In this real-life study 71 of myocardial infarctions were classified as type 2 AMI. Myocardial infarction type 2 T2MI has been a focus of attention.

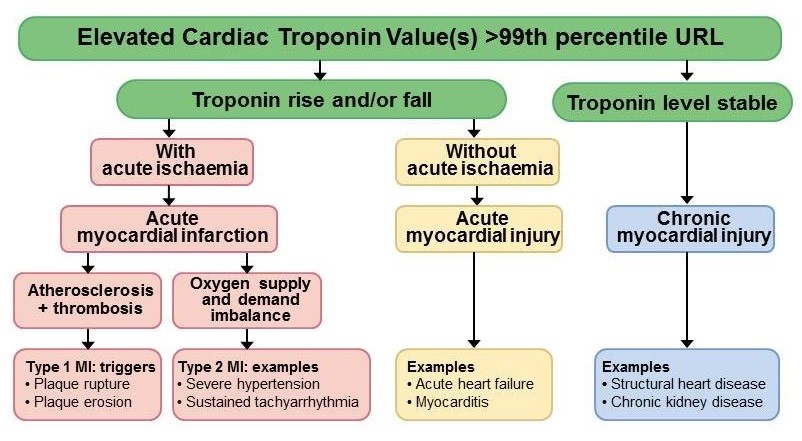
Type 2 myocardial infarction T2MI refers to myocardial necrosis caused by an imbalance in myocardial oxygen supply and demand and in the absence of acute coronary thrombosis.
Type 2 myocardial infarction. Type 2 myocardial infarction T2MI refers to myocardial necrosis caused by an imbalance in myocardial oxygen supply and demand and in the absence of acute coronary thrombosis. Despite growing recognition of this entity there remains little understanding of the pathophysiology and uncertainty over the diagnostic criteria for this subtype of MI. Type 2 MI is defined as myocardial infarction secondary to ischaemia due to either increased oxygen demand or decreased supply eg.
Coronary artery spasm coronary embolism anaemia arrhythmias hypertension or hypotension. Acute myocardial infarction MI can occur from increased myocardial oxygen demand andor reduced supply in the absence of acute atherothrombotic plaque disruption. A condition called type 2 myocardial infarction T2MI.
As with any MI subtype there must be clinical evidence of myocardial ischemia to make the diagnosis. Type 2 myocardial infarction T2MI is frequently encountered in clinical practice and associated with adverse outcomes. T2MI occurs most frequently due to noncoronary etiologies that alter myocardial oxygen supply andor demand.
The diagnosis of T2MI is often confused with acute nonischemic myocardial injury in part because of difficulties in delineating the nature of. This Viewpoint reviews what is known about myocardial infarction MI caused by oxygen supply-and-demand mismatch type 2 MI and differences from MI caused by coronary artery disease as well as proposes areas for further investigation to identify optimal management strategies. The definition of type 2 MI is 21 myocardial infarction secondary to ischaemia due to either increased oxygen demand or decreased supply eg.
Coronary artery spasm coronary embolism anaemia arrhythmias hypertension or hypotension. Troponin elevation occurs in a large number of clinical situations not considered to be an acute MI. Myocardial infarction type 2 T2MI has been a focus of attention.
Conceptually T2MI occurs in a clinical setting with overt myocardial ischemia where a condition other than an acute atherothrombotic event is the major contributor to a significant imbalance between myocardial oxygen supply andor demand. There is always an underlying condition but a Type 2 MI may be sequenced first if it was the diagnosis that after study occasioned the admission. If this were the case the DRG falls into the Acute Myocardial Infarction sets MS-DRGs 280-285 with higher weights than MS-DRG 311.
All myocardial infarctions are major CCs MCCs. Myocardial infarction type 2 2018 - New Code 2019 2020 2021 BillableSpecific Code I21A1 is a billablespecific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2021 edition of ICD-10-CM I21A1 became effective on October 1 2020.
That more accurately describes a patients SOI. Since the cause of Type 2 MI is not the same as Type 1 MI CDIS must be able to recognize the clinical indicators and treatment plan that are unique to Type 2 MI. The Third Universal Definition of Myocardial Infarction was published in the.
In this real-life study 71 of myocardial infarctions were classified as type 2 AMI. These patients were older predominantly women and had more comorbidities. Invasive treatment strategies and cardioprotective medications were less used.
Patients with type 2 AMI had higher crude mortality compared with type 1 patients with MI. DeFilippis et al Type 2 Myocardial Infarction TAT OF TH ART Circulation. 101161CIRCULATIONAHA119040631 November 12 2019 1663 that do not demonstrate a dynamic rising andor falling.
Acute myocardial infarction MI can occur from increased myocardial oxygen demand andor reduced supply in the absence of acute atherothrombotic plaque disruption. A condition called type 2 myocardial infarction T2MI. As with any MI subtype there must be clinical evidence of myocardial ischemia to make the diagnosis.
Most patients presenting with spontaneous myocardial infarction MI tend to have type 1 MI characterized by coronary plaque rupture or erosion and superimposed thrombosis. But a substantial proportion have type 2 MI characterized by an imbalance between myocardial oxygen supply and demand precipitated by an extracardiac stressor such as. On the other hand the oxygen deprivation in type 2 MI is not caused by atherosclerotic plaque rupture in a coronary artery but rather by an acute stressor such as an acute gastrointestinal bleed with a precipitous drop in hemoglobin or a sustained tachyarrhythmia with clinical manifestations of myocardial ischemia.
Incident type 2 myocardial infarction in a cohort of patients undergoing coronary or peripheral arterial angiography. 101161CIRCULATIONAHA116023052 Link Google Scholar.