1Uterine cervical neoplasms prevention and control. For most people an HPV infection clears by itself within two years especially in people under 30.

Screening in immune-deficient women.
Hpv screening guidelines 2017. There are no standard guidelines. New York HIV Clinical guidelines In order to receive state or Federal HIV funding health centers must perform routine anal pap smear in HIV-infected individuals. MSM ho anogenital condyloma and women with abnormal cervical andor vulvar histology.
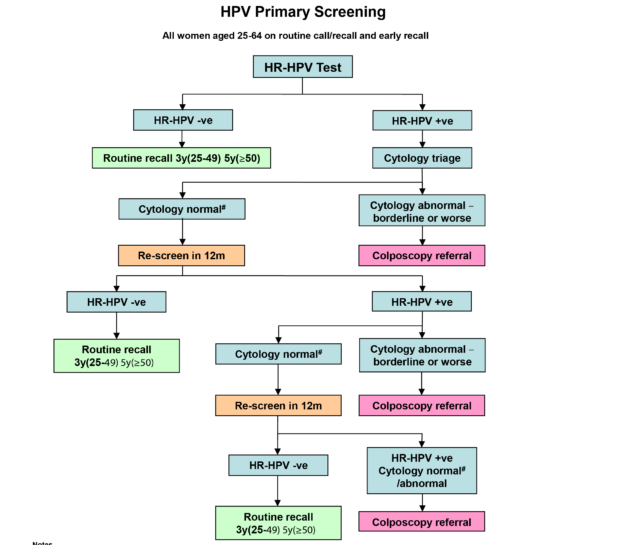
Added new guidance on primary HPV screening implementation. The role of the cervical screening provider lead. One is to start screening at a slightly older age and the other is to preferentially recommend a type of screening test called an HPV test.
ACS recommends cervical cancer screening with an HPV test alone every 5 years for everyone with a cervix from age 25 until age 65. Use HPV tests to screen women for cervical cancer prevention. With HPV testing the frequency of screening will decrease.
Once a woman has been screened negative she should not be rescreened for at least five years but should be rescreened within 10. This represents a major cost saving for health systems in comparison with other types of tests. After a successful evaluation of the feasibility of HPV-based screening in 2014 primary HPV testing for cervical screening was implemented in 2017.
The Netherlands has been one of the first countries worldwide to implement nationwide HPV-based screening and its experience with the new programme is therefore followed with great interest. In this manuscript we present an overview of the studies that were instrumental in the choice of HPV assay and triage strategy the adjustment of screening. Screen all pregnant women.
One time screening between ages 1565. Annually if at very high risk. Every 35 years if at increased risk Syphilis.
Screen all pregnant women and those at increased risk Sensory Screenings Eye Exam Up to age 39 years at discretion of clinician Every 12 years Hearing Assessment Unnecessary if asymptomatic. WHO guidelines for screening and treatment of precancerous lesions for cervical cancer prevention. 1Uterine cervical neoplasms prevention and control.
2Precancerous conditions diagnosis. 3Precancerous conditions therapy. Women ages 21 through 29 should be screened with a Pap test every 3 years.
Women ages 30 through 65 should be screened with any of three tests. Every 5 years with high-risk HPV testing alone. Every 5 years with Pap and high-risk HPV cotesting.
Every 3 years with a Pap test alone. Women who have had a total hysterectomy should stop cervical cancer screening. Men and women aged 50 y for all tests listed.
Guaiacbased fecal occult blood test gFOBT with at least 50 test sensitivity for cancer or fecal immunochemical test FIT with at least 50 test sensitivity for cancer or. Screening in Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander women. Screening after total hysterectomy.
Screening in women who experienced early sexual intercourse or victims of sexual abuse. Screening in immune-deficient women. Screening in DES-exposed women.
Signs and symptoms of cervical cancer. The new screening method will test for the presence of human papillomavirus HPV. About four out of five people have an HPV infection at some time in their lives.
There are many different types of HPV and some are more likely than others to lead to cervical cancer. For most people an HPV infection clears by itself within two years especially in people under 30. You might not even know youve had.
Cervical cancer testing screening should begin at age 25. Those aged 25 to 65 should have a primary HPV test every 5 years. If primary HPV testing is not available screening may be done with either a co-test that combines an HPV test with a Papanicolaou Pap test every 5 years or a Pap test alone every 3 years.
Self-collected vaginal swabs using polymerase chain reaction PCR for HPV are equal to clinician-collected cytology and HPV swabs for detection of. The American Academy of Pediatrics AAP in February 2017 recommended a 2-dose HPV vaccine series for non-immunocompromised children who begin the series before 15 years of age. Bivalent HPV vaccine 2vHPV CervarixTM and quadrivalent HPV vaccine 4vHPV Gardasil are currently not available in the United States.
Age matters for screening Otherwise healthy women need a Pap every three years from age 21 to 29 agree most US. Physician groups and the draft Task Force guidelines. It provides an update for clinicians regarding the changes to the National Cervical Screening Program NCSP to be implemented on December 1st 2017 at which time the Pap test will be replaced by primary human papillomavirus HPV testing.
Aus diesem Grund sollte ein Gebärmutterhalskrebs-Screening-Programm einen HPV-Test nur dann als Screening-Tool einsetzen wenn dieser nachweislich eine reproduzierbare und konstant hohe Sensitivität für CIN2- und CIN3-Läsionen sowie einen minimalen Nachweis von klinisch irrelevanten HPV-Infektionen erbringen kann 2. The adoption of the USPSTF guidelines expands the recommended options for cervical cancer screening in average-risk individuals aged 30 years and older to include screening every 5 years with primary high-risk human papillomavirus hrHPV testing. Primary hrHPV testing uses high-risk HPV testing alone no cytology with a test that is approved by the US.
Food and Drug Administration FDA for stand-alone screening. Consistent with prior guidance screening.