MCN Am J Matern Child Nurs. However it is not without risk.

After completing this continuing education activity you will be able to.
Pediatric intramuscular injections guidelines for best practice. Children receive numerous vaccines and pediatric nurses administer the majority of these vaccines via the intramuscular route and thus must be knowledgeable about safe and evidence-based immunization. Guidelines for best practice. MCN Am J Matern Child Nurs.
The administration of injections is a fundamental nursing skill. However it is not without risk. Children receive numerous vaccines and pediatric nurses administer the majority of these vaccines via the intramuscular route and thus must be knowledgeable about safe and evidence-based immunization programs.
Pediatric intramuscular injections. Guidelines for best practice. MCN Am J Matern Child Nurs.
The administration of injections is a fundamental nursing skill. However it is not without risk. Children receive numerous vaccines and pediatric nurses administer the majority of these vaccines.
AbstractThe administration of injections is a fundamental nursing skill. However it is not without risk. Children receive numerous vaccines and pediatric nurses administer the majority of these vaccines via the intramuscular route and thus must be knowledgeable about safe and evidence-based immunization programs.
Nurses may not be aware of the potential consequences associated with poor. GUIDELINES FOR BEST PRACTICE Pediatric Intramuscular Injections. Abstract The administration of injec-tions is a fundamental nursing skill.
However it is not without risk. Children receive numer-ous vaccines and pediatric nurses administer the major-ity of these vaccines via the intramuscular route and thus must be knowledgeable about. Pediatric intramuscular injections.
Guidelines for best practice. MCN Am J Matern Child Nurs 392107-12. Quiz 113-4 01 Mar 2014 Cited by.
2 articles PMID. These policies guidelines and best practice documents are available for download by a range of target audiences. WHO has also published the WHO guideline on the use of safety-engineered syringes for intramuscular intradermal and subcutaneous injections in health care settings the first evidence-based policy document that specifically addresses.
WHO best practices for injections and related procedures toolkit. WHOEHT1002 1Injections adverse effects. 3Needlestick injuries prevention and control.
6Cross infection prevention and control. An integrative review of the literature has resulted in the development of a guideline for evidence-based practice of IM injections. Use of this guideline can assist the clinician to maximize the therapeutic effects of administered medication while minimizing or eliminating patient injury and discomfort associated with IM injections.
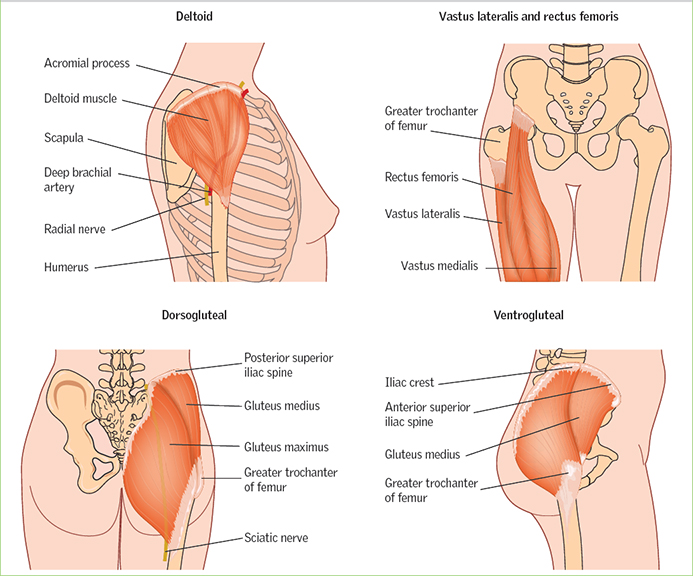
These are the usual IM injection sites. It is important to select an injection site that avoids major blood vessels and nerves. Do not use areas that are bruised tender swollen or scarred from surgeries or injury.
Rotate the sites so the areas do not get irritated and scarred. Adherence to safe injection practices and related infection control is part of that responsibility it protects patients and health workers. Medical treatment is intended to save life and improve health and all health workers have a responsibility to prevent transmission of health-care associated infections.
Immunization Training Guide Practice Procedure Manual For pediatricians physicians nurses medical assistants and office managers The recommendations in this publication do not indicate an exclusive course of treatment or serve as a standard of medical care. Variations taking into account individual circumstances may be appropriate. After completing this continuing education activity you will be able to.
Identify proper IM injection practices for use in the pediatric population. Select correct needle sizes and pain reduction techniques for children receiving IM injections. SC injections for vaccine recipients 12 months of age and older are usually given into the subcutaneous tissue of the upper triceps area of the arm.
SC injections should be administered at a 45 o angle. Pinching of the skin may be necessary to ensure injection into the subcutaneous tissue.