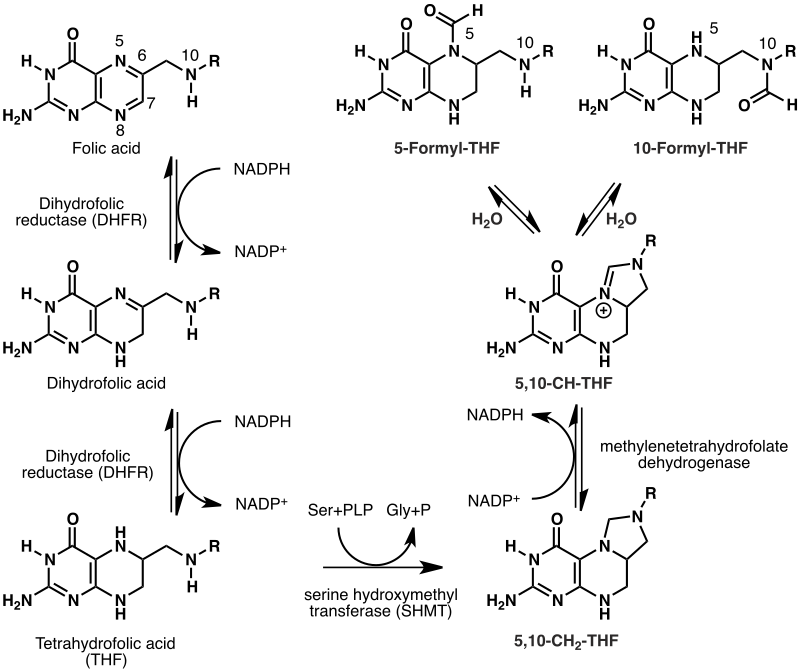
The reduced folate level in alcoholics may be due to reduced. Folic acid itself is biologically inactive but in the body it is converted to dihydrofolic acid which is further converted to tetrahydrofolate and other derivatives that are metabolically active.
Consuming 400 mcg of folic acid each day helps prevent neural tube defects even if you have an MTHFR C677T variant.
Significantly reduced folic acid conversion. MTHFR is an enzyme required to convert folic acid into an active form called L-methylfolate that is usable by our bodies. L-methylfolate plays an important role in making neurotransmitters such as serotonin dopamine and norepinephrine which help regulate mood. Some people carry a mutation in the MTHFR gene which limits their ability to create.
Folic acid plays a key role in the maintenance of genomic stability providing methyl groups for the conversion of uracil to thymine and for DNA methylation. Besides dietary habits folic acid metabolism is influenced by genetic polymorphism. The C677T polymorphism of the methylene-tetrahydrofolate reductase MTHFR gene is associated with a reduction of catalytic activity and is suggested to modify cancer risk differently depending on folate status.
In this work the effect of folic acid. Folic acid Vitamin B9 conversion to pmoll nmoll ngml ngdl ng100ml ng ngl µgl. Online conversion calculator for many types of measurement units in laboratory and medicine Folic acid Vitamin B9 Acide folique folates acide ptéroylglutamique vitamine B9 acide ptéroyl-monoglutamique.
Folic acid 200 mcg Folate Conversion to mcg DFE. Folate mcg DFE Folic acid mcg per serving 17 conversion factor for folic acid Folate mcg DFE 200 mcg 17 340 mcg DFE. Folic acid itself is biologically inactive but in the body it is converted to dihydrofolic acid which is further converted to tetrahydrofolate and other derivatives that are metabolically active.
The conversion of folic acid to its biologically active forms depends on the action of the enzyme dihydrofolate reductase. We recently got genetic testing done to identify which prescription drugs would work and which ones would not. With the genetic testing they checked his MTHFR.
The results came back as reduced folic acid conversion. Im wondering if anyone else can shed any light on this with their own experiences and if increasing folic acid has helped. I understand that I have to get his folates in check but am hoping.
Folic acid is reduced or converted to dihydrofolate and then becomes tetrahydrofolate which is converted once again to glycine and 510-methylene-THF. L-5-methyl-THF the principal folate form in the plasma is then formed through a final conversion from 510-methylene-THF in the presence of the riboflavin-dependent enzyme MTHFR. The MTHFR gene helps the body convert folic acid into its active form methyl-folate.
Methyl folate plays a huge role in your overall health. Supporting detoxification hormone balance and metabolism. 5 6 7 This gene is also responsible for helping the body break down an amino acid called homocysteine.
When you have the MTHFR gene mutation your body is unable to properly break. Low folate levels are furthermore linked to a poor response to antidepressants and treatment with folic acid is shown to improve response to antidepressants. A recent study also suggests that high vitamin B12 status may be associated with better treatment outcome.
Folate and vitamin B12 are major determinants of one-carbon metabolism in which S-adenosylmethionine SAM is formed. Alcoholism is associated with significantly reduced levels of tissue folate Vitamin B12 and B6 in humans. At intakes 30 gkgday there was a doubling in the level of DNA hypomethylation of lymphocytes.
The reduced folate level in alcoholics may be due to reduced. The irreversible conversion of MTHF into 5-methyltetrahydrofolate 5MTHF is catalyzed by methylenetetrahydrofolate reductase MTHFR. This conversion is dependent on the availability of folic acid in mammals an essential vitamin from the diet.
Mutations of MTHFR lead to hyperhomocysteinemia. Deficiency of folic acid during pregnancy has been linked to neural tube defects like spina bifida a birth defect. One of the folate coenzymes ie.
N5-methyl THF is involved in the conversion of homocysteine to methionine. Increased levels of plasma homocysteine have been associated with greater risk for developing heart disease. On the contrary a low intake of folic acid and consequent reduced production of the enzyme that is involved in the 510-MTHFR dalldUMP proper conversion to dTMP causes an increase in the incorporation of uracil into DNA with an increase in genomic instability.
An analysis of 10789 participants from this trial found that folic acid supplementation significantly reduced the risk of stroke by 73 among those who had a low platelet count and an elevated homocysteine level increasing their risk of stroke but had no significant effect on participants with a high platelet count and low homocysteine level. Folic acid in pregnancy is essential for this replication to happen. Folic Acid Helps in the Conversion Of Carbohydrates.
Folate also aids in the conversion of carbohydrates to energy for the absorption by the body. A pregnant mom needs the energy for the fetus to progress well and the placenta to work effectively. The maternal tissues also need the energy to keep regenerating.
The amount of folic acid you consume each day from foods fortified with folic acid and vitamins or supplements containing folic acid and. The length of time folic acid is consumed before becoming pregnant. Consuming 400 mcg of folic acid each day helps prevent neural tube defects even if you have an MTHFR C677T variant.
Taking a supplement with more than 400 mcg of folic acid. Deficiency may also occur if you have a disease or genetic anomaly that avoids your body from soaking up or converting folate to its functional type. Folate or folic acid is a type of B vitamin.
Produce red blood cells RBCs. Low folic acid can cause anemia. Anemia is a condition where you have too few RBCs.
Anemia can deprive your tissues of oxygen it.
