X-ray diffraction XRD and Fourier transform infrared FT-IR analysis indicate that the silica nanoparticles are amorphous and that the surface of silica nanoparticles is modified by the organics. More attractively their surface can be easily functionalized via the well-established silane technology.

Biomedical Applications of Nanosilica.
Silica nanoparticles preparation properties and uses. Silica-based nanoparticles are robust inorganic materials which possess high specific surface areas with high surface silanol concentrations which makes it easy to connect the functional groups. Preparation properties and uses Subject. New York NY Nova Science Publ 2012 Keywords.
Signatur des Originals Print. T 12 B 1497. Digitalisiert von der TIB Hannover 2012.
Preparation Properties and Uses. Biomedical Applications of Nanosilica. NOVA Science Publishers Inc New York USA.
Properties and Applications of Silica Nanoparticles 1. Protein adsorption and separation. Owing to the facile preparation low cost high specific surface area and.
Nucleic acid detection and purification. Silica nanoparticles have also been used for DNA detection separation and. X-ray diffraction XRD and Fourier transform infrared FT-IR analysis indicate that the silica nanoparticles are amorphous and that the surface of silica nanoparticles is modified by the organics.
The transmission electron microscopy TEM images of the sample show that good dispersion and uniform silica particles with an average diameter of about 10 nm are prepared. The results obtained in the mentioned method prove that the oil shale ash OSA. Silicon nanoparticles have attracted great attention in the past decades because of their intriguing physical properties active surface state distinctive photoluminescence and biocompatibility.
In this review we present some of the recent progress in preparation methodologies and surface functionalization approaches of silicon nanoparticles. Further their promising applications. Sol-gel method was used for the preparation of silica nanoparticles.
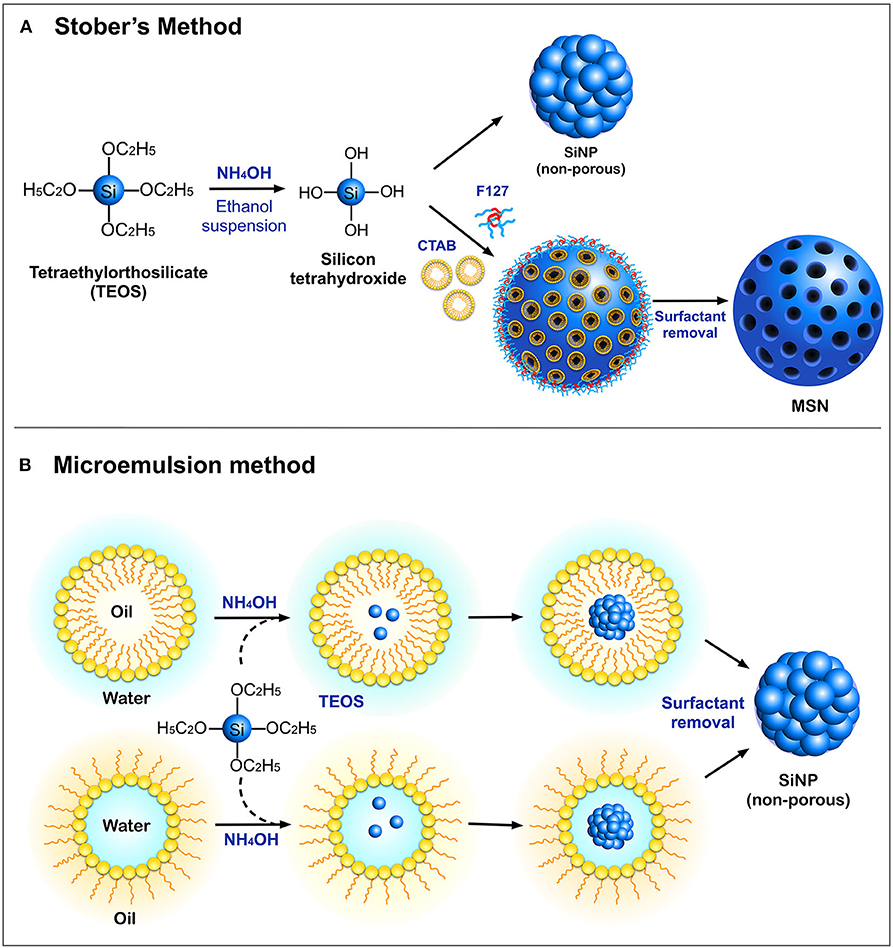
These n-SiO 2 particles were synthesized by hydrolyzing TEOS in a mixture of ethanol water ammonia and surfactant. TEOS ethanol and ammonia were used as silica precursor common solvent and catalyst respectively. For each experiments 10 ml ethanol 3 ml deionised water1 ml TEOS and 25 gm of non-ionic surfactant were added to the reaction container and stirred for 30 min for homogeneity.
The chief applications of silica nanoparticles are as an additive for the manufacture of rubber and plastics. As a strengthening filler for concrete and other construction composites. And as a stable non-toxic platform for biomedical applications such as drug delivery and theranostics.
This article was updated on the 11 th September 2019. Silica nanoparticles are used in many fields such as biomedical electrical textile and rubber sectors yet nowadays research is moving toward the biomedical field. Here silica nanoparticles are used in diagnosis and to control diseases by identifying and correcting the genetic disorders as a theranostics agent.
In addition some applications such as biosensor bioimaging drug delivery and. Silica SiO2nano powder is used as a carrier in the preparation of fungicides in which the antibacterial ion can be adsorbed and achieve the objective of sterilization. The application is used for the manufacture of items such as the refrigerator case the computer keyboard.
SiO2 Nanoparticles as Lubricating oil additives. Silica nanoparticles are the mostly used nanomaterials to build pH nanosensor. Silica nanoparticles are optically transparent of low toxicity inert to pH and some are degradable.
More attractively their surface can be easily functionalized via the well-established silane technology. The pH-sensitive dyes are in most cases chemically bonded on the surface of silica nanoparticles which is beneficial for. Terkko Navigator is a medical library community for the University of Helsinki and Helsinki University Central Hospital.
Personalize your own library of feeds journals books links and more. Nanoparticles can offer significant advantages over the conventional drug delivery in terms of high stability high specificity high drug carrying capacity ability for controlled release possibility to use in different route of administration and the capability. Here we utilize hollow silica nanoparticles to realize antireflection coatings which largely diminish light scattering and hence exhibit excellent transmission even at UV wavelengths.
The hollow silica nanoparticles were synthesized using a template-free approach and then dip coated onto fused silica substrates to form antireflection coatings. The coatings were found to exhibit nearly 100. The tribological properties of the SiO 2-B-N-GO prepared as anti-wear additives for enhanced lubrication were studied using a four-ball tester.
The experiment results indicated that SiO 2-B-N-GO exhibits excellent load-carrying anti-wear and anti-friction properties in a base oil especially at the optimal concentration of additives at 015 wt. The wear scar diameter decreased from 070 to 037. Layers made of hollow silica nanoparticles have potential applications as antireflection films with lower refractive index values compared with existing materials such as silica glass 150 and magnesium fluoride 138.
The advantages of such nanoparticles result. A nanoparticle or ultrafine particle is usually defined as a particle of matter that is between 1 and 100 nanometres nm in diameter. The term is sometimes used for larger particles up to 500 nm citation needed or fibers and tubes that are less than 100 nm in only two directions.
At the lowest range metal particles smaller than 1 nm are usually called atom clusters instead.