Memory B cells On secondary exposure to the same antigen the memory B cells will be stimulated and result in production of high-affinity heavy-chain class- switched antibodies. Germinal centre-independent memory B cells are generated from CD38 GL7 activated B cells.
So the correct answer is T-lymphocytes Answer verified by Toppr.
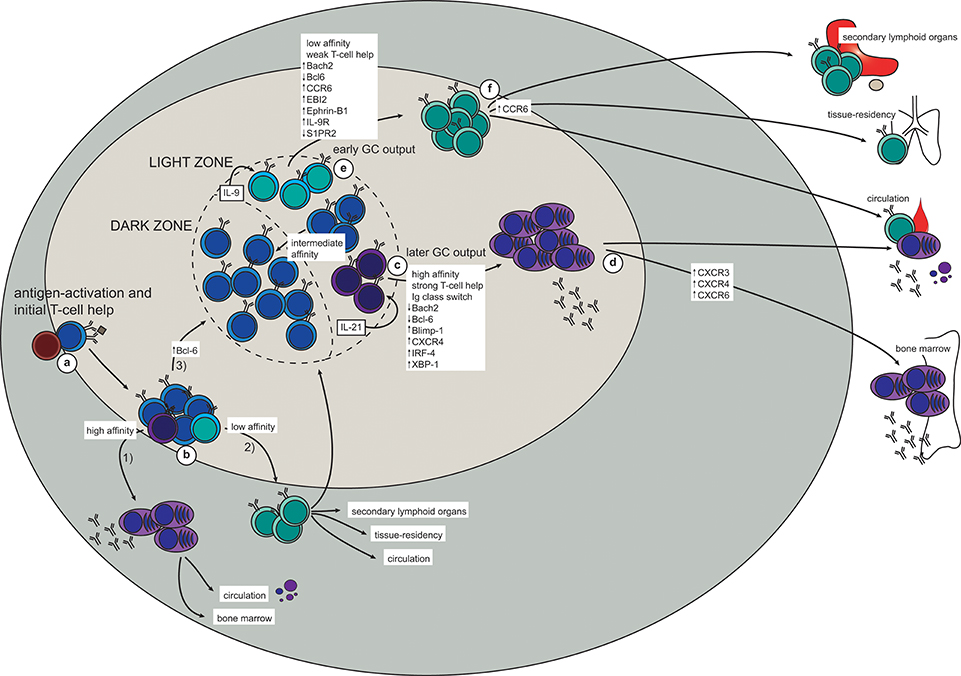
How are memory b cells formed. Memory B cells are generated in response to T-dependent antigens during the GC reaction in parallel to plasma cells Fig. Memory B cells are a B cell sub-type that are formed following a primary infection. In the wake of the first primary response infection involving a particular antigen the responding naïve cells ones which have never been exposed to the antigen proliferate to produce a colony of cells.
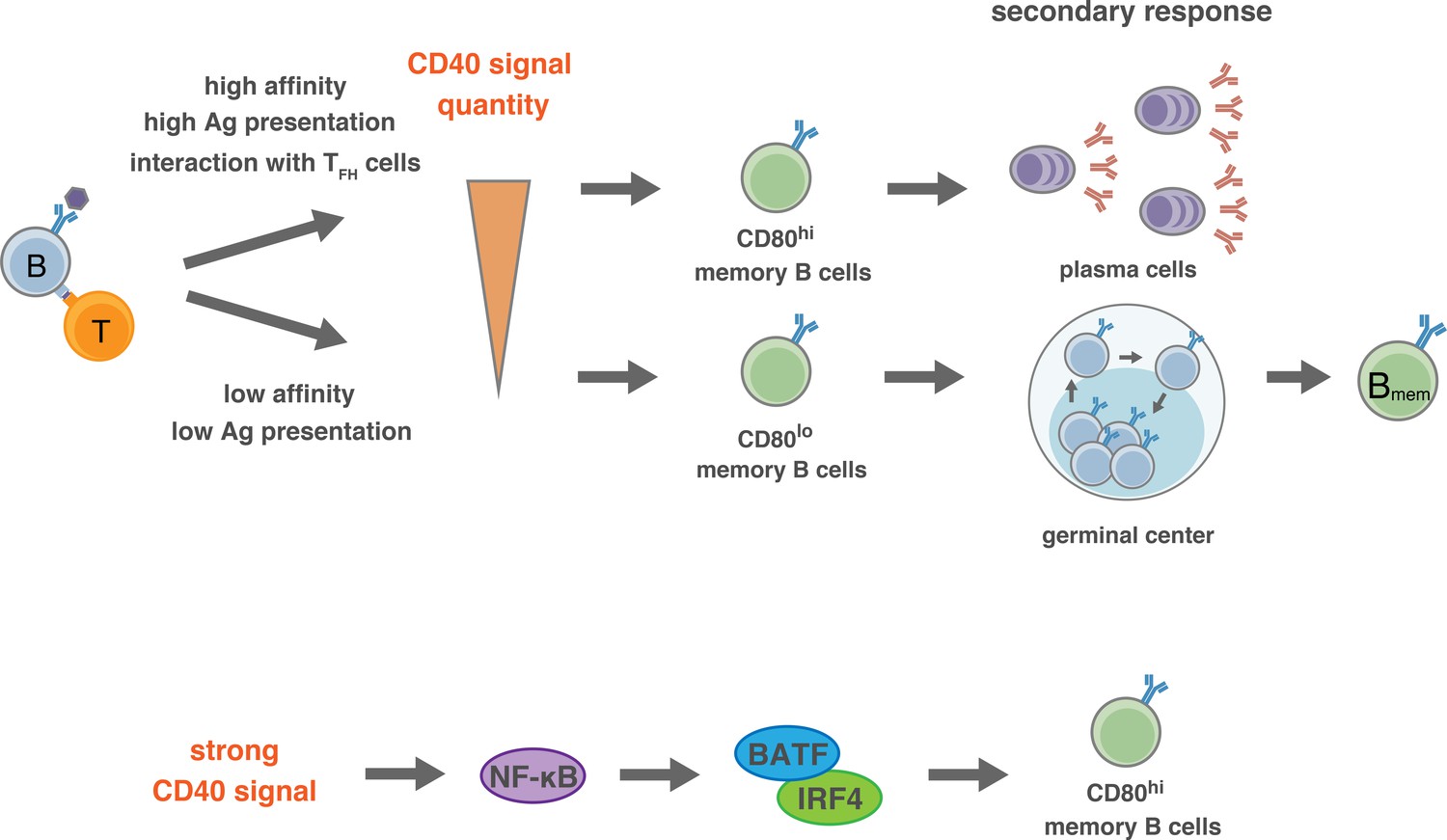
Two processes are necessary to produce plasma cells. First a naïve B cell must present an antigen to a helper T cell. The now-activated T cell must in return switch on the B cell.
This double authentication process turns a naïve B cell into an activated B cell. Only an activated naive B cell can divide to produce plasma cells or memory cells. When a naïve or memory B cell is activated by antigen with the aid of a helper T cell it proliferates and differentiates into an antibody-secreting effector cell.
Such cells make and secrete large amounts of soluble rather than membrane -bound antibody which has the same unique antigen-binding site as the cell-surface antibody that. The brain simmers with activity. Different groups of neurons nerve cells responsible for different thoughts or perceptions drift in and out of action.
Memory is the reactivation of a specific group of neurons formed from persistent changes in the strength of connections between neurons. At conclusion of primary immune response two sets of long-lived cells remain. Memory B cells On secondary exposure to the same antigen the memory B cells will be stimulated and result in production of high-affinity heavy-chain class- switched antibodies.
Making Memory B Cells. Memory B cells are a B cell sub-type that are formed following a primary infection. In the wake of the first primary response infection involving a particular antigen the responding naïve cells ones which have never been exposed to the antigen proliferate to produce a colony of cells.
Memory cells are formed from T-lymphocytes because memory T cells have the ability to recognized specific antigen. They will activate a stronger and faster immune response after they come across the same antigen again. So the correct answer is T-lymphocytes Answer verified by Toppr.
