This AHRQ-supported study discusses one of the best-studied tools to measure and assess patient safety culture. The process of adaptation included forward translation and backward translation method followed.

A cross-sectional study was conducted using anonymous and random sampling.
Saq safety attitudes questionnaire. This AHRQ-supported study discusses one of the best-studied tools to measure and assess patient safety culture. Investigators present the cumulative findings from administering the Safety Attitude Questionnaire SAQ to more than 10000 providers in 203 clinical areas and in 3 countries. The Safety Attitudes Questionnaire SAQ is an instrument to measure safety attitudes among health care providers.
The instrument aims to identify possible weaknesses in clinical settings and motivate quality improvement interventions leading to reductions in medical errors. The safety attitudes questionnaire SAQ tool was used to measure safety culture. This tool is widely used in literature and among researchers and has been used and validated in middle eastern cultures.
In addition it has a validated Arabic version. A cross-sectional study was conducted using anonymous and random sampling. I surveyed all ICU staff.
Factors the Safety Attitudes Questionnaire SAQ is a validated and widely used instrument to measure the patient safety climate in clinical areas. The objective of this study was to assess the psychometric properties of the German language version of the SAQ. A survey was carried out in two University Hospitals in Switzerland in.
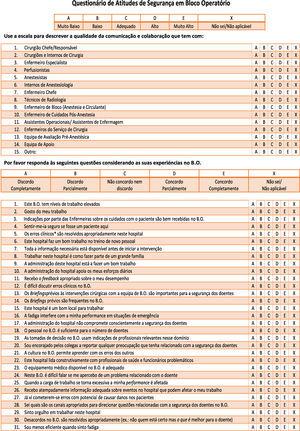
The Safety Attitudes Questionnaire as a tool for benchmarking safety culture in the NICU A culture of safety permeates many aspects of patient care and organisational functioning. The SAQ may be a useful tool for comparative performance assessments among NICUs. The Safety Attitudes Questionnaire was developed Bryan Sexton Eric Thomas and Bob Helmreich with funding from the Robert Wood Johnson Foundation and Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality.
The standard citation for the survey is. Sexton JB Helmreich RL Neilands TB Rowan K Vella K Boyden J Roberts PR Thomas EJ. The Safety Attitudes Questionnaire SAQ was easily answered and consistently well explained.
Second the group administration fully supported the survey and parallel studies showed an ongoing commitment to patient safety and maintaining a safety culture. This large national study examines the validity of the Safety Attitudes Questionnaire SAQ in predicting risk-adjusted morbidity and mortality outcomes for hospital patients on generalvascular services. The SAQ Sexton JB et al 2006 is a well-known psychometrically sound survey that has been used internationally for many years.
Patient safety has emerged as the key quality indicator of health care and safety culture among health care workers HCWs is also highlighted as it serves a foundational role in safety improvement endeavors. This study developed and validated the Korean version of the Safety Attitudes Questionnaire SAQ-K and administered it to HCWs in a large hospital. This works presents a multicentre cross-sectional study.
Data collection was obtained by means of The Safety Attitudes Questionnaire SAQ a self-completed questionnaire translated to the. Covering six patient safety related factors the Safety Attitudes Questionnaire SAQ is a validated and widely used instrument to measure the patient safety climate in clinical areas. The objective of this study was to assess the psychometric properties of the German language version of the SAQ.
Safety culture has been shown to be related to patient outcomes and Safety Attitude Questionnaire SAQ is one of the measures of safety culture that has good psychometric properties. The present study attempts to adapt the short version of the Generic SAQ for use in Malaysian healthcare setting. The process of adaptation included forward translation and backward translation method followed.
Provider attitudes about issues pertinent to patient safety may be related to errors and adverse events. We know of no instruments that measure safety-related attitudes in the outpatient setting. To adapt the safety attitudes questionnaire SAQ to the outpatient setting and compare attitudes among different types of providers in the outpatient setting.
The Safety Attitudes Questionnaire SAQ is commonly used to assess staff perception of safety climate within their clinical environment. The psychometric properties of the SAQ have previously been explored with confirmatory factor analysis and found to have some issues with construct validity. Background The Safety Attitudes Questionnaire SAQ is one of the most widely used instruments to assess safety culture among healthcare providers.
The ambulatory version of the SAQ SAQ-AV can be used in the primary care setting. Our study objective was to examine the underlying factors and psychometric properties of the Dutch translation of the SAQ-AV in out-of-hours primary. The Safety Attitudes Questionnaire.
SAQ The Safety Attitude Questionnaire was developed over 15 years to assess the quality of safety and teamwork related norms and behaviours of individual. Safety culture has been shown to be related to patient outcomes and Safety Attitude Questionnaire SAQ is one of the measures of safety culture that has good psychometric properties. The present study attempts to adapt the short version of the Generic SAQ for use in Malaysian healthcare setting.
The process of adaptation included forward translation and backward translation method followed. The Safety Attitudes Questionnaire SAQ is a validated widely used instrument to investigate multiple factors of safety climate at the clinical level in a variety of inpatient and outpatient settings. 4 Variations on the definition of safety culture exist.
5 Safety culture and safety climate are sometimes used interchangeably but in the literature different meanings tend to be. Safety climate in healthcare can be assessed by the Safety Attitudes Questionnaire SAQ which provides insight by scoring six dimensions. Teamwork Climate Job Satisfaction Safety Climate Stress Recognition Working Conditions and Perceptions of Management.