This pattern was first described by McGinn and White in 1935 and is fairly well known as an indication of acute pulmonary embolism. General ECG features include.
Anterior and Posterior Fascicular Blocks.
Strain pattern ecg definition. Strain pattern is usually observed in patients with left ventricular hypertrophy andor dilation such as in systemic hypertension or aortic valve disease. However all patients with left ventricular hypertrophy do not show strain pattern. Strain pattern itself is NOT an ECG sign of myocardial ischemia.
Strain is defined as shortening or lengthening of myocardium. Shortening occurs when myocardium contracts and lengthening occurs when myocardium relaxes stretches out. These two deformations can be studied by means of echocardiography.
ECG strain pattern is associated with a higher cardiovascular risk abnormal LV structure and function incident heart failure stroke and coronary artery disease ECG Strain in Aortic Stenosis. More recent studies utilizing cardiac MRI have examined ECG strain in relation to myocardial tissue changes in patients with aortic stenosis AS. Whether the typical electrocardiographic ECG strain pattern Strain in leads V5 andor V6 which is associated with left ventricular hypertrophy LVH and LV systolic dysfunction is independently associated with LV diastolic dysfunction is unknown.
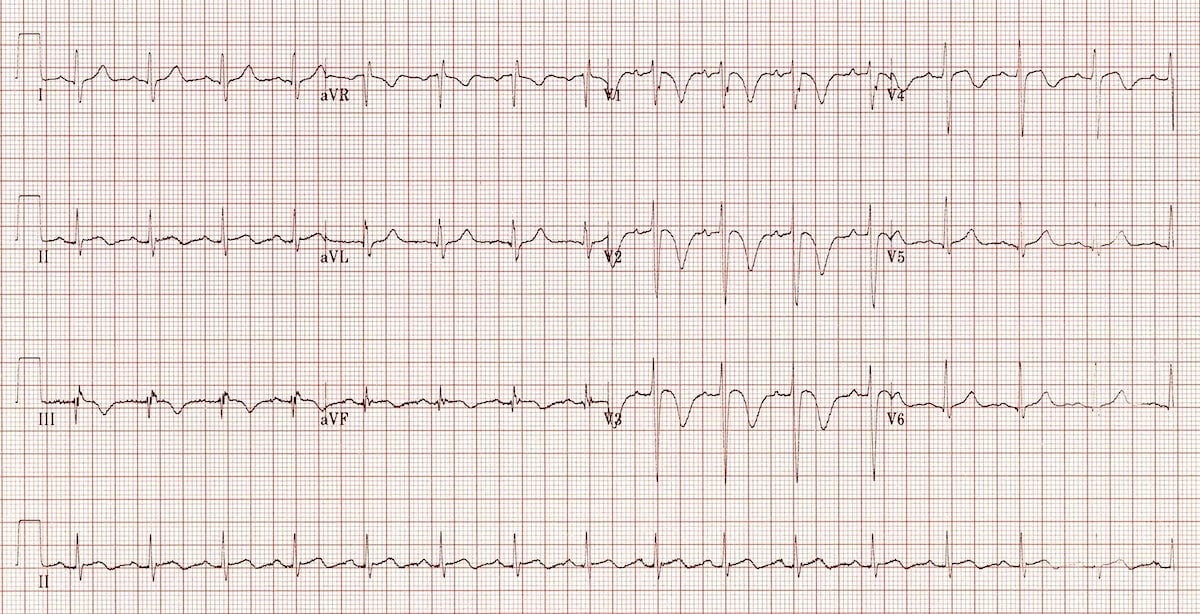
Left ventricular strain pattern The Premier EKG Resource for Medical Professionals EKG MD Dr. Anthony Kashou Left ventricular strain pattern Definition. EKG pattern characteristic of marked LVH.
Accompanied by ST-segment T-wave changes negativity of ST segment T wave as well as QRS complex changes. LV strain pattern with ST depression and T-wave inversions in I aVL and V5-6. ST elevation in V1-3.
Prominent U waves in V1-3. Severe LVH such as this appears almost identical to left bundle branch block the main clue to the presence of LVH is the excessively high LV voltages. It is typical that the ST-segment bulges upwards Figure 1 and 2 in these leads.
These ECG changes were previously referred to as strain pattern because it was believed that it indicated left ventricular exhaustion. Ventricular strain is usually associated with hypertensive heart disease and coronary artery disease. It is a type of ECG pattern seen in ECGs consistent with ventricular hypertrophy.
It usually indicates a compensatory response to uncontrolled hypertension and. In this context there is a particular pattern that can be seen on the EKG that is referred to as strain There are many different possible causes of the strain pattern on the EKG. One of the possible causes is poor blood supply to the heart and this is the cause that is most concerning in a person that is about to have elective surgery.
In electrocardiography a strain pattern is a well-recognized marker for the presence of anatomic left ventricular hypertrophy LVH in the form of ST depression and T wave inversion on a resting ECG. It is an abnormality of repolarization and it has been associated with an adverse prognosis in a variety heart disease patients. The ECG strain pattern of lateral ST depression and T-wave inversion is a marker for left ventricular hypertrophy LVH and adverse prognosis in population studies.
However whether ECG strain is an independent predictor of cardiovascular CV morbidity and mortality in the setting of aggressive antihypertensive therapy is unclear. Right Ventricular Hypertrophy with Strain Pattern ECG. Anterior and Posterior Fascicular Blocks.
Anterior and Posterior Fascicular Blocks. The S1Q3T3 pattern describes the presence of an S wave in lead I a Q wave in lead III and an inverted T wave in lead III. This pattern was first described by McGinn and White in 1935 and is fairly well known as an indication of acute pulmonary embolism.
General ECG features include. QRS amplitude voltage criteria. Ie tall R-waves in LV leads deep S-waves in RV leads Delayed intrinsicoid deflection in V6 ie time from QRS onset to peak R is 005 sec Widened QRST angle ie left ventricular strain pattern or ST-T.
The electrocardiographic strain pattern is a marker of left ventricular hypertrophy and adverse cardiovascular prognosis. Right ventricular strain pattern ST depression T wave inversion in the right precordial V1-4 and inferior II III aVF leads. S1 S2 S3 pattern far right axis deviation with dominant S waves in leads I II and III.
Deep S waves in the lateral leads I aVL V5-V6. Other abnormalities caused by RVH.