number of diseases. However along with these advances and their ensuing expanded use have come many unique adverse effects.
In this article dermatologists review how to manage cutaneous adverse effects. Patients receiving a TKI should be monitored for increasing side effects anemia neutropenia folliculitis skin rash edema nausea vomiting and diarrhea if an inhibitor of CYP3A4 is coadministered. The Effect of Enzyme Inducers on TKIs Rifampin is an inducer of most CYP450 enzymes and has been shown to reduce the AUC of most TKIs.
Although fastidious for the patients the appearance of side effects particularly skin toxicity and hair loss is associated with significant tumor response. Finally TKIs can lead to hypothyroidism. Various hypotheses have been proposed to explain their effects on thyroid function.
Tyrosine kinase inhibitors are quickly moving to the forefront of therapy for multiple malignancies. Although they lack the traditional adverse effects observed with cytotoxic chemotherapeutic agents toxicity can be severe with these medications. Tyrosine kinase inhibitors TKIs block chemical messengers enzymes called tyrosine kinases.
Tyrosine kinases help to send growth signals in cells so blocking them stops the cell growing and dividing. Cancer growth blockers can block one type of tyrosine kinase or more than one type. TKIs that block more than one type of tyrosine kinase are called multi-TKIs.
Single TKI Multi TKI. Examples of TKIs include. Sorafenib is a small molecule inhibitor of many tyrosine kinase receptors such as VEGFR-2.
Side effects are in most cases mild to moderate such as rash hand-foot skin reaction diarrhea and dermatitis and occur in about 33-38 patients using sorafenib.
