
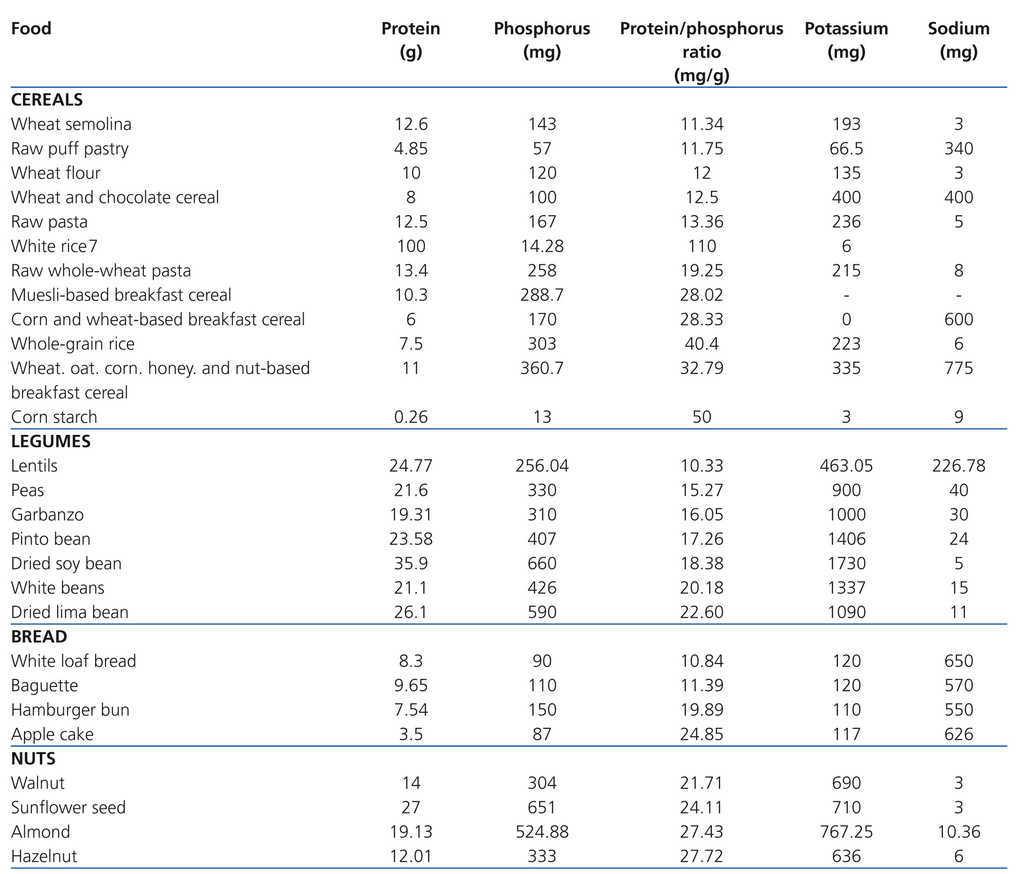
People with kidney disease may need to control the amount of protein sodium potassium phosphorus and calcium in their diet. Familiarise phosphorus content of common foods.
Your body absorbs less of the phosphorus.
Recommended phosphorus intake for kidney disease. Let us segregate the phosphorus intake according to age- For infants from 0 to 6 months 100 mg of phosphorus For infants from 7 to 12 months 275 mg of phosphorus For children 1 to 3 years old 460 mg phosphorus For children from 4 to 8 years 500 mg of phosphorus For children from 9. Healthy kidneys get rid of the extra amounts not needed in the body. It is recommended that healthy adults get between 800 mg and 1200 mg of phosphorus each day.
A balanced nutritious diet provides plenty of phosphorus because its found naturally in so many foods. How much phosphorus you need depends on your kidney function. If you have early-stage kidney disease or youre on dialysis you may need to limit phosphorus.
Nearly every food contains some phosphorus so this can be hard to do. Current guidelines recommend choosing natural foods instead of processed foods that have phosphorus added to them. Your body absorbs less of the phosphorus.
Limiting your phosphorus intake on a kidney disease diet is an important task for better odds of normal kidney function. Looking into a study published by Nephrology News in August 2020. In this article the research suggested that a modified low phosphorus diet may safely broaden food options for patients on dialysis.
Healthy kidneys can help remove extra phosphorus in your blood. Phosphorus and calcium control are very important for your overall health. What is a safe blood level of phosphorus.
A normal phosphorus level is 25 to 45 mgdL. Ask your kidney doctor or dietitian what your last phosphorus level was and write it down to help keep track of it. Will dialysis help with phosphorus control.
Dialysis can remove some phosphorus from your blood. Daily phosphorus requirement varies especially depending on your kidney functionality. In general phosphorus allowance for individual with chronic kidney disease is 800-1000mgday.
Familiarise phosphorus content of common foods. Phosphorus and Nutrition in Chronic Kidney Disease 1. Daily phosphorus ingestion is approximately 1200mg of which 950mg are absorbed.
Around 29 of body. Protein Intake and Phosphorus. In its clinical practice guideline for CKD mineral and bone disorder the Kidney Disease.
Improving Global Outcomes guidelines development group recommends that patients with stage 35 more severe CKD limit dietary phosphorus intake either alone or in combination with other treatments to reduce phosphate levels. However the group notes that clinical trial data showing that treatments. People with kidney disease may need to control the amount of protein sodium potassium phosphorus and calcium in their diet.
If your kidney disease gets worse you may need to limit other nutrients as well. Your dietitian or healthcare provider will tell you if you need to do this based on your blood test results. If you in your early stages the chances are high that there will be no limits or little limits for your appetite.
As the kidney disease starts to worsen the doctor may recommend that you should limit the intake of fluids Potassium and Phosphorus. Lets know about some of the minerals 1. Phosphorus is a mineral that builds up in the blood as kidney failure progresses.
You may be advised to reduce high protein foods that are high in phosphorus if your level goes above normal. Milk yogurt cheese dried beans and peas nuts and seeds peanut butter and some soy products are high in protein and phosphorus. How is protein managed.
People who are at risk for a heart attack or stroke because of a condition such as high blood pressure or kidney disease should limit their daily sodium intake to no more than 1500 mg. Choosing sodium-free or low-sodium food products will help them reach that goal. The restriction of protein intake in non-dialysis CKD patients is generally associated with a lower phosphorus intake.
The direct relationship between protein and phosphorus dietary content is well known. On average a mixed diet contains 1214 mg of phosphorus per gram of protein 4 5. The tolerable upper level intake for phosphorus is 4000mg for those ages 19-70 years and 3000mg for those 71 years and up.
Why is phosphorus important for kidney disease. Those with kidney disease probably know that one of the first things to start staying away from in the diet is phosphorus. This is because normal functioning kidneys are able to rid of excess phosphorus while damaged and.
Northwest Kidney Centers offered the following insights for a Dialysis patients daily consumption of phosphorus potassium and sodium. Phosphorus - If you are on Dialysis limit phosphorus to about 1000 milligrams mg per day. Potassium - If you are on Hemodialysis limit potassium to 2000 milligrams mg per day.
Controlling your calcium and phosphorus levels is typically recommended for those with kidney disease. If you are suffering from pruritus you may need to. How much potassium is safe.
Its recommended that healthy men and women over the age of 19 consume at least 3400 mg and 2600 mg of potassium. Median daily sodium potassium and phosphorus intake was 3089 mg 2294-4243 2384 mg 1804-3076 and 1206 mg 894-1612 respectively. Sodium and phosphorus consumptions were higher than recommended in all age groups.
Caloric intake decreased with.