
Eligible for inclusion were studies of pulse oximetry index test as a screening method for critical congenital heart defects in asymptomatic newborn babies during the first 28 days of life. Eligible for inclusion were studies of pulse oximetry index test as a screening method for critical congenital heart defects in asymptomatic newborn babies during the first 28 days of life.
Question at issue What is the diagnostic accuracy for pulse oximetry in screening of asymptomatic newborns before discharge from the well baby nursery and does pulse oximetry.
Pulse oximetry screening for congenital heart defects in newborn infants. Use of this screening method for early detection of congenital heart defects is based on the rationale that clinically undetectable hypoxaemia is present to some degree in most potentially life-threatening cases. Pulse oximetry has been assessed as a screening method for congenital heart defects in newborn babies in many studies. Congenital heart defects is based on the rationale that clinically undetectable hypoxaemia is present to some degree in most potentially life-threatening cases.
Pulse oximetry has been assessed as a screening method for congenital heart defects in newborn babies in many studies1425 The results of a systematic review26 in 2007 drew. We assessed the accuracy of pulse oximetry for screening major congenital heart defects in newborn babies and the contribution of this method after antenatal screening with ultrasonography. Newborn infants were recruited prospectively and studied according to methods stated in the protocol.
Pulse oximetry is an accurate screening test for critical congenital heart defects in newborns. Pulse oximetry is simple to use widely available and. Both techniques have a fairly low detection rate for isolated defects and many babies are discharged from hospital before diagnosis8 9 10 11 12 Pulse oximetry has been developed as a screening method to detect the defects in newborn babies.
1 The rationale for use of this method is that most critical congenital heart defects have a degree of hypoxaemia that would not necessarily. Background Introducing neonatal screening procedures may not be readily accepted by parents and may increase anxiety. The acceptability of pulse oximetry screening to parents has not been previously reported.
Objective To assess maternal acceptability of pulse oximetry screening for congenital heart defects and to identify factors predictive of participation in screening. Screening with pulse oximetry POX of asymptomatic newborns before discharge from the well baby nursery in order to detect critical congenital heart defects CCHD. Question at issue What is the diagnostic accuracy for pulse oximetry in screening of asymptomatic newborns before discharge from the well baby nursery and does pulse oximetry.
Based on the rationale that most newborn babies with CCHD have a degree of hypoxaemia the use of pulse oximetry to screen asymptomatic babies for CCHD was first explored over 10 years ago4 5 Further initial studies mainly in single centres with relatively few babies and a low prevalence of CCHD were then undertaken2 6 Although demonstrating proof of concept the data were insufficient to recommend universal screening. Pulse oximetry as a screening test for congenital heart defects in newborn infants. A test accuracy study with evaluation of acceptability and cost-effectiveness AK Ewer AT Furmston LJ Middleton JJ Deeks JP Daniels HM Pattison R Powell TE Roberts.
Pulse oximetry was performed on asymptomatic newborns in all studies. Three studies excluding newborns with an antenatal diagnosis of congenital heart disease. Either functional or fractional oxygen saturation was measured by pulse oximetry with oxygen.
Study finds that pulse oximetry is a safe accurate test that is acceptable to parents and staff as a screening test for congenital heart defects CHDs in newborn infants. It is likely to identify cases of critical CHDs that would otherwise go undetected and is expected to be cost-effective. Pulse oximetry as a screening test for congenital heart defects in newborn infants.
T E Roberts 1 P M Barton 1 P E Auguste 1 L J Middleton 2 A T Furmston 2 A K Ewer 3 4. 1 Health Economics Unit School of Health and Populations Science University of Birmingham Birmingham UK. It has been shown to improve the early diagnosis of congenital heart disease CHD in newborn infants 56 as a degree of hypoxaemia is present in the majority of infants with CHD.
Pulse oximetry screening will also detect other significant pathologies which produce hypoxaemia that may otherwise have gone undetected prior to discharge for instance. Although pulse oximetry was regarded as more promising than either the current practice or other options the report called for further research to improve estimates of test performance and to inform timing diagnostic and management strategies and to investigate the psychosocial effects of newborn screening for congenital heart disease p 127. 100 Another report has suggested families.
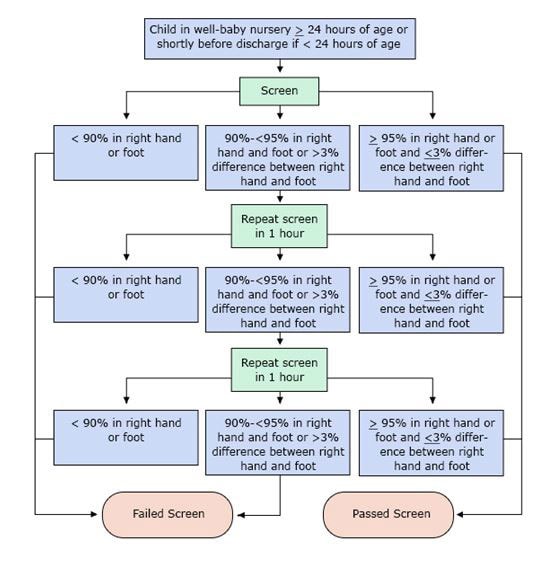
Pulse oximetry screening for critical congenital heart defects. Pulse oximetry is a highly specific and moderately sensitive test for detection of CCHD with very low false-positive rates. Current evidence supports the introduction of routine screening for CCHD in asymptomatic newborns before discharge from the well-baby nursery.
Eligible for inclusion were studies of pulse oximetry index test as a screening method for critical congenital heart defects in asymptomatic newborn babies during the first 28 days of life. Included studies were reported to have been conducted in a variety of newborn-care settings. Pulse Oximetry as a screening test for critical congenital heart defects and other significant diagnoses in new-born infants a cost-effectiveness analysis.
Background Critical Congenital Heart Defects CCHD are potentially life-threatening and it is vital to for them to be detected early in order to improve outcomes for infants. Because early infancy intervention is essential for babies with CCHD adding CCHD to newborn screening is an important strategy to assure that all newborns are screened. Some states now mandate that all newborns be screened by pulse oximetry for CCHD as part of newborn screening.
Pulse oximetry screening for congenital heart defects in newborn infants PulseOx. A test accuracy study. Ewer AK Furmston AT Middleton LJ Deeks JJ Daniels AJ Pattison HM Powell R Roberts TE Barton P Augusts P Bhoyar A Thangaratinam S Tonks AM Satodia P Deshpande S Kumararatne B Sivakumar S Mpanemunda R Khan KS.