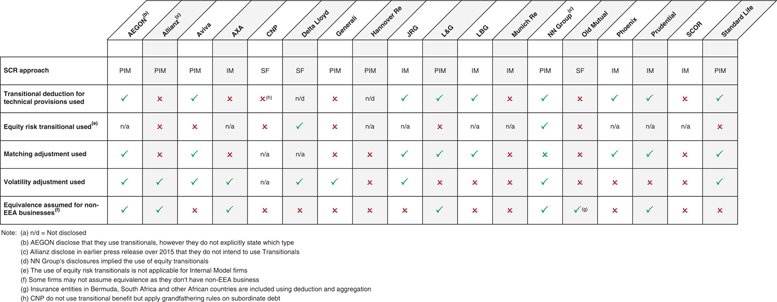
This CP is relevant to all UK Solvency II firms including in respect of the Solvency II groups provisions and to the Society of Lloyds and its managing agents. Classes 1 to 18 of non-life insurance business in Point A of Annex I to the Solvency II7 Directive.
Segmentation into Solvency II classes Under Solvency II insurers will be required to segment their reserves between a prescribed set of classes.
Solvency ii classes of business. 25 Solvency II Classes of Business 7 26 Geographical Region Information 7 27 Premium Risk Volume Measures 7 28 Application of Outwards Reinsurance 7 29 Assumptions and Simplifications 8 210 Treatment of Annuities stemming from Non-Life and Health contracts including PPOs 9. Article 136 - Identification and notification of deteriorating financial conditions by the insurance and reinsurance undertaking. Article 137 - Non-Compliance with technical provisions.
Article 138 - Non-Compliance with the Solvency Capital Requirement. Article 139 - Non-Compliance with the Minimum Capital Requirement. Solvency II is a risk-based approach to prudential requirements which brings harmonisation at EEA level.
The Solvency II Directive applies to all insurance and reinsurance companies with gross premium income exceeding 5 million or gross technical provisions in excess of 25 million. Member states have the option to impose lower limits. Life insurance business shall be segmented into 16 lines of business.
Contracts with profit participation clauses 2. Contract where policyholder bears the investment risk 3. Other contracts without profit participations clauses 4.
Accepted reinsurance which should be further segmented into. A Contracts where the mail risk driver is death. Lines of Business under Solvency II Annex I 201535 Medical Expense Insurance.
Medical expense insurance obligations where the underlying business is not pursued on a similar technical basis to that of life insurance other than obligations included in the. Solvency II Directive activities7. Part II RAO Activities.
Part III RAO Investments. Taking up and carrying on direct non-life insurance business. Classes 1 to 18 of non-life insurance business in Point A of Annex I to the Solvency II7 Directive.
This discussion document considers authorisation classes as set out in the Solvency II Directive and compares international best practice and regulatory guidance in recommending authorisation classes of business both life and non-life for use within SAM. The purpose of the Guidelines is to adopt a consistent and convergent approach to Solvency II preparation across Europe and to mitigate the risk that supervisors will adopt their own approaches at a national level CBI Solvency II Matters 7 May Consultation open until 19 June. All insurance and reinsurance undertakings should have as an integrated part of their business strategy a regular practice of assessing their overall solvency needs with a view to their specific risk profile own-risk and solvency assessment.
That assessment neither requires the development of an internal model nor serves to calculate a capital requirement different from the Solvency Capital Requirement or the. Segmentation into Solvency II classes Under Solvency II insurers will be required to segment their reserves between a prescribed set of classes. Although the reserving analysis can be undertaken using whatever segmentation of business is considered appropriate the insurer must be able to allocate the results between the Solvency II classes.
This CP is relevant to all UK Solvency II firms including in respect of the Solvency II groups provisions and to the Society of Lloyds and its managing agents. Non-Directive firms are out of the scope of this CP. This consultation closes on Wednesday 31 March 2021.
Figure 11 Simplified illustration of a Solvency II balance sheet The technical provisions are a direct input into the balance sheet. They are therefore also a key input into the Solvency Capital Requirement SCR calculation which models the potential movement in the Solvency II balance sheet over a one year time horizon. Thus if we get our technical provisions.
Life insurance product reporting codes August 2015 Notes on product categories. Whole life and endowment regular premium business only includes policies made paid-up excludes single premium bonds which are technically whole of life. Single premium bond includes investment bond and with-profits bond.
The business written by the Company across eight Solvency II lines of business is a mix of bespoke specialty and property classes of general insurance and reinsurance business written directly or through Managing General Agents MGAs. Under Solvency II and for general insurers the technical provisions TP are made up of Claims Provision Premium Provision Risk Margin The claims provision is the discounted best estimate of all future cash flows claims payments expenses and future premiums relating to claim events prior to the valuation date eg. C Classes 1 fourth indent 4 6 7 and 12.
Marine and Transport Insurance. D Classes 1 fourth indent 5 7 and 11. E Classes 8 and 9.
Insurance against Fire and other Damage to Property. F Classes 10 11 12 and 13. G Classes 14 and 15.
Credit and Suretyship Insurance. All insurance and reinsurance undertakings should have as an integrated part of their business strategy a regular practice of assessing their overall solvency needs with a view to their specific risk profile own-risk and solvency assessment. That assessment neither requires the development of an internal model nor serves to calculate a capital requirement different from the Solvency Capital Requirement or the.
This is to protect policyholders consumers businesses and the stability of the financial system as a whole. Solvency rules stipulate the minimum amounts of financial resources that insurers and reinsurers must have in order to cover the risks to which they are exposed. Equally importantly the rules also lay down the principles that should guide insurers overall risk management so that they can.