Thus imprudent and extensive usage of bacitracin in food animals may serve as a non-colistin usage risk factor for the transmissible colistin resistance. Using controlled systems in this study we observed that MCR-1 confers cross-resistance to bacitracin a popular in-feed antibiotic used in food animals.
This is the first report of the prevalence of human faecal carriage of mcr-1 in.
Mcr 1 antibiotic resistance. Using controlled systems in this study we observed that MCR-1 confers cross-resistance to bacitracin a popular in-feed antibiotic used in food animals. Thus imprudent and extensive usage of bacitracin in food animals may serve as a non-colistin usage risk factor for the transmissible colistin resistance. Specifically the impact of mcr-1 on membrane permeability and antibiotic resistance of E.
Coli was assessed by constructing an mcr-1 deletion mutant and by a complementation study. The removal of the mcr-1 gene from plasmid pHNSHP45 not only led to reduced resistance to colistin but also resulted in a significant change in the membrane permeability of E. Seven wastewater treatment plants WWTPs with different population equivalents and catchment areas were screened for the prevalence of the colistin resistance gene mcr-1 mediating resistance against last resort antibiotic polymyxin E.
The abundance of the plasmid-associated mcr-1 gene in total microbial populations during water treatment processes was quantitatively analyzed by qPCR analyses. Plasmid-borne colistin resistance mediated by mcr-1 may contribute to the dissemination of pan-resistant Gram-negative bacteria. Here we show that mcr-1 confers resistance to colistin-induced.
The plasmid-encoded mcr-1 gene confers bacterial resistance to the antibiotic colistin which is used as a medication of last resort for multidrug-resistant infections. The mcr-1 gene was detected predominantly in Escherichia coli. Antibiotic-susceptibility testing on 12 mcr-1 positive Enterobacteriaceae isolates revealed variable susceptibility profiles with no detection of carbapenem-resistant Enterobacteriaceae.
This is the first report of the prevalence of human faecal carriage of mcr-1 in. A novel plasmid-mediated colistin-resistant phosphoethanolamine transferase identified from a poultry isolate of Klebsiella pneumoniae. Identifying novel β-lactamase substrate activity through in silico prediction of antimicrobial resistance.
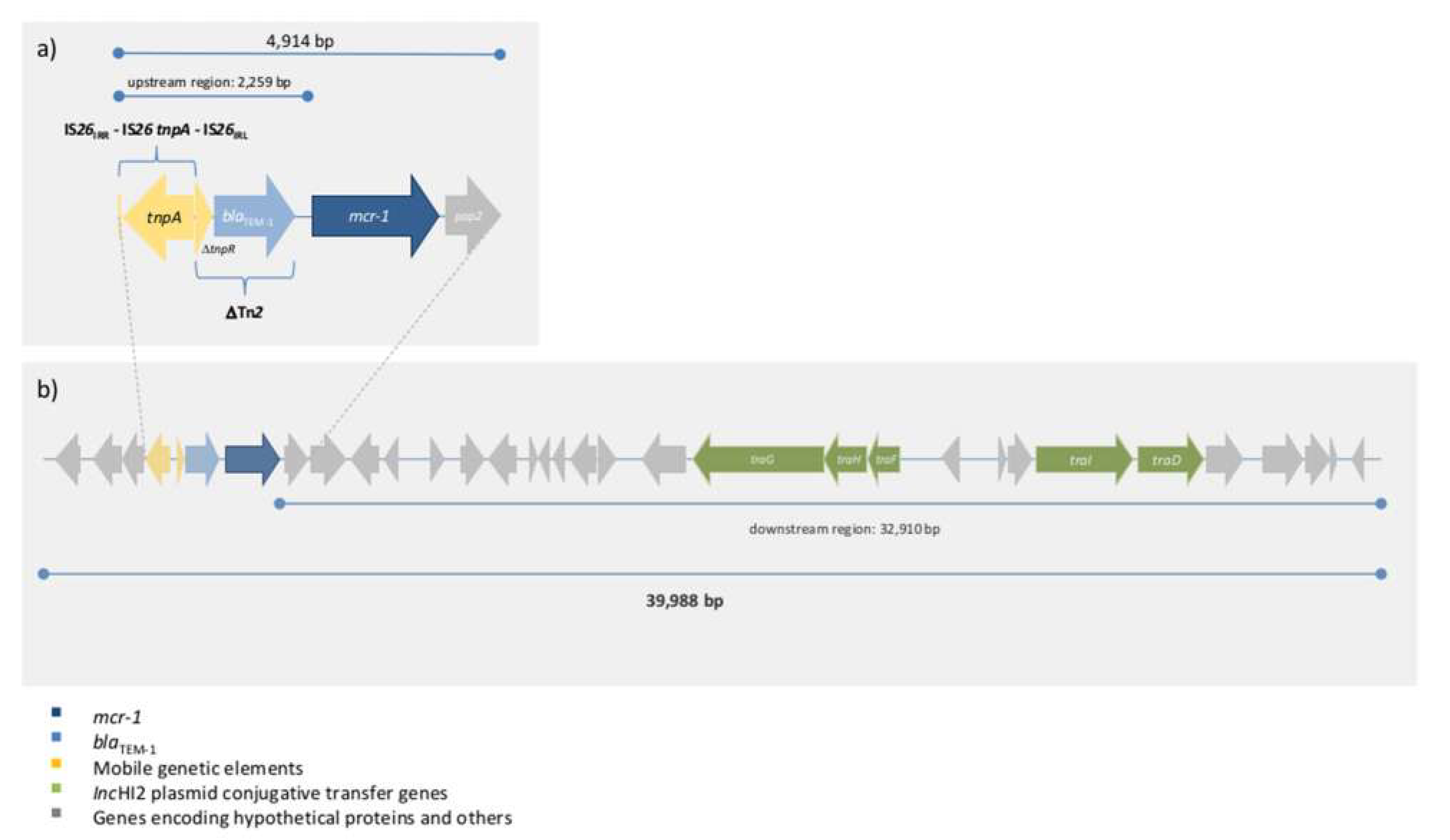
