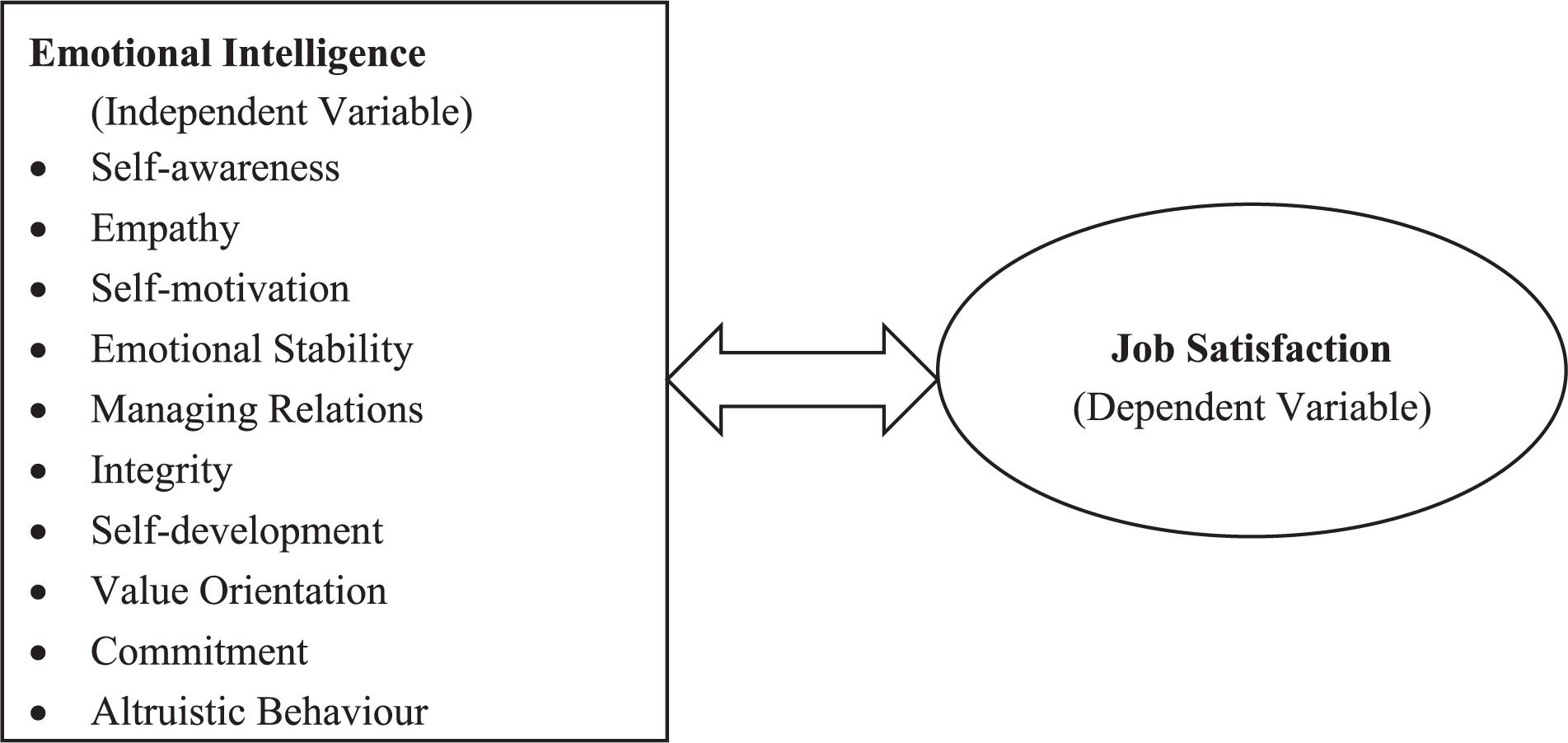
The model states that there are five core job characteristics skill variety task identity task significance autonomy and feedback which impact three critical psychological states experienced meaningfulness. The current version of the model proposes that high job demands lead to strain and health impairment the health impairment process and that high resources lead to increased motivation and higher productivity the motivational process.
Components of job satisfaction The Pennsylvania State University 2010.
Job satisfaction model field 2008. Job Satisfaction Model for retention Posted by Justin Field on April 11 2008 Ive been studying turnover and retention recently and it led me to wonder about the real reasons for turnover. Everybody understands that some turnover is functional or beneficial to the organisation and some turnover is dysfunctional bad for the organisation. Job Satisfaction Model Field 2008.
