Further investigation into the use of sorafenib in combination therapy is needed. In addition sorafenib inhibits the VEGFR-2PDGFR-beta signaling cascade thereby blocking tumor angiogenesis.

Specifically the combination of sorafenib.
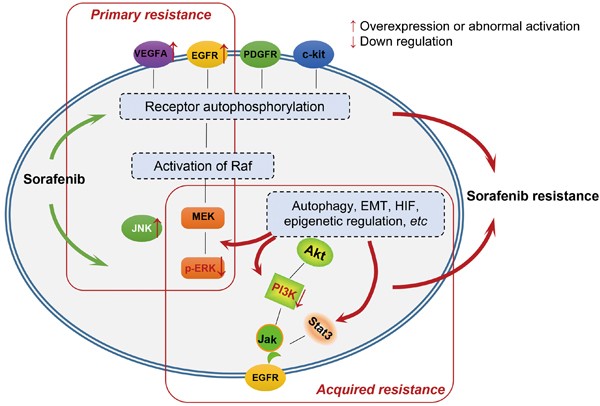
Sorafenib mechanism of action. Molecular mechanisms of sorafenib action in liver cancer cells Sorafenib a multikinase inhibitor recently received FDA approval for the treatment of advanced hepatocellular carcinoma HCC. However as the clinical application of sorafenib evolves there is increasing interest in defining the mechanisms underlying its anti-tumor activity. Based on its mechanism of action and findings in animals NEXAVAR may cause fetal harm when administered to a pregnant woman.
Sorafenib caused embryo-fetal toxicities in animals at maternal exposures that were significantly lower than the human exposures at the recommended dose of 400 mg twice daily. Advise pregnant women and females of reproductive potential of the potential. Sorafenib blocks the enzyme RAF kinase a critical component of the RAF MEK ERK signaling pathway that controls cell division and proliferation.
In addition sorafenib inhibits the VEGFR-2PDGFR-beta signaling cascade thereby blocking tumor angiogenesis. Sorafenib a multikinase inhibitor recently received FDA approval for the treatment of advanced hepatocellular carcinoma HCC. However as the clinical application of sorafenib evolves there is increasing interest in defining the mechanisms underlying its anti-tumor activity.
Considering that this specific inhibitor could target unexpected molecules depending on the biologic context a precise. A review of the mechanism of action and clinical applications of sorafenib in advanced osteosarcoma 1. Osteosarcoma is the most common bone tumour in children adolescents and young adults 1 2.
The terms sorafenib OR Nexavar and osteosarcoma were used. Sorafenib a multikinase inhibitor recently received FDA approval for the treatment of advanced hepatocellular carcinoma HCC. Sorafenib targets serinethreonine and receptor tyrosine kinases including those of Raf VEGFR-2 VEGFR-3 PDGFR-beta c-KIT fmslike tyrosine kinase3 FLT-3.
In particular preclinical evidence that supports the different mechanisms of action of sorafenib is discussed. Mol Cancer Ther 2008710312940 Mol Cancer Ther 2008710312940 In vivo and in vitro studies have shown that the oral multikinase inhibitor sorafenib inhibits tumor growth and disrupts tumor microvasculature through antiproliferative antiangiogenic andor proapoptotic. In mechanism of action studies sorafenib inhibited the phosphorylation of both ERK and eIF4E reduced the microvessel area assessed by CD34 immunohistochemistry and induced tumor cell apoptosis assessed by terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase-mediated nick end labeling in PLCPRF5 tumor xenografts.
These results suggest that the antitumor activity of sorafenib in HCC. Sorafenib interacts with multiple intracellular CRAF BRAF and mutant BRAF and cell surface kinases KIT FLT-3 VEGFR-2 VEGFR-3 and PDGFR-ß. Several of these kinases are thought to be involved in angiogenesis thus sorafenib reduces blood flow to the tumor.
Sorafenib is unique in targeting the RafMekErk pathway. By inhibiting these kinases genetic transcription. Mechanism of multikinase inhibitor action.
Tumour development involves the dysregulation of normal cell processes such as cell growth and proliferation as. Sorafenib Nexavar Price Information  Sorafenib Mechanism of Action Sorafenib Nexavar inhibits many kinases that are involved in tumour cell growth and its blood supply. In isolation sorafenib was shown to only provide brief clinical benefit due to various described mechanisms.
However when combined with other drugs that addressed its weaknesses or other aspects of the pathogenesis of osteosarcoma it proved to be effective in reducing disease progression in a variety of advanced cases. Further investigation into the use of sorafenib in combination therapy is needed. Specifically the combination of sorafenib.
Sorafenib is a multikinase inhibitor capable of facilitating apoptosis mitigating angiogenesis and suppressing tumor cell proliferation. In late-stage hepatocellular carcinoma HCC. Mechanism of Action.
Sorafenib May 21 2013 Sorafenib is small molecule inhibitor approved for the treatment of primary kidney cancer and advanced primary liver cancer. Sorafenib a multikinase inhibitor recently received FDA approval for the treatment of advanced hepatocellular carcinoma HCC. However as the clinical application of sorafenib evolves there is increasing interest in defining the mechanisms underlying its antitumor activity.
Considering that this specific inhibitor could target unexpected molecules depending. Sunitinib sold under the brand name Sutent is a medication used to treat cancer. It is a small-molecule multi-targeted receptor tyrosine kinase RTK inhibitor that was approved by the FDA for the treatment of renal cell carcinoma RCC and imatinib -resistant gastrointestinal stromal tumor GIST on.