R-R interval 12 R-R interval and QT-interval. QT correction method exercise stress test B.
The QT interval should be deter-mined as a mean value derived from at least 35 cardiac cy-cles heartbeats and is measured from the beginning of the earliest onset of the QRS complex to the end of the T wave.
How to measure qt interval. Measure the QT interval using the tangent technique and the preceding RR interval. QT correction method exercise stress test B. Define the end of the T wave as the intersection of a tangent from the steepest slope of the last limb of the T wave and the baseline The baseline is defined as the QQ line to provide a consistent reference.
Measuring the QT Interval The QT interval is best measured on lead II V5 or V6. Measure the distance between the start of the Q wave and the end. Compare QT intervals between sequential ECGs in order to determine change in QT.
Tangent Method In order to accurately measure the QT interval draw a. The QT interval extends from the beginning of the QRS complex to the end of the T wave. Since the report of Jervell and Lange-Nielsen in 1957 it has been difficult to determine whether to measure a QT or a QU interval.
U waves are more prominent in the left chest leads and less prominent in lead II with the end of the T wave in lead II corresponding to the end of significant repolarization in any other lead. How to measure the QT interval. The QT interval should be measured in either lead II or V5-6.
Several successive beats should be measured with the maximum interval taken. Large U waves 1mm that are fused to the T wave should be included in the measurement. Smaller U waves and those that are separate from the T wave should be excluded.
Waves such as U waves. The QT interval should be deter-mined as a mean value derived from at least 35 cardiac cy-cles heartbeats and is measured from the beginning of the earliest onset of the QRS complex to the end of the T wave. The QT measurement should be made in leads II and V5 or V6 with the longest value being used.
QT INTERVAL IN STABLE SINUS RHYTHM The QT interval is measured from the begin- ning of depolarization of the QRS complex to the end of the T wave This seemingly innocuous definition is fraught with problems. The first of these is whether. About Press Copyright Contact us Creators Advertise Developers Terms Privacy Policy Safety How YouTube works Test new features Press Copyright Contact us Creators.
R-R interval 12 R-R interval and QT-interval. The QT interval is defined as the measurement from the beginning of the QRS complex to the end of the T-wave. Physiologically it represents the total duration of time of the ventricular electrical activity depolarization and repolarization.
It is measured from the beginning of the QRS complex to the end of the T wave. Normally the QT interval is 036 to 044 seconds 9-11 boxes. The QT interval will vary with patient gender age and heart rate.
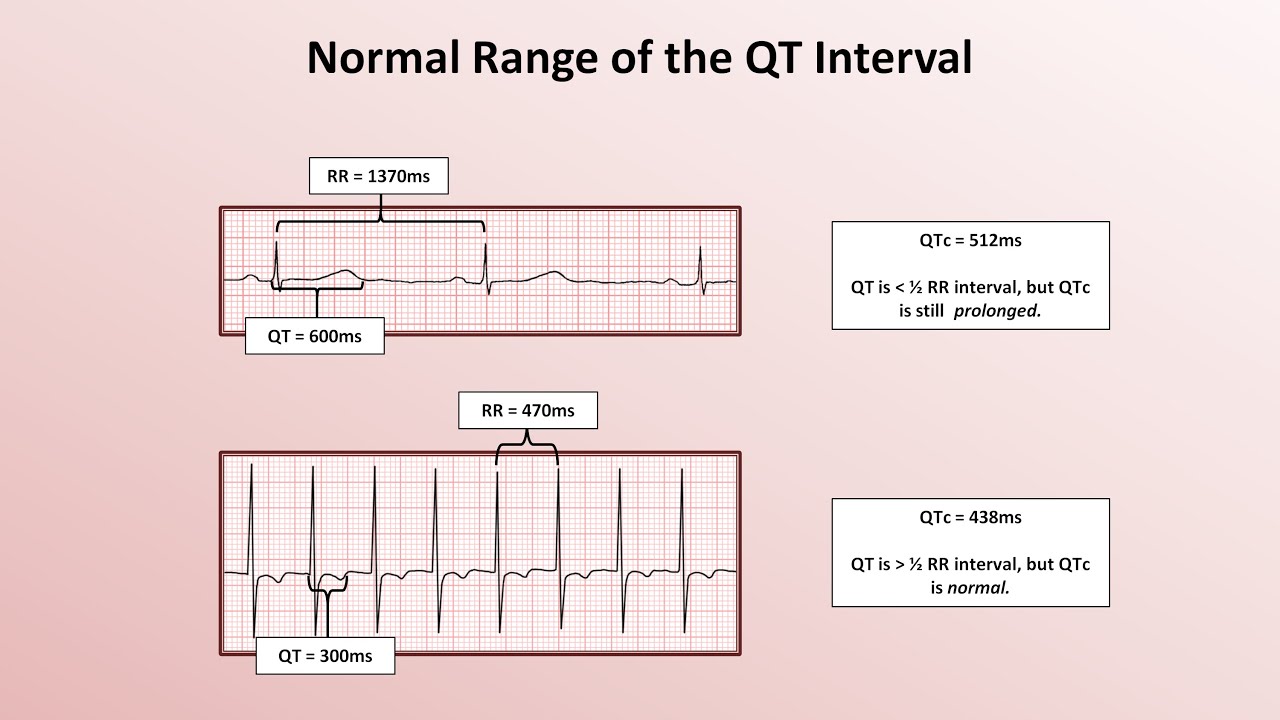
Another guideline is that normal QT Intervals is less than half of. The QT interval is measured on the surface 12-lead ECG or telemetry or smartphone-enabled mobile ECG from the beginning of the QRS complex to the end of the T wave. The QT interval is influenced by heart rate.
With a longer QT interval at slower heart rates and shorter QT interval at faster heart rates. Therefore the QT interval must be corrected for the patients heart rate to generate the patients QTc. The QT interval is measured from the beginning of the QRS complex to the end of the T-wave and s.
The evaluation of every electrocardiogram should also include an effort to interpret the QT interval to assess the risk of malignant arrhythmias and sudden death associated with an aberrant QT interval. The measurement of important electrocardiographic intervals usually includes the PR interval the QRS interval and the QT interval. At a standard paper speed of 25 mmsecond the width of each small square 1mm represents 004 seconds.
One large square 5mm represents 02 seconds. Previous Next. Toggle unit to use msec or small boxes.
1 small box 40 msec see below for example where QT interval 4 small boxes. The QT interval is longer when the heart rate is slower and shorter when the heart rate is faster. So its necessary to calculate the corrected QT interval QTc using the Bazett formula.
QT interval divided by the square root of the R-R interval. The R-R interval is measured from one R wave to the next R wave that comes before the QT interval being measured. For example if the QT interval measures 044.
Since the report of Jervell and Lange-Nielsen in 1957 it has been difficult to determine whether to measure a QT or a QU interval. U waves are more prominent in the left chest leads and less prominent in lead II with the end of the T wave in lead II corresponding to the end of. The QT interval should be measured manually preferably by using one of the limb leads that best shows the end of the T wave on a 12-lead ECG.
The QT interval should be measured from the beginning of the QRS complex to the end of the T wave and averaged over 3 to 5 beats. U waves possibly corresponding to the late repolarization of cells in the mid myocardium should be included in the measurement.
