Analysis of the WGS data provided explanations for the discordant results between TBS and WGS data revealed the true phylogenetic relationships between different species of Shigella and identified emerging pathoadapted lineages. Determined that the nucleotide similarity between Shigella and E.
The nomenclature is historically based and the discrimination of these genera developed as a result of the epidemiological need to identify the cause of shigellosis a severe disease caused by Shigella species.
How to distinguish between e coli and shigella. Brenner et al. Determined that the nucleotide similarity between Shigella and E. Coli was 80 to 90 whereas other Escherichia species are genetically distant.
Shigellae are phylogenetically E. Coli that were later classified as separate species on the bases of. Shigella can be differentiated from E.
Coli and accurately identified to the species level by use of kmer comparisons and MLST. Analysis of the WGS data provided explanations for the discordant results between TBS and WGS data revealed the true phylogenetic relationships between different species of Shigella and identified emerging pathoadapted lineages. It is possible to differentiate Shigella and all E.
Coli including EIEC by using multiple tests including ipaH-gene PCR physiological and biochemical typing and serological typing. Based on literature study a key is designed for daily use in diagnostic laboratories to identify Shigella and all E. Both Escherichia coli E.
Coli and Shigella spp. Produce a potent shigatoxin during infection that causes severe and life-threatening disease. These species are very closely related and have some similarity in their symptomology but E.
Coli infections are a particularly serious problem in children. Symptoms include fever and bloody diarrhea. The first step distinguished between 2 classes Shigella species and E.
Coli and the second step distinguished among 5 classes S. If results from the 2-class genus-level and 5-class species-level models were consistent eg if the results showed agreement with respect to genus identification then the species-level identification. IcsA expression on the surface of Shigella is sufficient to direct actin-based motility 5455.
Coli expressing IcsA can synthesize actin tails in cytoplasmic extracts 5455. During infection IcsA is also detected as a 95-kDa amino-terminal fragment of the 120-kDa full-length protein. Is one of the problems faced by a diagnostic microbiology laboratories and may reflect the fact that.
And all four. Species are very closely on the basis of the DNA-DNA relationship. However biochemical reactions are of considerable value in the differentiation of members of the genus.
Shigella bacteria are genetically similar organisms to E. Coli 3 18 and the genetic resemblance can cause misidentification of Shigella as E. Coli especially in DNA-based testing schemes.
The plate was able to detect and identify the target organisms with various degrees of success. Shigella organisms may be very difficult to distinguish biochemically from Escherichia coli. Brenner 1 considers Shigella organisms and E.
Coli to be a single species based on DNA homology. Salmonella is a rod shaped microbe. Shigella is a slender shaped microbe.
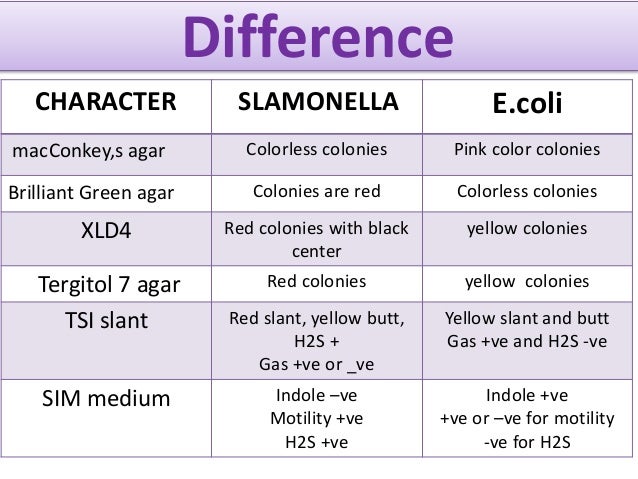
Salmonella is motile with peritrichous flagella. Shigella is non-motile in nature. Differential Media Hektoen Agar Salmonella colonies in Hektoen Agar appear black in color.
Shigella colonies in Hektoen Agar will appear green in color. Traditional microbiology differentiates Shigella from E. Coli based on their physiological and biochemical characteristics with EIEC being more metabolically active than Shigella Edwards and.
For the toxin that is produced by certain strains of Shigella and E. Coli bacteria see Shiga toxin. Shigella is a genus of bacteria that is Gram-negative facultative anaerobic non-spore-forming nonmotile rod-shaped and genetically closely related to E.
The genus is named after Kiyoshi Shiga who first discovered it in 1897. Shigella species are so closely related to Escherichia coli that routine matrix-assisted laser desorptionionizationtime of flight mass spectrometry MALDI-TOF MS cannot reliably differentiate them. Biochemical and serological methods are typically used to distinguish these species.
However inactive isolates of E. Coli are biochemically very similar to Shigella species and thus pose. Coli-Shigella species are a cryptic group of bacteria in which the Shigella species are distributed within the phylogenetic tree of E.
The nomenclature is historically based and the discrimination of these genera developed as a result of the epidemiological need to identify the cause of shigellosis a severe disease caused by Shigella species. Shigella species are a cryptic group of bacteria in which the Shigella species are distributed within the phylogenetic tree of E. The nomenclature is historically based and the discrimination of these genera developed as a result of the epidemiological need to identify the cause of shigellosis a severe disease caused by Shigella species.
The lactose permease gene lacY is present in all E. Coli strains but absent in Shigella spp whereas β-glucuronidase gene uidA is present in both E. Coli and Shigella spp.
Thus uid A gene and lac Y gene based duplex real-time PCR assay could be used for easy identification and differentiation of Shigella spp. Coli and in particular EIEC. Ecoli Escherichia coli E.
Coli is the name of a type of bacteria that lives in your intestines. Most types of E. However some types can make you sick and cause diarrhea.
One type causes travelers diarrhea. The worst type of E. Coli causes bloody diarrhea and can sometimes cause kidney failure and even death.
Introduction the distinction between E. Coli and Shigella species was not always that clear-cut. Coli are capable of causing illnesses similar Historically Shigella and Escherichia coli were established as to shigellosis andor are not able to convert lactose.
