The best way to diagnose personality disorders will be dictated by the goals of the patient time constraints and other contextual issues. 1 Neurobiological studies have suggested.
All other things being equal the ideal personality.
Hyperthymic personality disorder diagnosis. Their research criteria for hyperthymic temperament include onset before age 21 habitual sleep of less than 6 hours even on weekends excessive use of denial and traits described originally by Schneider et al that include being overoptimistic self-assured grandiose overtalkative warm and people-seeking uninhibited promiscuous and meddlesome. 1 Neurobiological studies have suggested. A Hyperthymic personality has been suggested as a possible precursor for Bipolar Disorder.
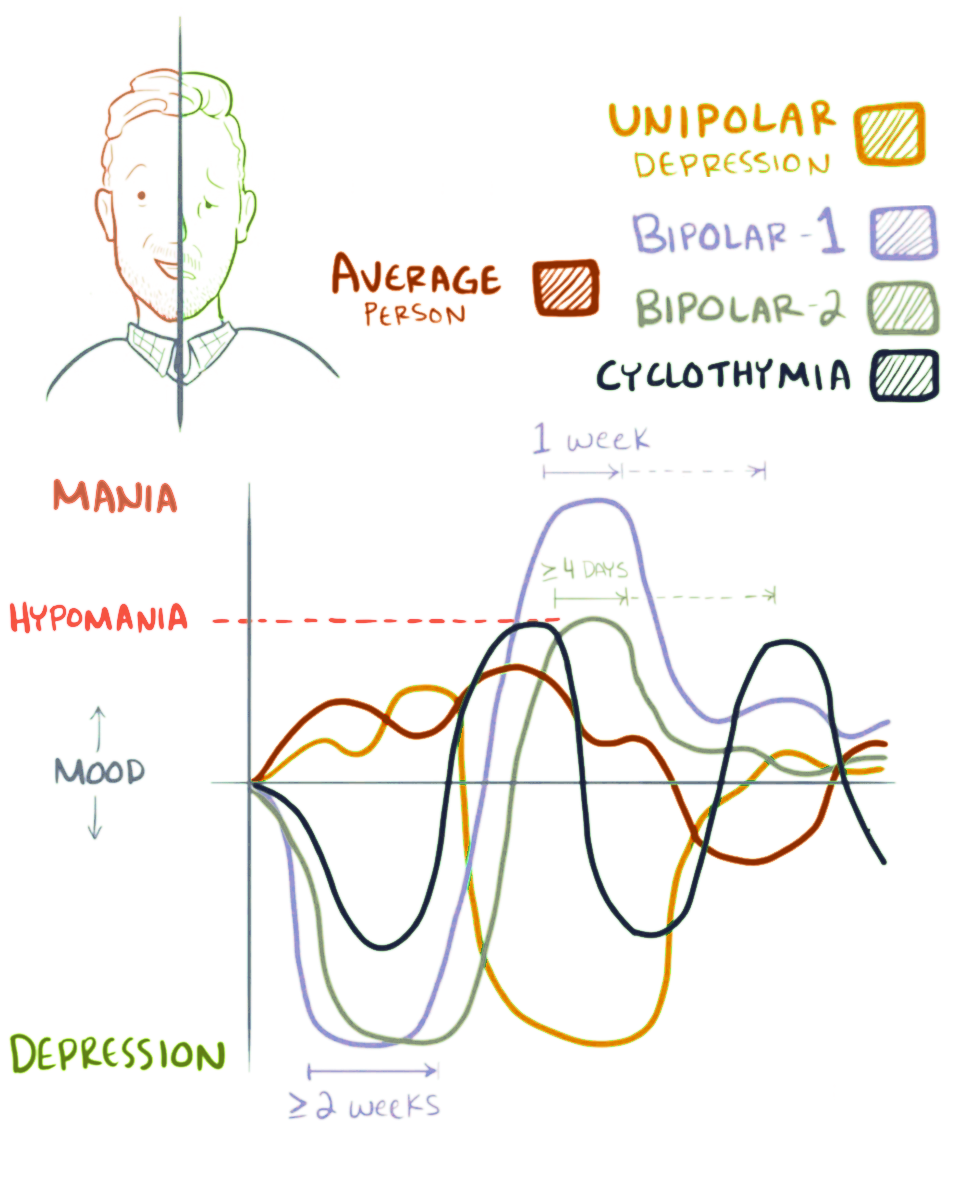
Currently the DSM-4 includes diagnoses for Bipolar I the most severe kind and the Bipolar II variety with less visible mania but not necessarily less severe as the choices. Some theoreticians have suggested that there are also some soft bipolar disorders They have suggested designations of. The semi-structured Diagnostic Interview for Genetic Studies was administered by masterslevel psychologists to a random sample of an urban area n3719.