Prevalence of TEM-1 among the sequenced genomes plasmids and whole-genome shotgun assemblies available at NCBI for 221 important pathogens see methodological details and complete list of analyzed pathogens. Thus the deletion of mcr-1 also increases resistance to hydrophilic antibiotics. Mcr-1 confers colistin resistance through the addition of cationic phosphoethanolamine pEtN to phosphate groups on the lipid A component of LPS which reduces the net anionic charge of the cell surface Jeannot et al 2017.
The gene MCR-1 is notable because it produces a chemical that makes bacteria resistant to colistin a powerful antibiotic that has fallen out of favour due to its dangerous side effects but one. The mcr-1 gene makes bacteria resistant to the antibiotic colistin which is used as a last-resort drug to treat patients with multi-drug-resistant infections including carbapenem-resistant Enterobacteriaceae CRE. The plasmid-mediated transfer of the mobile colistin resistance gene mcr-1 represents a novel mechanism for antibacterial drug resistance and also poses new threats to public health.
However the mechanistic aspects of the MCR-1 colistin resistance are not fully understood. Here we report comparative genomics of two new mcr-1-harbouring plasmids isolated from the human gut microbiota. Antibiotic resistance is ancient and the resistome is a dynamic and mounting problem.
Causes of the global resistome are overpopulation enhanced global migration increased use of antibiotics in clinics and animal production selection pressure poor sanitation wildlife spread and poor sewerage disposal system12 Antibiotic treatment is one of the main approaches of. The Comprehensive Antibiotic Resistance Database gratefully acknowledges recent funding from the Genome Canada Canadian Institutes of Health Researchs Bioinformatics Computational Biology program allowing integration of the Antibiotic Resistance Ontology ARO with the Genomic Epidemiology Ontology IRIDA platform and OBO Foundry see Genome Canada press release. The first plasmid-borne polymyxin resistance gene mcr-1 was detected in a livestock isolate in China in November 201516 Subsequently several variants of the mcr genes mcr-1 to -5 have been reported in a number of countries1723 The mcr gene has been identified globally in various Gram-negative bacteria isolated from animals meat processed meat products vegetables and humans24.
ECDCEFSAEMA first joint report on the integrated analysis of the consumption of antimicrobial agents and occurrence of antimicrobial resistance in bacteria from humans and food-producing animals. Joint Interagency Antimicrobial Consumption and Resistance Analysis JIACRA Report. In addition to conferring resistance to polymyxin antibiotics mcr -1 could also confer bacterial resistance toward lysozyme 15.
The situation gets exacerbated by the fact that mcr-1 could.