The World Health Organization WHO defines IPV as any behavior within an intimate relationship by an intimate partner that causes physical psychological or sexual harm to those in the relationship. Bisexual women are 18 times more likely to report ever having experienced IPV than heterosexual women see Table I.
The term intimate partner violence describes physical sexual or psychological harm by a current or former partner or spouse.
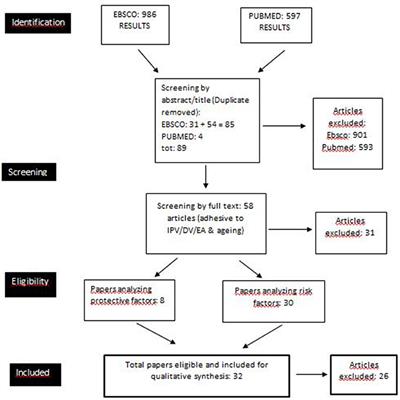
Scholarly articles on intimate partner violence. Intimate partner violence IPV is a prevalent worldwide health problem affecting women more commonly than men. It can include physical emotional. With personal movement limited and people confined to their homes advocates expressed concern about a potential increase in intimate partner violence IPV.
Violence against women Intimate partner violence Intimate partner violence is one of the most common forms of violence against women and includes physical sexual and emotional abuse and controlling behaviours by an intimate partner. Intimate partner violence1 IPV occurs in all settings and among all socioeconomic religious and cultural groups. Issues related to intimate partner violence IPV in married cohabiting and dating couples have generated a great deal of interest from scholars social activists and the public.
Intimate partner violence IPV is a global health problem characterized as any behaviour within an intimate relationship that causes physical psychological or sexual harm 1. At present it is well-documented that IPV can cause extensive mental health consequences among its victims 2 3 4 5. In this paper intimate partner violence describes physical violence directed against a woman by a current or ex-husband or boyfriend.
The term intimate partner violence often includes sexual violence and can also include psychological abuse. Both these forms of abuse often but not always accompany physical violence. Scholarly and Creative Works for Minnesota State University Mankato.
It has been accepted for inclusion in All Theses Dissertations and Other. Intimate partner violence IPV and domestic violence have devastating effects on the health and well-being of people exposed to abuse. It is known that up to 75 of IPV episodes occur after a.
Intimate partner violence IPV is a serious preventable public health problem that affects millions of Americans. The term intimate partner violence describes physical sexual or psychological harm by a current or former partner or spouse. Intimate partner violence IPV is a global concern with a significant public health impact 1 2.
The World Health Organization WHO defines IPV as any behavior within an intimate relationship by an intimate partner that causes physical psychological or sexual harm to those in the relationship. Each year in the United States nearly 12 million people are the victims of some form of intimate partner violence IPV or domestic abuse. Under normal circumstances IPV is an incredibly difficult public health and socio-judicial issue to address by nature IPV is behind closed doors and thus stigma shame and embarrassment as well as concerns over safety and.
Intimate partner violence has been a public health issue since the 1960s. A World Health Organization multi-country study found that the prevalence of intimate partner violence for women is 15 to 71 percent. Rape is now known to occur more frequently than reported with.
The term intimate partner violence is used to describe physical sexual or psychological harm done to an individual by a current or former partner or spouse. This type of violence can occur among heterosexual or samesex couples Centers for Disease Control and Prevention 2014. Abstract Intimate partner violence IPV is a major public health concern that has profound impacts on women across the globe.
Though it cuts across race socioeconomic status age geography and sexual orientation those communities plagued by poverty experience disproportionate rates. The term intimate partner violence is used to describe physical violence sexual violence stalking and psychological aggression by a current or former intimate partner to include current or former spouses boyfriendsgirlfriends dating partners or sexual partners Breiding et al 2015. Intimate partner violence IPV defined as behaviour by an intimate partner that causes physical sexual or psychological harm including acts of physical aggression sexual coercion psychological abuse and controlling behaviours remains a prevalent global health problem.
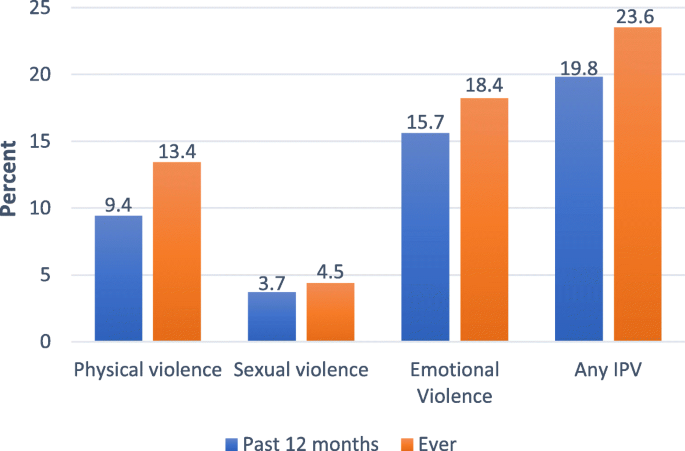
Intimate partner violence IPV and sexual violence SV are widespread among adolescents and place them on a lifelong trajectory of violence either as victims or perpetrators. The aim of this review was to identify effective approaches to prevent adolescent IPV and SV and to identify critical knowledge gaps. According to the CDCs National Intimate Partner and Sexual Violence Survey NISVS there is a higher prevalence of lifetime experiences of IPV among bisexual women than heterosexual women Walters et al 2013.
Bisexual women are 18 times more likely to report ever having experienced IPV than heterosexual women see Table I.