
These proteins stabilize the individual strands of DNA to prevent them from reconnecting. SSBP means Single-Stranded Binding Proteins.
Replication protein A RPA the major eukaryotic ssDNA binding protein has two important roles in DNA metabolism.
Proteins for dna replication. The Steps and Proteins involved in DNA Replication Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic It is now well established that DNA Replication occurs semi conservatively copying each strand of DNA separately to produce two new DNA double helices. Each is composed of an old Parent strand and a newly synthesized one. If left unchecked this would make it very difficult to complete replication before DNA damage would occur.
Another protein called the single-strand bindingprotein SSB stabilizes the single-stranded regions by binding tightly to theseportions of the molecule. The presence of this DNA-binding protein protects the single-stranded regions from hydrolysis by the nucleases. DNA replication proteins are those proteins which support the process of replication and are also reported to be important in drug design and discovery.
This information depicts that DNA replication proteins have a very important role in human bodies however to study their mechanism their identification is necessary. Enzymes and proteins in dna replication 1. Enzymes and proteins in DNA replication Presented by RParthasarathy 2.
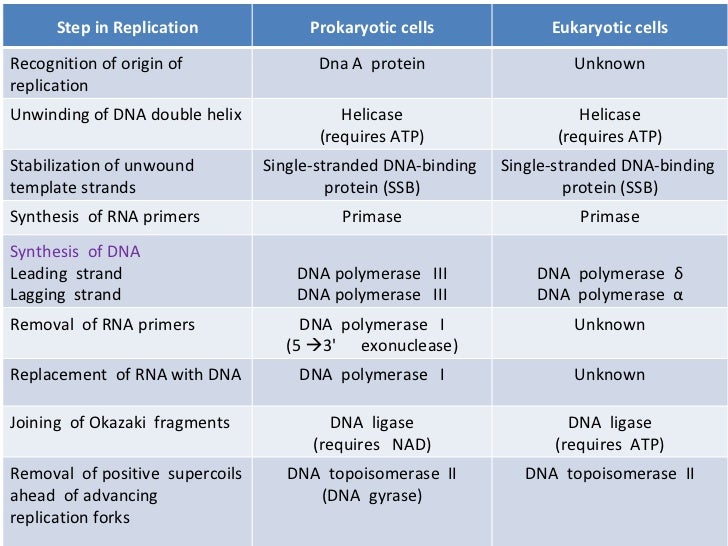
Introduction Multiple proteins are required for DNA replication at a replication fork These include DNA. DnaA Protein The base sequence at. Some of the major proteins in DNA replication include the following.
An enzyme that opens the double helix by breaking the hydrogen bonds between complimentary base pairs. Single-strand DNA- binding proteins SSBPs. These proteins stabilize the individual strands of DNA to prevent them from reconnecting.
Single-strand bonding protein SSB binds to single strands of DNA and prevents the helix from reforming before it can be used as a template for replication topoisomerase. Microbe somehow survives without key proteins for replicating its DNA. Life 23 March 2021.
To copy DNA the enzymes helicase. Replication follows several steps that involve multiple proteins called replication enzymes and RNA. In eukaryotic cells such as animal cells and plant cells DNA replication occurs in the S phase of interphase during the cell cycle.
The process of DNA replication is vital for cell growth repair and reproduction in organisms. For comparison another ring-shaped protein involved in DNA replication human PCNA diffuses at 224 kbp 2 s 1 116 µm 2 s 1 31 under similar buffer conditions to ours 150 mM potassium. The DNA replication proteins which bound to PCNA-Sepharose included DNA polymerase δ and ε PCNA the 37 and 40 kDa subunits of RFC the 70 kDa subunit of RPA NDH II and topoisomerase I.
No evidence for the binding of DNA polymerase α DNA ligase I. SSBP means Single-Stranded Binding Proteins. It has a very important role in DNA Replication in EColi.
Single-stranded binding proteins bind to and stabilize single-stranded DNA during DNA replication until the single-stranded DNA can be used as a template for a new strand to bind to. It is the first protein which binds to DNA to initiate DNA replication. Dna-B proteins Mw- 300000- It is a primosome constituent and consists of six subunits.
It unwinds DNA during replication. It is responsible for the extension of open complex during replication. DNA replication is all-or-none process in the cell meaning once the DNA replication begins it proceeds to completion.
Hence to achieve maximum control of DNA replication eukaryotic cells employ a multi-subunit initiator protein complex known as pre-replication complex or DNA replication licensing complex DNA replication LC. About 20 molecules of Dna A proteins binds with 9 mer repeats along with ATP which causes DNA to wraps around dnaA protein forming initial complex. The dna A protein and ATP trigger the opening of 13 mer repeats froming open complex.
Two copies of dnaB proteins helicase binds to. Replication protein A RPA the major eukaryotic ssDNA binding protein has two important roles in DNA metabolism. 1 in binding ssDNA to protect it and to keep it unfolded and 2 in coordinating the assembly and disassembly of numerous proteins and protein.
The repairing is really the process of replication. There are 2 processes in protein synthesis. Transcription DNA makes all 3 forms of RNA in the nucleus Translation DNA plus all 3 forms of RNA together make proteins at the ribosome in the cytoplasm Transcription DNA makes all 3 forms of RNA in the nucleus.
Processing of DNA in replication repair and recombination pathways in cells of all organisms requires the participation of at least one major single-stranded DNA ssDNA-binding protein. This protein protects ssDNA from nucleolytic damage prevents hairpin formation and blocks DNA reannealing until the processing pathway is successfully completed.