
6 Competition model simulations for Runs 3 and 4 see Table 6. Luxury consumption of soil nutrients.
Describe the soil colloidal complex indicate its various components.
Luxury consumption of nutrients. Luxury consumption has been shown to occur during nutrient flushes Chapin 1980 and may simply continue if levels are increased eg. The selective pressure was not therefore the benefit of preventing other species from taking the nutrients up and thereby outcompeting the slowgrowing plants but that of enabling continued growth when nutrients. Luxury consumption of soil nutrients.
A possible competitive strategy in above-ground and below-ground biomass allocation and root morphology for slow-growing arctic vegetation. During the flushes luxury consumption and these reserves are then used to support growth when external nutrients are not available for plant uptake Chapin 1980. Fast-growing herbaceous species tend to show phenotypic plasticity and clear responses in allocation to root vs.
Shoot biomass when subjected to experi-mental nutrient enrichment. The increased investment in roots in the fertilized plots found in the field could be explained in the competition model in terms of luxury consumption of nutrients ie. The absorbance of nutrients in excess of the immediate plant growth requirements.
Luxury consumption has been shown to occur during nutrient flushes Chapin 1980 and may simply continue if levels are increased eg. The selective pressure was not therefore the benefit of preventing other species from taking the nutrients up and thereby outcompeting the slowgrowing plants but that of enabling continued growth when nutrients. The increased investment in roots in the fertilized plots found in the field could be explained in the competition model in terms of luxury consumption of nutrients ie.
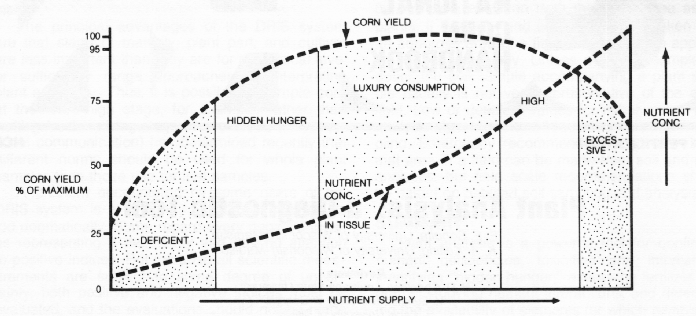
The absorbance of nutrients in excess of the immediate plant growth requirements. Luxury consumption of plant nutrients is the absorption of nutrients beyond what the plant needs. For example a plant may absorb potassium past the level that is optimal for plant growth if large quantities are present in the soil.
Chapter 12 Problem 15SQ is solved. The remaining K nutrient is attended in plant body as storage or freezing condition. There are some special type of plants which storage K nutrient in their body.
The storage of excess amount k nutrient in plant body is called luxury consumption of K Potassium. Elements of Nature and Properties of Soil Student Value Edition 3rd Edition Edit edition. Problem 15SQ from Chapter 12.
What is luxury consumption of plant nutrients and what are. 1 Answer to What is luxury consumption of plant nutrients and what are its advantages and disadvantages. How does phosphorus that forms relatively insoluble inorganic compounds in soils find its way into streams and other waterways.
The incorporation of large amounts of wheat straw into a soil may bring about. What is luxury consumption of plant nutrients and what are it advantages and disadvantages. Students also viewed these Earth sciences questions.
Describe the soil colloidal complex indicate its various components. And explain how it tends to serve a tank for plant nutrients. The term luxury consumption is used to describe nutrient absorption by the plant that does not influence yield.
Excessive or toxic When the concentration of essential or other elements is high enough to reduce plant growth and yield then it is said to be toxic. Excessive nutrient concentration can cause an imbalance in other. Luxury consumption is useful not only for sustaining growth when nutrients become scarce Chapin 1980 but also contributes to reducing nutrient availability and out-competing neighboring plants.
The capacity for luxury consumption differed between nutrients and was growth rate dependent. At low growth rates the coefficient of luxury consumption R sat for P was ca. Four times that for N.
The set of all possible relationships between N and P cell quota under these conditions was reported and these values were then used to establish the cellular NP niche boundaries for S. Luxury consumption occurs when soil nutrient levels are above optimum and plants take up more of a nutrient than needed for functioning and production. Potassium K is commonly taken up in excess.
The toxicity level is the nutrient level at which there is so much. It is suggested that the luxury consumption of potassium followed by translocation and reutilization of the potassium in the plant is an important process in the assimilation of potassium by plants. Journal of the American Society of Agronomy 2013USUS2013_22rdf.
Luxury consumption of soil nutrients. A possible competitive strategy in above-ground and below-ground biomass allocation and root morphology for slow. 6 Competition model simulations for Runs 3 and 4 see Table 6.
A Biomass of Plants 1 and 2 - - Plant 1 without increased root length. B Biomass of Plants 1 and 2 - - Plant 1 with increased root length. C N-availability in the soil using Plant 1 with heavy line and without light line increased root length.
- Luxury consumption of soil nutrients. What is luxury consumption of plant nutrients and what are its advantages and disadvantages. How does phosphorus that forms relatively insoluble inorganic compounds in soils find its way into streams and other waterways.