A novel multi-system pathway in which neuroendocrine signaling induces expression of the checkpoint receptor. PD-1 expression was confined to CD56 dim NK cells and if present to CD56 neg NK cells whereas the CD56 bright subset was consistently PD-1 neg.
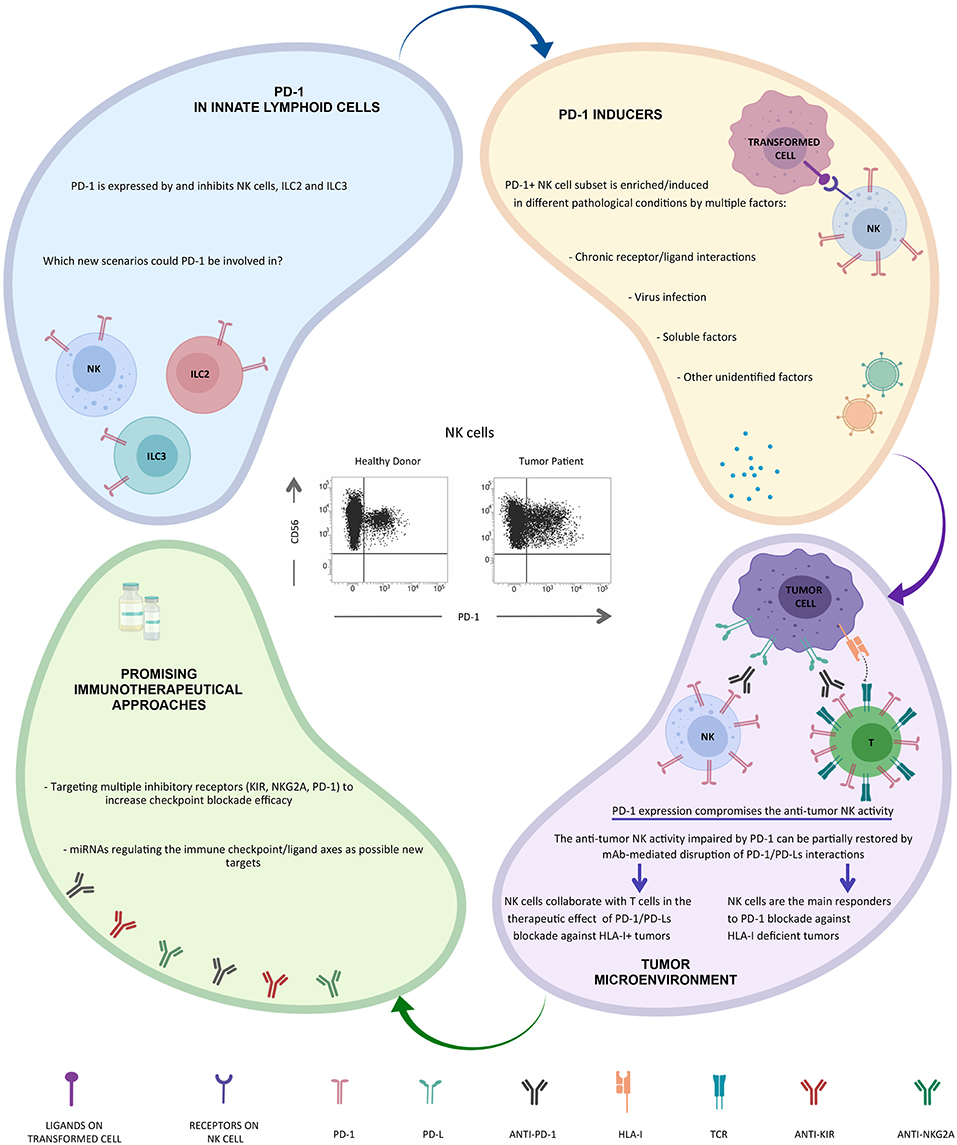
Although PD-1 was shown to be a hallmark of T cells exhaustion controversial studies have been reported on the role of PD-1 on NK cells.
