The correlation between stress and the elevation of liver enzymes has not been found since there are certain conditions for this to occur. The study also found that in the part of the brain that.
Stress is a process that originates when environmental demands exceed the adaptive capacity of a human being.
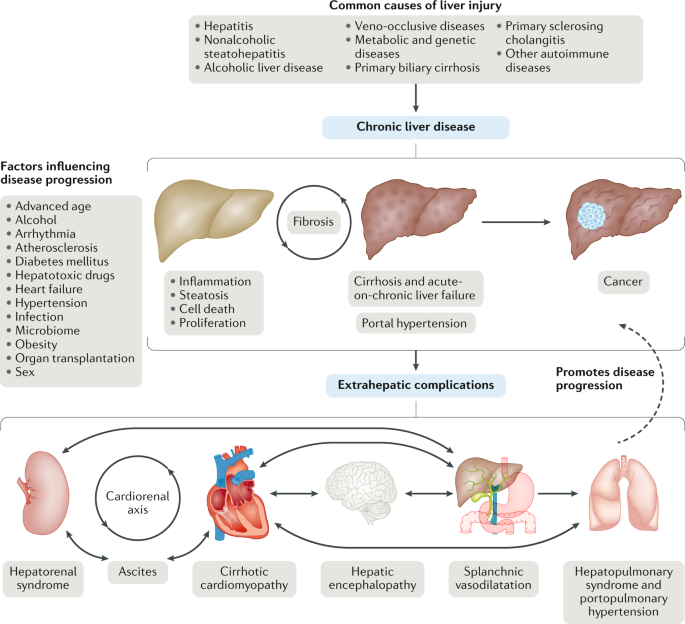
Stress and liver disease. The implications of stress for disease risk and progression is a relatively new frontier for numerous conditions including fatty liver disease. Here we discuss everything you need to know about stress stress-related conditions and fatty liver disease. How stress affects your liver health In a recent publication in the Journal of Gastroenterology and Hepatology it was noted that during stressful times natural killer cells are expanded in the liver and in some cases contributed to liver cell death and made the liver disease worse.
The study also found that in the part of the brain that. Although anecdotal comments on detrimental effects of psychosocial stress on liver diseases can be found even in the early literature only recently has scientific evidence been reported. The present article reviewed such evidence to demonstrate how stress exacerbates liver diseases.
A search of the. Stress is anamnestically reported by patients during the course of disease usually accompanied by a decline in their overall health status. As the mechanisms involving glucocorticoids and catecholamines have been deciphered and their actions on immune cell function deeper understood it has become clear that stress has an impact on hepatic.
Living with chronic liver disease renders affected individuals more vulnerable to stress. Despite the many sources manifestations and reactions to stress health professionals understand that people with a compromised liver are in greater need of stress relief than. Depression anxiety and stress levels have been shown to increase the risk of death by liver disease.
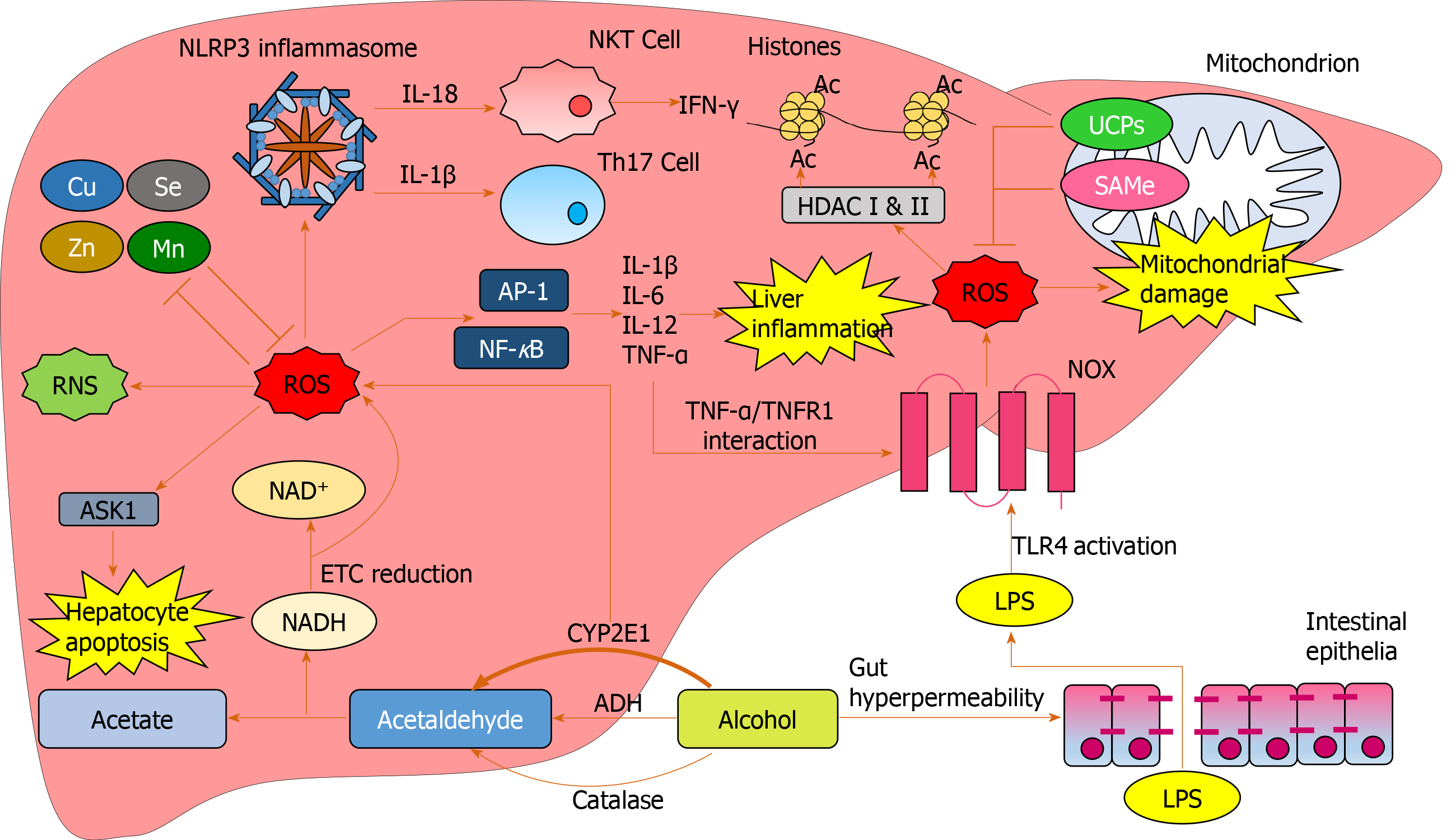
The findings come from the University of Edinburgh and its the first study to identify a. Numerous studies from human liver samples and animal disease models have indicated a crucial role of ER stress and UPR signaling pathways in the pathogenesis of liver diseases including non-alcoholic fatty liver disease alcoholic liver disease alpha-1 antitrypsin deficiency cholestatic liver disease drug-induced liver injury ischemia. First it may explain the pathogenesis of various liver disorders.
