Authors Robin E Ferner 1 James W Dear D Nicholas Bateman. In adults the initial treatment for paracetamol overdose is gastrointestinal decontamination.

In adults the initial treatment for paracetamol overdose is gastrointestinal decontamination.
Management of paracetamol overdose. Management of paracetamol overdose with acetylcysteine depends on the risk of liver damage based on the dose and timing of ingestion. If the patient is at risk of liver damage see Indications for immediate treatment below immediately give acetylcysteine intravenously see Dosing below. Patients who are malnourished have been fasting take enzyme inducing drugs or regularly drink alcohol to excess are at higher risk of liver damage.
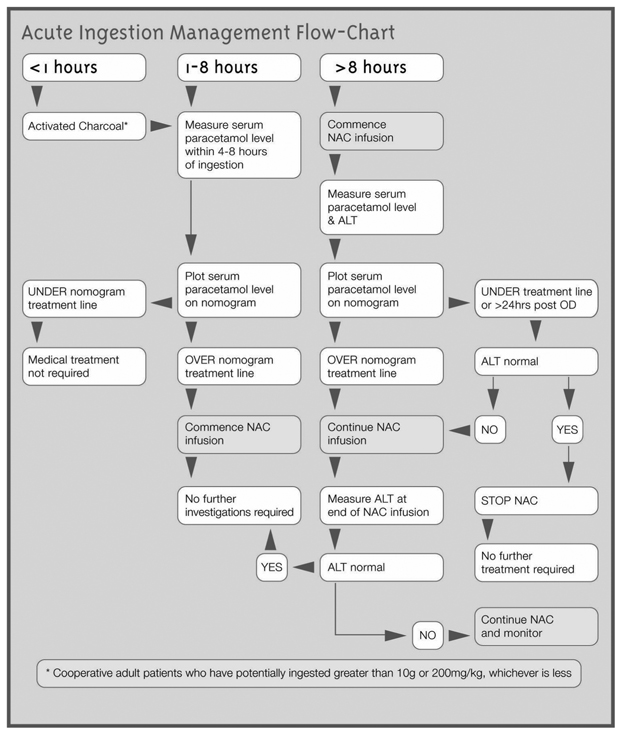
Treat patients who have ingested too much paracetamol within eight hours of ingestion whenever possible. If the patient has taken a staggered overdose of paracetamol at multiple time intervals within the last 8 hours treat the patient as per the 8 hours scenario in the Acute Ingestion Management Flow-chart. If it has been MORE than 8 hours since the first dose treat the patient as per the 8 hours scenario in the Acute Ingestion.
How is paracetamol overdose treated. Immediate management will require resuscitation and stabilisation. If the patient is unstable - such as having low blood pressure - or there is overwhelming liver failure they will need to be treated on an intensive care unit.
Hepatotoxicity is extremely rare in patients treated with acetylcysteine within 8 hours of an acute paracetamol overdose. The efficacy of acetylcysteine decreases subsequent to the first 8 hours following an acute paracetamol overdose with a corresponding stepwise increase in hepatotoxicity with increasing treatment delays between 8 and 16 hours. The optimal management of most patients with paracetamol overdose is usually straightforward.
However several differing nomograms and. Interventions for paracetamol acetaminophen overdose. Cochrane Database Syst Rev 2018.
Buckley NA Whyte IM OConnell DL Dawson AH. Activated charcoal reduces the need for N-acetylcysteine treatment after acetaminophen paracetamol overdose. Paracetamol concentration and time from ingestion can be prevented by prompt treatment with antidote.
However young and otherwise healthy patients still risk serious liver injury especially if they present more than a few hours after overdose or take staggered overdoses over hours or days4 How does paracetamol cause damage and who is at risk. Paracetamol is the commonest drug taken in overdose in the United Kingdom. While the management of early paracetamol poisoning is straightforward the management of late presenting cases cases presenting after a staggered overdose and patients with risk factors for paracetamol poisoning can be much more complex.
Paracetamol overdose during pregnancy should be treated with either oral or intravenous NAC according to the regular protocols in order to prevent maternal and potentially fetal toxicity. Unless severe maternal toxicity develops paracetamol overdose does not appear to increase the risk for adverse pregnancy outcome. There is little evidence to guide management in repeated supratherapeutic doses.
Potential toxicity should be assessed and a toxicologist consulted when. 200 mgkg or 10 g ingested over a 24 hour period 150 mgkgday or 6 g ingested over a 48 hour period. In adults the initial treatment for paracetamol overdose is gastrointestinal decontamination.
Paracetamol absorption from the gastrointestinal tract is complete within two hours under normal circumstances so decontamination is most helpful if performed within this timeframe. Serum paracetamol levels should be used to assess the need for N-acetylcysteine administration in all patients with deliberate paracetamol self-poisoning regardless of the stated dose. Clinical or biochemical evidence of liver injury may not be apparent for up to 24 hours after acute paracetamol overdose.
Management of paracetamol poisoning BMJ. Authors Robin E Ferner 1 James W Dear D Nicholas Bateman. Affiliation 1 West Midlands Centre for Adverse Drug Reactions City Hospital Birmingham UK.
When should N-acetyl cysteine be started in management of paracetamol overdose. In single dose paracetamol ingestion as per the recommendation of current UK guidelines N -acetyl cysteine should be started after the serum paracetamol level measured at 4 hours is above the treatment line ie. Paracetamol Overdose - Assessment and Management This document reflects what is currently regarded as safe practice.
However as in any clinical situation there may be factors which cannot be covered by a single set of guidelines. This document does not replace the need for the.