The lifetime prevalence was 10 for BP-I 08 for BP-II 10 for OSBARD and 3 for hyperthymic personality. Most doctors I am aware of would have upgraded your diagnosis to Cyclothymia and probably even to Bipolar II disorders. The shorthand way of understanding this is that Hypothermic people are annoyingly cheerful and full of energy Meaning that they can keep going until they wear mere mortals out.
Once you progressed to revved up most doctors would say you are going too fast. DSM-IV-TR diagnoses were bipolar I N1 bipolar II N9 major depressive disorder N34 and depressive disorder not otherwise specified N2. Excluding one bipolar I patient who had both cyclothymic and hyperthymic temperaments patients with bipolar II12 N32 and IV N13 as well as bipolar II N9 were classified into the soft bipolar spectrum although there was considerable.
Differentiating overextended personality disorder from what has been called the hyperthymic personality 3 may prove difficult and the two conditions frequently overlap and co-occur. Hyperthymic Temperament HYT and a closely related trait Hypomanic Personality HYP have both been related to bipolar affective disorder BAD. Intensity dependence of auditory evoked potentials IAEP is a suggested inverse indicator of serotonergic neurotransmission and has been found to be elevated in BAD.
Therefore the present study explored for the first time whether. Ious-depressive hyperthymic irritable anxious-somatic and depressive-cyclothymic 16. The Arabic CIDI 30 was used as the diagnostic instru-ment for DSM-IV disorders.
The CIDI included two parts. Part I assessed core disorders depression mania panic phobias generalized anxiety disorder intermittent explosive. Specific personality disorders F60-.
F60 Specific personality disorders. F600 Paranoid personality disorder. F601 Schizoid personality disorder.
F602 Antisocial personality disorder. F603 Borderline personality disorder. F604 Histrionic personality disorder.
F605 Obsessive-compulsive personality disorder. Please also keep in mind that without a publicly known professional diagnosis much of this is simply speculation based on observed behavior. Famous People with Personality Disorders.
Anna Nicole Smith A number of psychologists claim that Smith exhibited many of the symptoms of histrionic personality disorder. The public watched as she displayed excessive emotions abused. The best way to diagnose personality disorders will be dictated by the goals of the patient time constraints and other contextual issues.
All other things being equal the ideal personality. The total lifetime prevalence of DSM-5 bipolar and related disorders with and without Hyperthymic personality was 58 and 28 respectively. Table 1 shows the lifetime and 12 month prevalence estimates for all diagnostic categories for the overall sample and according to gender.
Out of 3719 individuals who underwent the psychiatric evaluation. Intense emotional experiences excitement hypomanic periods and moods alternating with depressive periods and moods. Pleasurable activities and experiences.
Becomes excessively involved in pleasurable activities with lack of concern for the high potential of. The essential features of a personality disorder are impairments in personality self and interpersonal functioning and the presence of pathological personality traits. To diagnose a personality disorder iteria must be met.
Significant impairments in self identity or self-direction and interpersonal empathy or intimacy functioning. Borderline personality disorder Borderline personality disorder is a complex diagnosis characterized by mood instability impulsivity and disturbed relationships. The affective instability in borderline personality disorder does not resemble classical bipolar disorders and can be distinguished from hypomania.
The semi-structured Diagnostic Interview for Genetic Studies was administered by masterslevel psychologists to a random sample of an urban area. The lifetime prevalence was 10 for BP-I 08 for BP-II 10 for OSBARD and 3 for hyperthymic personality. Subjects with OSBARD were more severely affected than subjects without a history of mood disorders regarding almost all clinical correlates.
Compared to those with MDD they also revealed an elevated risk of suicidal attempts lower global functioning more treatment seeking and more lifetime comorbidity including anxiety substance use and impulse-control disorders. An affective disorder characterized by periods of depression and hypomania. These may be separated by periods of normal mood.
Chronic mood disturbance of at least 2 years duration involving numerous hypomanic episodes separated by periods of depression or loss of pleasure or interest.