Coli RNA polymerase alpha subunit C-terminal domain. Reeves R Nissen MS.
Coli RNA polymerase regulation by ppGpp is suggested by the structure of their complex.
Structure of e coli rna polymerase. Here the crystal structure of E. Coli alphaCTD alpha subunit residues 245-329 determined to 20 A resolution is reported. Crystals were obtained after reductive methylation of the recombinantly expressed domain.
The crystals belonged to space group P2 1 and possessed both pseudo-translational symmetry and pseudo-merohedral twinning. Cryo-EM structure of Escherichia coli σ 70 RNA polymerase and promoter DNA complex revealed a role of σ non-conserved region during the open complex formation First step of gene expression is transcribing the genetic information stored in DNA to RNA by the transcription machinery including RNA polymerase RNAP. The structure of E.
Coli core RNA polymerase RNAP has been determined to approximately 23 A resolution by three-dimensional reconstruction from electron micrographs of flattened helical crystals. The structure analysis of the peptides obtained by cleavage of the protein with cyanogen bromide and trypsin has confirmed the amino acid sequence of the beta-subunit deduced from the nucleotide sequence analysis. The beta-subunit of E.
The central enzyme of transcription is the DNA-dependent RNA polymerase RNAP a large macromolecular assembly consisting of at least five subunits. Historically much of our fundamental information on the process of transcription has come from genetic and biochemical studies of RNAP from the model bacterium Escherichia coli. The 25 angstrom resolution x-ray crystal structure of the Escherichia coli RNA polymerase RNAP alpha subunit amino-terminal domain alphaNTD which is necessary and sufficient to dimerize and assemble the other RNAP subunits into a transcriptionally active enzyme and contains all of the sequence elements conserved among eukaryotic alpha.
The mechanism of E. Coli RNA polymerase regulation by ppGpp is suggested by the structure of their complex. 2013 Mol Cell 50.
Escherichia coli RNA polymerase E6 70 promoters and the kinetics of the steps of transcription initiation. Escherichia coli and Salmonella cellular and molecular biology. Reeves R Nissen MS.
The AT-DNA-binding domain of mammalian high mobility group I chromosomal. Coliphage HK022 Nun blocks superinfection by coliphage λ by stalling RNA polymerase RNAP translocation specifically on λ DNA. To provide a structural framework to understand how Nun blocks RNAP translocation we determined structures of Escherichia coli RNAP ternary elongation complexes TECs with and without Nun by single-particle cryo-electron microscopy.
Analysis of the E. Coli genome sequence suggests that UP elements consisting of either one or two subsites with no more than two mismatches to consensus occur in more than one-third of stable RNA promoters but are also found in about 4 of mRNA promoters Estrem et al. CryoEM structure of Ecoli RNA polymerase elongation complex bound with NusG.
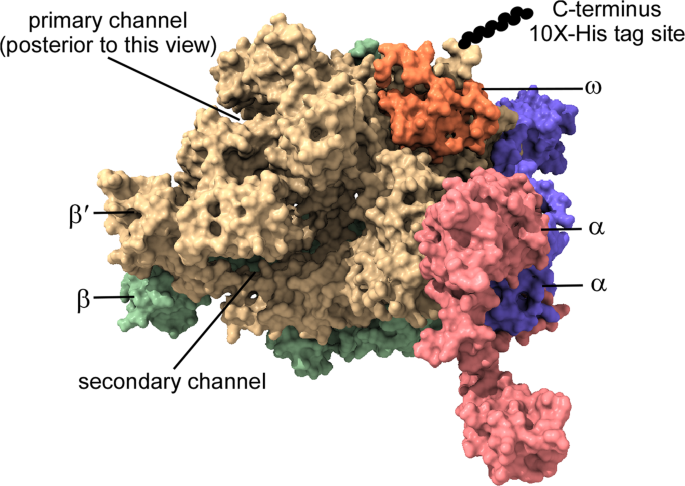
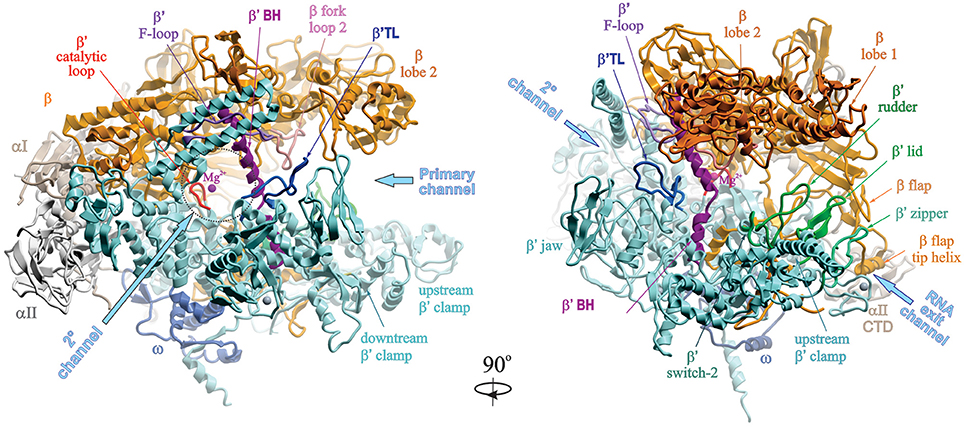
Escherichia coli Escherichia coli K-12. Coli RNA polymerase Eco RNAP is a multisubunit enzyme composed of a catalytically active core ββα 2 ω. Subunits that are evolutionarily related to β β α and ω are present in DNA-dependent RNAPs of all organisms.
The high-resolution crystal structure of a primase comprising the catalytic core of the Escherichia coli DnaG protein was determined. Escherichia coli RNAP comprises an essential catalytic core of two α subunits each 365 kD one β subunit 1506 kD and one β subunit 1552. Crystal structure of E.
Coli RNA polymerase alpha subunit C-terminal domain. Autogenerated by for capsmetro27. Created on Wed 2014-07-09 1248 last updated on Fri 2016-11-18 1550.
This Model was. RNA polymerase RNAP is the essential enzyme responsible for transcribing genetic information stored in DNA to RNA. Understanding the structure and function of RNAP is important for those who study basic principles in gene expression such as the mechanism of transcription and its regulation as well as translational sciences such as antibiotic development.
Recently we crystallized and solved the structure of the σ 70 holoenzyme of the E. Coli RNA polymerase at 38 Å resolution YZ. And TAS unpublished data.