This study evaluated 251 adult patients in. Early signals suggested that survival might be increasing in this population.
The goal of this study was to assess trends in survival rates over time in cancer patients admitted to the ICU for sepsis or septic shock over the last 2 decades.
Septic shock in cancer patients. Cancer affects up to 20 of critically ill patients and sepsis is one of the leading reasons for ICU admission in this setting. Early signals suggested that survival might be increasing in this population. However confirmation studies have been lacking.
The goal of this study was to assess trends in survival rates over time in cancer patients admitted to the ICU for sepsis or septic shock over the last 2 decades. Mortality rates over 50 in OP were reported during the 1990s while more recently cancer patients with sepsisseptic shock mortality rates lower than 35 have been reported. Therefore our results are in agreement with the hypothesis that cancer patients with sepsis are a high-risk group in terms of worse outcomes but these results also indicate improvement in outcomes in this group in the past few years.
Cancer is one of the most common comorbid medical conditions present among sepsis patients. Although sepsis-related mortality rates in cancer patients are decreasing over time similar to the general population their incidence and mortality rates still remain unacceptably high. Because of their underlying cancer diagnoses and immunologic states cancer patients require special attention and.
For cancer patients an infection can turn serious or even deadly very fast. SEPSIS is a complication caused by the bodys overwhelming and life-threatening response to infection which can lead to tissue damage organ failure and death. For a person with cancer any infection that is anywhere in your body can lead to sepsis.
Survival in cancer patients with septic shock from pulmonary origin is substantial even when organ dysfunctions are not rapidly reversible. Delayed ICU management is an independent predictor of death. Studies assessing survival benefits from early ICU management are warranted.
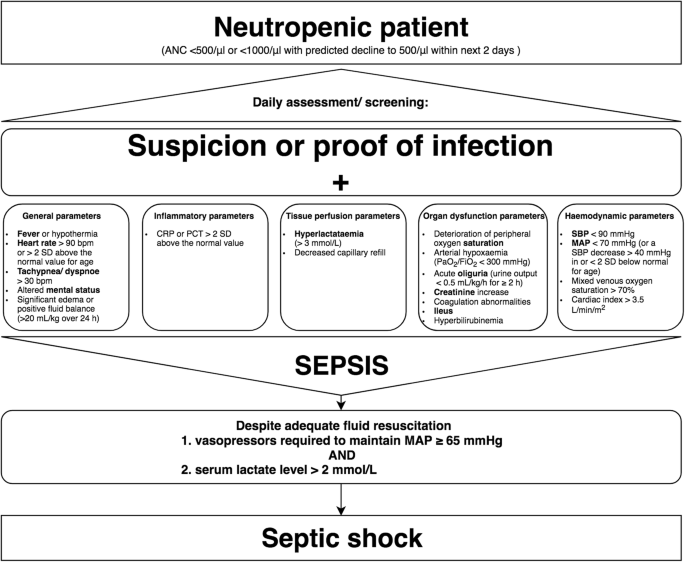
Septic shock is an infrequent but not uncommon oncologic emergency. An understanding of the risk factors pathophysiology and current issues in the management of septic shock can contribute to better patient care through early recognition and prompt and knowledgeable intervention. Cancer patients with neutropenic septic shock.
Etiology and antimicrobial resistance MDR bacteria were prevalent in patients with chemotherapy-induced neutropenic septic shock. Therefore piperacillin-tazobactam or carbapenem may be considered as empiric antibiotics if MDR bacteria are suspected to be causative agents. Sepsis and septic shock are major causes of mortality during chemotherapy-induced neutropenia for malignancies requiring urgent treatment.
Thus awareness of the presenting characteristics and prompt management is most important. Improved management of sepsis during neutropenia may reduce the mortality of cancer therapies. However optimal management may differ between neutropenic and non.
The hospital mortality rate is 37 68 in patients with septic shock according to the new definition and 60 according to old definition between 2013 and 2016. To predict hospital mortality the SOFA score has an area under the receiver operating characteristic curve of 074 95 confidence interval CI 068-079 the qSOFA of 065 95 CI 059-070 and the SIRS criteria of 058 95 CI 052-063. Patients with septic shock die mainly due to refractory shock.
