
Health Maintenance for People With Sickle Cell Disease Chapter 2. This guideline covers managing acute painful sickle cell episodes in children young people and adults who present at hospital from presentation until when they are discharged.
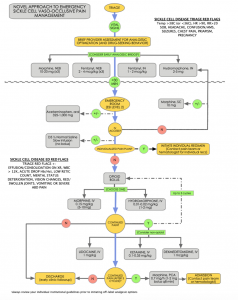
Pharmacotherapeutical strategies in the prevention of acute vaso-occlusive pain in sickle cell disease.
Sickle cell disease pain management guidelines. The management of acute and chronic pain for individuals living with sickle cell disease SCD is a clinical challenge. This reflects the paucity of clinical SCD pain research and limited understanding of the complex biological differences between acute and chronic pain. These issues collectively create barriers to effective targeted interventions.
Optimal pain management requires. ASH Releases New Clinical Practice Guidelines on Management of Pain in Sickle Cell Disease Jun 19 2020 Pain guideline is the latest in Societys evidence-based series of clinical practice guidelines for sickle cell disease aiming to improve and personalize care for individuals with this complex condition. The Sickle Cell Society helped develop these most recent guidelines for management of pain crises in sickle cell.
If you are a healthcare professional please read the guidelines. Despite these guidelines existed we are concerned that we still hear complaints from people who have had a crisis and been denied pain medication or it is not administered in a timely fashion. The American Society of Hematology ASH released evidence-based 2020 guidelines on the management of acute and chronic pain in pediatric and adult patients with sickle cell disease SCD.
The guidelines aim to support patients clinicians caregivers hematologists and other healthcare workers with decisions associated with pain management in SCD. Management of Acute and Chronic Pain In 2016 ASH initiated an effort to develop clinical practice guidelines on Sickle Cell Disease SCD. The American Society of Hematology ASH convened 5 guideline panels to develop clinical practice recommendations addressing 5 management areas of highest importance to individuals living with sickle cell disease.
Pain cerebrovascular complications pulmonary and kidney complications transfusion and hematopoietic stem cell transplant. Panels were multidisciplinary and consisted. Pain Management Guidelines for Sickle Cell Disease.
Sickle cell anemia is an inherited disease that is caused by an abnormal version of hemoglobin known as hemoglobin S or sickle hemoglobin. Patients with the disease often experience acute or chronic pain. Opioids sometimes may be used to manage this pain.
The American Society of Hematology recently published the 2020 guidelines for sickle cell disease management of acute and chronic pain. 38 They suggest that given the high prevalence of psychologic comorbidities that often coexist in the context of pain routinely screening for depression and anxiety and targeted screening for other psychologic comorbidities is considered good clinical practice. The APS makes the following recommendations for the treatment of pain in patients with sickle cell disease.
Pain management should be aggressive to ease pain and enable. The American Society of Hematology 2020 guidelines panel for management of acute and chronic pain in sickle cell disease noted two theoretical concerns of rapid treatment and tailored dosing of opioids. Rapid pain treatment and higher doses could increase euphoria and the risk of opioid tolerance and higher opioid dosing could increase perceptions of opioid misuseHowever the panel.
These protocols are guidelines in use at the Sickle Cell Center at Grady Health System and they are intended for use by heath care providers treating patients with sickle cell syndromes. These guidelines supplement to current texts in general medicine surgery and pediatrics. These guidelines address more than 40 specific issues such as abdominal pain congestive heart failure and infections.
For adult patients with SCD who have chronic pain from the SCD-related identifiable cause avascular necrosis AVN of the bone the ASH guideline panel suggests the use of serotonin-norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors SNRIs or NSAIDs in the context of a comprehensive disease and pain management plan Conditional recommendation. Very low certainty in the evidence about. This is an overarching guideline covering the principles of how to manage an acute painful sickle cell episode in hospital.
Local protocols should be referred to for specific management plans including drug choice and dosages. This guideline includes the management of acute painful sickle cell episodes in. This guideline covers managing acute painful sickle cell episodes in children young people and adults who present at hospital from presentation until when they are discharged.
It aims to reduce variation in how acute episodes are managed in hospital. The purpose of these guidelines is to help people living with sickle cell disease SCD receive appropriate care by providing the best science-based recommendations to guide practice decisions. The target audience is primary care providers and other clinicians nurses and staff who provide emergency or continuity care to individuals with SCD.
The guidelines on management of acute and chronic pain in sickle cell disease SCD were published on June 23 2020 by the American Society of Hematology ASH. 1 Use of. Health Maintenance for People With Sickle Cell Disease Chapter 2.
Health Maintenance for People With Sickle Cell Disease Prevention of Invasive Pneumococcal Infection 1. Administer oral penicillin prophylaxis 125 mg for age. Sins JWR Mager DJ Davis SCAT et al.
Pharmacotherapeutical strategies in the prevention of acute vaso-occlusive pain in sickle cell disease. Brandow AM Carroll CP Creary S et al. American Society of Hematology 2020 guidelines for sickle cell disease.
Management of acute and chronic pain.