Pd 1 expression on nk cells. Although PD-1 was shown to be a hallmark of T cells exhaustion controversial studies have been reported on the role of PD-1 on NK cells. Here we found by flow cytometry and single cell RNA sequencing analysis that PD-1 can be expressed on MHC class I-deficient tumor-infiltrating NK cells. The increased PD-1 expression on NK cells indicates poorer survival in esophageal and liver cancers.
Blocking PD-1PD-L1 signaling markedly enhances cytokines production and degranulation and suppresses apoptosis of NK cells in vitro. PD-1PD-L1 exerts inhibitory effect through repressing the activation of PI3KAKT signaling in NK cells. Further studies in vitro revealed that PD-1 expression on NK cells is associated with diminished natural cytotoxicity but enhanced ADCC.
Together these data suggest that PD-1 may contribute to the regulation of NK cell effector functions during malaria and possibly other infections. Expression of programmed cell death protein 1 PD-1 on natural killer NK cells has been difficult to analyze on human NK cells. By testing commercial clones and novel anti-PD-1 reagents we found expression of functional PD-1 on resting human NK cells in healthy individuals and reconstituting NK cells early after allogeneic hematopoietic stem.
Low-density PD-1 expression is found on resting NK cells and scFv PD-1 sequences enhance NK cell cytolytic and cytokine production function. Minimal PD-1 Expression in Mouse and Human NK Cells Under Diverse Conditions - PubMed. PD-1 expression is a hallmark of both early antigen-specific T cell activation and later chronic stimulation suggesting key roles in both naive T cell priming and memory T cell responses.
In particular PD-1 expression was shown on NK cells from some healthy individuals and in most cancer patients including Kaposi sarcoma ovarian and lung carcinoma and Hodgkin lymphoma where it can negatively regulate NK cell function 7378. Immune responses have the potential to induce life-threatening conditions. A novel multi-system pathway in which neuroendocrine signaling induces expression of the checkpoint receptor.
PD-1 is an inducible costimulatory molecule expressed on T cells B cells natural killer NK cells dendritic cells DCs and monocytes upon activation 15 17. Previous study has examined that PD-1 is not expressed on resting T cells but is inducibly expressed within 24 h after stimulation 18. PD-L1 expression on the NK cells identifies them as charged or highly activated and can demonstrate anti-tumor activity.
Further when bound by the anti-PD-L1 antibody. Programmed cell death protein 1 also known as PD-1 and CD279 cluster of differentiation 279 is a protein on the surface of cells that has a role in regulating the immune systems response to the cells of the human body by down-regulating the immune system and promoting self-tolerance by suppressing T cell inflammatory activity. This prevents autoimmune diseases but it can also prevent the.
PD-1 expression was confined to CD56 dim NK cells and if present to CD56 neg NK cells whereas the CD56 bright subset was consistently PD-1 neg. By comparing the PD-1 and PD-1 neg NK cells derived from the same healthy donor we found that the. Overall PD-1 expression on NK cells was consistently minimal in marked contrast with TIGIT expression in all TME samples assessed.
In contrast intratumoral T cell expression of PD-1 was consistently and significantly higher with T cell populations also expressing TIGIT Figure 7 I and J. PD-1 is differentially expressed on primary human NK cells as a function of MM disease activity. A By flow cytometry PD-1 expression was measured in CD56 CD3 NK cells isolated from healthy donors n 5 donors.
Evidence that PD-1 can be expressed on human NK cells has recently emerged in several cancer indications including Hodgkins lymphoma 40 44 but mechanistic in vivo studies examining whether and how PD-1 inhibits NK cell responses to tumors and whether PD-1PD-L1 blockade mobilizes NK cell responses are still lacking. PD-1 was expressed on NK cells within transplantable spontaneous and genetically induced mouse tumor models and PD-L1 expression in cancer cells resulted in reduced NK cell responses and generation of more aggressive tumors in vivo. NK cell expression of PD-1 has been reported in patients with multiple myeloma and in vitro NK cell activity against autologous myeloma cells was enhanced by anti-PD-1 antibodies.
We show that PD-1 upregulation is restricted to the cytolytic CD56 dim NK cell subset and not in the cytokine-producing CD56 bright cells. Annonse for your researchWorldwide leading provider for rapid flexible and reliable analysis. We Offer a Variety Of Custom Capabilities.