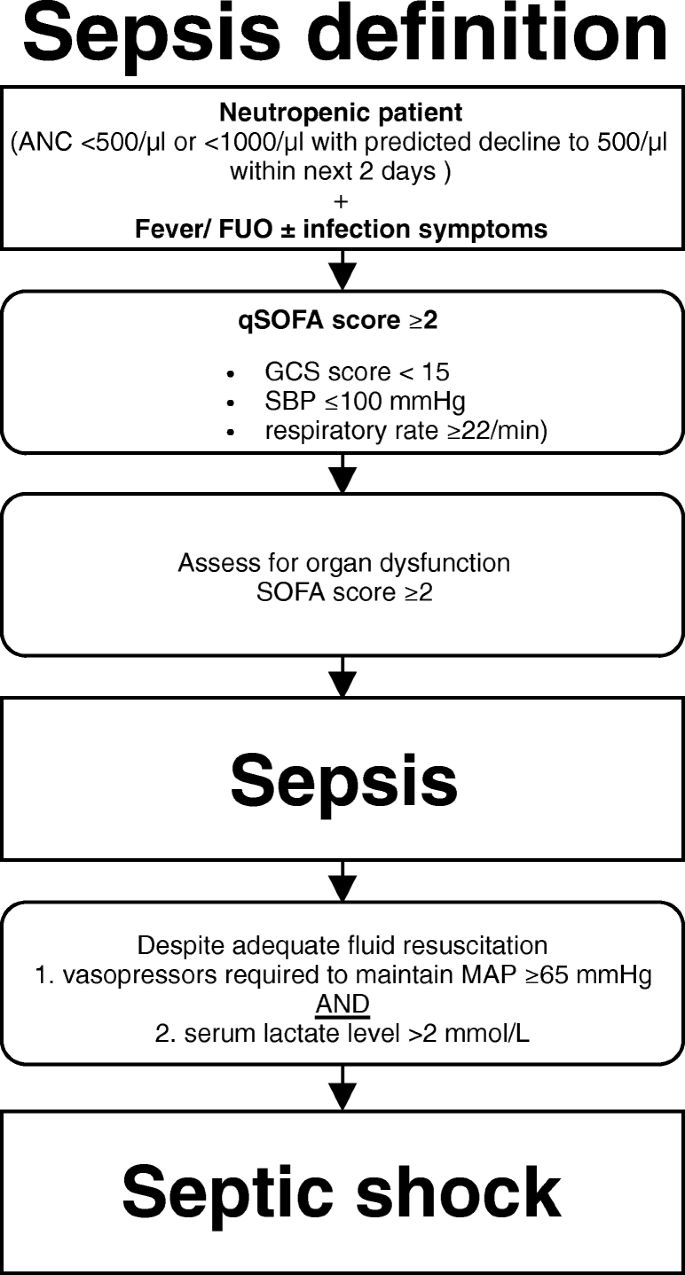
Vasopressin is commonly used as an adjunct to catecholamines to support blood pressure in refractory septic shock but its effect on mortality is unknown. We hypothesized that vasopressin as compared with norepinephrine would decrease mortality among cancer patients with septic shock. Sepsis is defined as a life-threatening organ dysfunction caused by an abnormal host response to infection.
A subset of patients with sepsis will show signs of circulatory and metabolic. Septic shock is when you experience a significant drop in blood pressure that can lead to respiratory or heart failure stroke failure of other organs and death. It is thought that the.
Patients who are at a higher risk for developing sepsis include. Very young less than 1 year old and older patients. Chronically ill and immuno-compromised patients diabetes kidney or lung disease or cancer Have wounds injuries or invasive devices such as catheters or tracheostomy.
Sepsis may lead to a low. Sepsis involves life-threatening organ dysfunction owing to a dysregulated inflammatory response to infection and septic shock is a subset of sepsis with. We intended to develop a scoring system to predict mechanical ventilator dependence in patients who survive sepsisseptic shock with respiratory failure.
This study evaluated 251 adult patients in. One case of septic shock has been reported in a patient receiving docetaxel for a colangiocarcinoma6as well as in 3 patients treated with docetaxel for advanced or recurrent gastric cancer78In a review of clinical trials with docetaxel for metastatic breast cancer 6 cases of ischemic colitis were identified two of them were fatal9.