Most of these cells then die and memory cells are thought to be formed in low numbers. These are continuously exposed to cytokines chemicals that cells produce and they are then ready and primed so that when the infection happens again they can be reactivated in a quicker response. A normal naïve adaptive response can take 72 hours whereas.
B memory cells are there and they maintain persistence specific elevated antibodies life timeif new antigen trigger is there stimulated B cells cause production of antibodiesso in. Germinal centre-independent memory B cells are generated from CD38 GL7 activated B cells. These memory B cells may maintain broad reactivity to.
Activated by the binding of an antigen to a specific matching receptor on its surface a B cell proliferates into a clone. Some clonal cells differentiate into plasma cells which are short-lived cells that secrete antibody against the antigen. Memory cells begin in bone marrow.
A memory cell starts its life in the bone marrow where lymphocytes are made. It is then transported around the body in lymph a clear liquid that among other functions transports lymphocytes to regions of infection. Lymph is transported around the body via the lymphatic system a network of vessels and tissues throughout the body.
Toward the end of each battle to stop an infection some T-cells and B-cells turn into Memory T-cells and Memory B-cells. As you would expect from their names these cells remember the virus or bacteria they just fought. These cells live in the body for a long time even after all the viruses from the first infection have been destroyed.
Model A supports the hypothesis that memory T cells are derived from naïve T cells. Model B suggests that a subset of effector cells gives rise to memory T. Memory cells arise from T-cell dependent reactions in the germinal center and are the critical cell type for immune response to re-challenge from an antigen.
Although like plasma cells memory B cells differentiate from the GC reaction they do not secrete antibody and can persist independently of. GCs containing rapidly proliferating cells ie centroblasts were first described in 1884 but were identified as the main site for high-affinity antibody-secreting plasma cell and memory B-cell generation a century later. 57 It is within GCs where SHM and purifying selection produce the higher affinity B-cell clones that form the memory.