Social information processing organizational characteristics Based mainly on Festingers 1954 Social Comparison Theory Jex 2002 explains that during social information processing employees look to co-workers to make sense of and develop attitudes about their work environment. According to Bernstein Nash 2008 job satisfaction has emotional cognitive and behavioral components Locke 1976 defined job satisfaction as a pleasurable or positive emotional state resulting from the appraisal of ones job or job experiences. Components of job satisfaction The Pennsylvania State University 2010.
Job Satisfaction and Job Performance. Is the Relationship Spurious. August 2008 Allison Laura Cook BA Purdue University Chair of Advisory Committee.
Newman The link between job satisfaction and job performance is one of the most studied relationships in industrialorganizational psychology. Meta-analysis Judge Thoresen Bono Patton 2001 has estimated the magnitude of. We consider that job satisfaction represents a feeling that appears as a result of the perception that the job enables the material and psychological needs Aziri 2008.
Job satisfaction can be considered as one of the main factors when it comes to efficiancy and effectiveness of business organizations. In fact the new managerial paradigm wich insists that employees should be treated. Job satisfaction is the extent to which people like satisfaction or dislike dissatisfaction their jobs 21 and refers to an attitude or emotional response to ones tasks as well as to the.
Franěk and Večera 2008 undertook a research on a sample of Czech workers and came to the following conclusions. -In larger organisations job satisfaction is. Hackman Oldham proposed the Job Characteristics Model which is widely used as a framework to study how particular job characteristics impact on job outcomes including job satisfaction.
The model states that there are five core job characteristics skill variety task identity task significance autonomy and feedback which impact three critical psychological states experienced meaningfulness. Major process theories of job satisfaction and motivation are Vrooms expectancy theory Adams equity theory Lockes goal-setting theory and Skinners reinforcement theory. 21 Content Theories Maslows hierarchy of needs is a popular pioneer theory of job satisfaction and motivation revolving around lower-level and higher-level needs.
It states that people are motivated by five basic needs namely. The aptly titled Job Satisfaction Hoppock 1935. While pay and benefits are not the only reason employees find satisfaction in their workplaces research going back more than 30 years eg Gerhart 1987 shows that pay and benefits at least according to how employees view themselves in their roles has ranked high on lists of job satisfaction factors.
Rewards and recognition. Job satisfaction or employee satisfaction is a measure of workers contentedness with their job whether they like the job or individual aspects or facets of jobs such as nature of work or supervision. Job satisfaction can be measured in cognitive evaluative affective or emotional and behavioral components.
Researchers have also noted that job satisfaction measures vary in the extent to. The phenomenon job satisfaction is simply based on the missing subjectivism and the miss-ing complexity of the individual and the situation. A new complex and theoretical model of job satisfaction CMJSKMA was developed which is focused on the main criticism to solve this problem and where all important research is integrated.
In the model the facts of quality scale preference and varying. Although the human resources management literature posits positive effects of leadership behaviors on employee job satisfaction the causal path between the two is unclear due to potential endogeneity issues inherent in this relationship. To address the issue we first provide theoretical explanations about why and how transformational and transactional leadership behaviors would enhance employee job satisfaction.
There are many theories and models dealing with job attitudes. One of the most researched job attitudes is job satisfaction. It refers to positive viewpoints people hold toward their jobs.
Job satisfaction has three important areas. Evaluative cognitive and behavioral. Evaluative refers to how an employee feels about the job whether heshe likes it or not.
Cognitive refers to what an employee. Hackman Oldham proposed the Job Characteristics Model which is widely used as a framework to study how particular job characteristics impact on job outcomes including job satisfaction. The model states that there are five core job characteristics skill variety task identity task significance autonomy and feedback which impact three critical psychological states experienced meaningfulness.
Job satisfaction is significant because a persons attitude and beliefs may affect his or her behavior. Attitudes and beliefs may cause a person to work harder or the opposite may occur and he or she may work less. Job satisfaction also affects a persons general well-being for the reason that people spend a good part of the day at work.
Consequently if a person is dissatisfied with their work this. The job satisfaction is a single concept and employees produce the overall attitude or opinion to the work. The representatives of this view are Hoppock et al.
In the year 1935 Hoppock in his doctoral thesis Job Satisfaction described the job satisfaction as the employees subjective reflections to working scenarios ie. Abstract The Job Demands-Resources model JD-R model became highly popular among researchers. The current version of the model proposes that high job demands lead to strain and health impairment the health impairment process and that high resources lead to increased motivation and higher productivity the motivational process.
This chapter reviews the assumptions and development of the JD-R model.