Moreover monitoring oxidative markers among hepatocytes offers the potential to diagnose the degree of liver damage and ultimately to observe the response to pharmacological therapies. The present report focuses on the role of oxidative stress in selected liver diseases. Stress levels linked to risk of liver disease death study shows Date.
May 19 2015 Source. University of Edinburgh Summary. Suffering from anxiety or.
A fatty liver is associated with obesity high cholesterol high blood pressure in essence the entire metabolic syndrome of poor health that predisposes to cardiovascular disease. The stress hormone cortisol is often implicated in a fat stomach as well as a fatty liver but how exactly this happens has not been understood. Risk factors for cardiovascular disease such as obesity and hypertension have been associated with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease.
Psychological distress symptoms of anxiety and depression is a risk factor for cardiovascular disease so it might also be associated directly or indirectly with liver disease. Link between depression and liver disease Getty Images A 10-year study has revealed a startling link between high levels of anxiety and an increased risk of death from liver disease. Constipation belly bloat and ongoing indigestion all relate to liver stress.
The liver is supposed to release bile that helps to break down food and lubricate the intestines. In weak or stressed livers this process is compromised. The liver helps to purify and produce new blood.
ER stress and the UPR have been implicated in the pathogenesis of human diseases including liver diseases. 1 This review discusses the contribution of ER stress and three UPR pathways in major liver disorders with a focus on non-alcoholic fatty liver disease NAFLD and current therapeutic approaches targeting ER stress. The correlation between stress and the elevation of liver enzymes has not been found since there are certain conditions for this to occur.
Stress is a process that originates when environmental demands exceed the adaptive capacity of a human being. This can lead to biological and psychological changes which in turn can cause disease.