Common causes of malignant pleural effusion are lymphoma and cancers of the breast lung and ovary. Of 16 cases of RM the direct.
Kwee WS Veldhuizen RW Alons CA Morawetz F Boon ME.
Malignant mesothelial cells in pleural fluid. Patients with malignant mesothelioma pleural effusions had statistically decreased mean pleural fluid pH compared with patients with other malignant pleural effusions. Decreased levels of pleural fluid pH and pleural fluidserum glucose ratios have negative prognostic significance and probably correlate with the degree of tumor bulk affecting the pleural surface. E is false.
These are three carcinoma markers pCEA MOC31 BerEP4 and only one malignant pleural mesothelioma marker which also is frequently expressed in ovarian carcinomas. For workup of malignant pleural mesothelioma at least two carcinoma markers and two mesothelial markers should be used. Effusion occurs when there is an imbalance in the production or reabsorption of fluids or both.
1 In MPE formation neoplastic cells infiltrate the pleural space via hematogeneous direct or lymphatic spread. 1 Accumulation of pleural effusion can be a consequence of lymphatic blockage. 1 Recent studies have proposed that increased vascular permeability is a significant mechanism of MPE.
Contained at least 5 mesothelial cells. Pleural fluid cytological studies showed ma-lignant cells in 33 of 43 patients with effu-sions due to tumor. More than 50 of the effusions with originally inconclusive pleural fluid cytological findings were proved to be due to neoplasm.
When tumor is suspected at least three separate pleural fluid speci-. When cancer grows in the pleural space it causes a malignant pleural effusion. This condition is a sign that the cancer has spread or metastasized to other areas of the body.
Common causes of malignant pleural effusion are lymphoma and cancers of the breast lung and ovary. A malignant pleural effusion is treatable. 12 rader All cases of RM and MM were from specimens of pleural fluids.
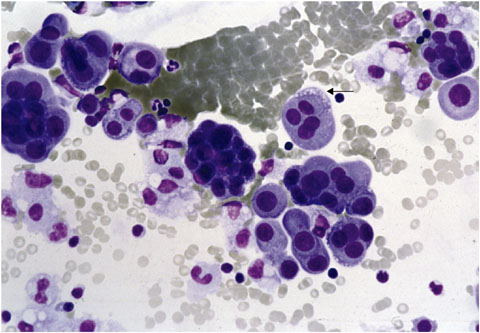
Of 16 cases of RM the direct. The cytological diagnosis of pleural effusions can be difficult and usually detects only 5060 of malignant pleural effusions 1 especially in specimens containing abundant reactive mesothelial cells. Distinguishing carcinoma cells from reactive mesothelial cells in such fluids is particularly challenging when there are relatively few carcinoma cells.
2 Additional techniques such. The occurrence of these polyploid cells was considered to be the result of mitotic abnormalities in the affected pleural area. Since polyploid mesothelial cells are not rare in certain non-malignant pleural fluids a trial to establish the diagnosis of malignancy based on.
Mesothelial cells are found in variable numbers in most effusions but their presence at greater than 5 of total nucleated cells makes a diagnosis of. Pleural Fluid Reactive Mesothelial Cells Schnauzer Miniatura Efficacy of two fluorescence in situ hybridization FISH probes for diagnosing malignant pleural effusions Semantic Scholar Cytological approach for pleural fluid analysis One year study Mesothelial Cells Images Stock Photos Vectors Shutterstock Body Fluids MLS Flashcards Quizlet. Cytological examination of pleural fluids is often the first line of investigation to detect and type the neoplastic cells based on their subtle morphological features.
5 Pleural metastases are more common in the visceral pleura and tend to be focal in the parietal pleura which is why pleural fluid cytology is a more sensitive diagnostic test than closed percutaneous pleural biopsy. Malignant cells were present in pleural fluid of 28 patients. Out of them 8929 samples were exudative and 1071 were transudative.
7143 of malignant effusions were hemorrhagic. Diagnosis of metastatic adenocarcinoma was made in pleural fluid cytological examination of nine cases. In this study we investigated whether GATA-3 could also stain benign mesothelials cells and therefore be a source for a potential false positive diagnosis of malignancy.
The Allegheny General Hospital Pathology database was searched for pleural and peritoneal effusion specimens with cytologic interpretations of benign mesothelial cells during the period from January 2014 to August. Epithelial or lining cells most commonly mesothelial cells1 The appearance and presentation of nucleated cells found in pleural fluid and whether they are considered commonbenign or abnormal is discussed below. Common cells present in pleural fluid include neutrophils lymphocytes monocytes mesothelial cells and red blood cells.
Treatment of malignant mesothelioma MM at an early stage results in increased survival. Cytologic examination of pleural effusions is one of the first diagnostic techniques attempted in these patients. The objective of this study was to define the role of cytologic examination of pleural fluid in facilitating early diagnosis.
Quantitative and qualitative differences between benign and malignant mesothelial cells in pleural fluid. Kwee WS Veldhuizen RW Alons CA Morawetz F Boon ME. Quantitative as well as qualitative cellular parameters were investigated in 20 cases of reactive mesothelial proliferations and 40 cases of primary pleural mesotheliomas.
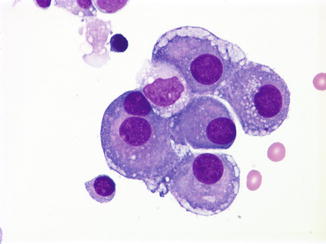
Archival paraffin-embedded cell blocks of pleural and peritoneal fluids from 52 patients with malignant mesothelioma MM and 64 patients with reactive mesothelial. Body fluid mesothelial cells in pleural fluid. Mesothelial cells may exhibit reactive morphology that can be confused with plasmacytes histiocytes or tumor cells.
The morphological evaluation of cytological specimens from body cavity fluids presents difficulties in the differential diagnosis between benign reactive mesothelial rm cells and adenocarcinoma ac or malignant. Pleural Fluid Right Thoracentesis. - Negative for malignant cells.
- Reactive mesothelial cells present in a background of abundant lymphocytes. Additional sampling should be considered within the clinical context. Specific diagnoses - benign Eosinophilic pleuritis General.
This has a large DDx. Trauma with air in the pleural cavity.