Bony injuries including occipital condyle fractures atlas fractures most odontoid. The motion of the upper cervical spine UCS has a great interest for analyzing the biomechanical features of this joint complex especially in case of instability.
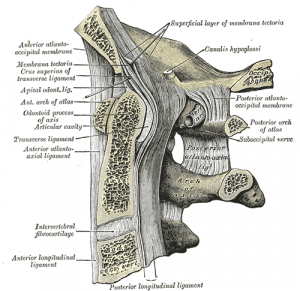
The Posterior Longitudinal Ligament runs up.
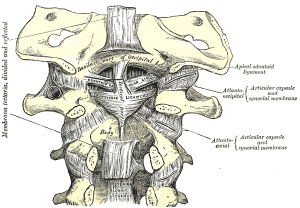
Ligaments of the upper cervical spine. Cervical spine ligaments ordered from anterior to posterior include. Anterior longitudinal ligament ALL anterior atlanto-occipital membrane. Alar ligaments paired cruciate ligament of the atlas.
Joins the body of the axis to the foramen magnum. The motion of the upper cervical spine UCS has a great interest for analyzing the biomechanical features of this joint complex especially in case of instability. Although investigators have analyzed numerous kinematics and musculoskeletal characteristics there are still little data available regarding several suboccipital ligaments such as occipito-atlantal atlantoaxial and cruciform ligaments.
Ligaments The Ligamentum Flavum forms a cover over the dura mater. A layer of tissue that protects the spinal cord. The Anterior Longitudinal Ligament attaches to the front anterior of each vertebra.
This ligament runs up and down the. The Posterior Longitudinal Ligament runs up. There are six major ligaments to consider in the cervical spine.
The majority of these ligaments are present throughout the entire vertebral column. Present throughout Vertebral Column. Anterior and posterior longitudinal ligaments long ligaments that run the length of the vertebral column covering the vertebral bodies and intervertebral discs.
Cervical spine ligaments The cervical spine ligaments are a combination of ligaments that continue from lower regions of the vertebral column that change names as they reach C2 and ligaments that are unique to the cervical spine. Ligaments that continue from below C7 from anterior to. The unique anatomy of the upper cervical spine and the typical mechanisms of injury yield a predictable variety of injury patterns.
Traumatic ligamentous injuries of the atlanto-occipital joint and transverse atlantal ligament are relatively uncommon have a poor prognosis for healing and often respond best to surgical stabilization. Bony injuries including occipital condyle fractures atlas fractures most odontoid. Upper back muscle that is the cervical and thoracic back muscles are divided in three layers.
The middle and upper part of your spine is called the thoracic region and it helps to support your upper body. Muscles ligaments and tendons your thoracic spine has a lot of soft tissues that support it. The right treatment can help relieve the pain.
The neck has seven to 10 ligaments all serving a purpose in the structure and motion of the neck. It runs from the neck to the upper back. Neck anatomy explained the neck begins at the base of the skull and connects to the thoracic spine the upper back.
Contains cervical vertebrae and postural muscles. The majority of these nerves control the functions of the upper extremities and allow. In the upper back region the trapezius rhomboid major and levator scapulae muscles anchor the scapula and clavicle to the spines of several the trapezius arises from ligaments at its origins along the nuchal crest of the occipital bone and the spinous processes of the cervical and thoracic vertebrae.
The upper cervical spine has the first and second vertebrae the atlas and axis and forms a unit with the occiput. The atlas A thick anterior arch remains extending into and joining the two lateral masses on which are the superior atlantal joint facets which articulate with the occipital condyles. And the inferior joint facets of the axis.
Cervical spine disorders are illnesses that affect the cervical spine which is made up of the upper first seven vertebrae encasing and shielding the spinal cordThis fragment of the spine starts from the region above the shoulder blades and ends by supporting and connecting the skull. The cervical spine contains many different anatomic compositions including muscles bones ligaments. It is a fibro-elastic membrane which extends from occiput to spine of all cervical vertebrae.
It helps in stability of head and neck especially in head flexion acceleration injuries. It limits flexion and provides an attachment to Trapezius and Splenius capitis. Anatomy of the Upper Cervical Spine Craniocervical Junction The upper cervical spine is a complex three-unit joint that includes the bones of the occiput atlas and axis their synovial articulations and the associated ligamentous structures.
The six synovial joints in this complex include the paired occipitoatlantal joints the anterior and posterior median atlantoodontoid joints and the. The supraspinous ligament thickened in the cervical spine as the nuchal ligament interspinous ligaments fibrous capsules of the facet joints which are ligamentous in structure and therefore also function to limit motion ligamentum flavum and posterior longitudinal ligament are all located posterior to the axis of motion for flexion and extension of the spine. Therefore they all limit.
Ligamentous damage showed an average significant decrease of the PADI of 137 mm in the first step and of 357 mm in the second step in flexion while it is reduced about 161 mm and 041 mm in the extended and similarly in the neutrally positioned spine. Alar and transverse ligaments are both of obvious importance in order to prevent AAS and movement-related spinal cord compression. Magnetic resonance imaging MRI is an essential modality in evaluating the ligamentous and soft tissue elements of the upper cervical spine.
This region has horizontally oriented facets and no intervertebral discs. Ligaments and membranes are thus crucial in stabilization at these levels.