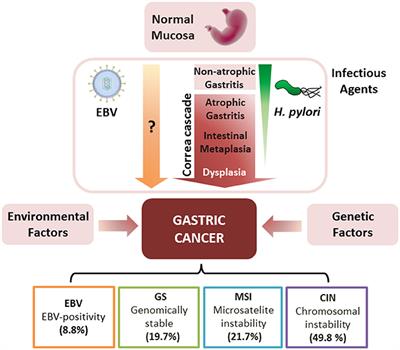
Pylori with the development of gastric cancer. However some clinicians still doubt the causal association of H.
Pylori are also up to 8 times more likely to get a certain kind of stomach or gastric cancer.
Helicobacter pylori and cancer. Helicobacter pylori and Cancer What is Helicobacter pylori. What is gastric cancer. What evidence shows that H.
Pylori infection causes non-cardia gastric cancer. What is the evidence that H. Pylori infection may reduce the risk of some cancers.
Pylori infection decrease the risk of. Yes infection with Helicobacter pylori H. Pylori increases the risk of some cancers But it can decrease the risk of oesophageal cancer For most people H.
Pylori will not cause any problems and it can be treated. Helicobacter pylori is a gastric pathogen that colonizes approximately 50 of the worlds population. Pylori causes chronic inflammation and significantly increases the risk of developing duodenal and gastric ulcer disease and gastric cancer.
Helicobacter pylori is human gastric pathogen that causes chronic and progressive gastric mucosal inflammation and is responsible for the gastric inflammation-associated diseases gastric cancer and peptic ulcer disease. Specific outcomes reflect the interplay between host- environmental- and bacterial-specific factors. Helicobacter pylori is now well known as an important pathogen related to the development of gastric cancer.
However some clinicians still doubt the causal association of H. Pylori with the development of gastric cancer. To summarize the recent clinical data on the link between H.
Pylori and gastric cancer we reviewed related articles published over the past 3 years after the award of the. Helicobacter pylori and esophageal cancer risk. We conducted this meta-analysis to examine the association between Helicobacter pylori and esophageal adenocarcinoma EAC and esophageal squamous cell carcinoma.
We searched the PubMed database the ISI database and the references of the selected articles. Although gastric cancer has been investigated for centuries the association with Helicobacter pylori infection has been recognized for only the past few decades. Although the disease has been declining in most industrialized countries it remains the second most common cause of cancer death worldwide and is in theory a largely preventable disease.
We have gained many new insights and. Among the long-term consequences of H. Pylori infection is gastric malignancies particularly gastric cancer GC and gastric mucosa-associated lymphoid tissue MALT lymphoma.
Pylori has been recognized as a class I carcinogen by the International Agency for Research on Cancer. Despite a close causal link between H. Pylori infection and the development of gastric malignancies.
Gallbladder cancer GBC is a rare but leading cause of cancer-related deaths worldwide. The incidence of GBC is increasing at an alarming rate in the Varanasi region and its etiology remains obscure. A total of 108 patients 54 with GBC and 54 with gallstone diseases GSD were examined for Helicobacter pylori H.
Pylori in gallbladder specimens by rapid. Helicobacter pylori was classified by the World Health Organization as a type I carcinogen in 1994 1 2Approximately 89 of non-cardia gastric cancers GCs accounting for 78 of total GCs are attributable to H. Pylori infection Several randomized controlled trials have demonstrated a reduction in the risk of developing primary and secondary GC after the removal of H.
Helicobacter pylori infection is the most important risk factor for gastric cancer but no association with cardia cancer has been recognized. However a heterogeneous distribution of etiologically distinct types of cardia cancer may contribute to explain conflicting findings between studies in high- and low-risk settings. We aimed to quantify the association between H.
Background Recent studies and clinical samples have demonstrated that Helicobacter pylori could induce the downregulation of miR375 in the stomach and promote gastric carcinogenesis. Gastric cancer is strongly associated with Helicobacter pyloriH. We conducted a previous systematic review and meta-analysis that suggested eradication therapy reduced future incidence of gastric cancer but effect size was uncertain and there was no reduction in gastric cancer-related mortality.
Pylori and Gastric Cancer. Studies have linked Helicobacter pylori H. Pylori infection with the development of gastric stomach cancer.
Pylori is a spiral-shaped bacterium that lives in the stomach and duodenum the section of intestine just below the stomach. It has the ability to adjust to the harsh conditions in the stomach. Helicobacter pylori is a gram-negative spiral-shaped bacteria that is found in half the worlds population.
In the United States estimates suggest about 35 of the population is infected. H pylori infection is believed to occur most commonly through the oral-to-oral or fecal-to-oral route. A chronic inflammatory response occurs to some degree in all individuals who are infected with H pylori.
Infektionen mit Helicobacter pylori sind ein Risikofaktor für Magenkrebs. Womöglich begünstigen sie aber auch die Entstehung von Darmkrebs wie Wissenschaftler jetzt aus einer Studie in der Fachzeitschrift Cancer Epidemiology Biomarkers Prevention berichteten. There is biological plausibility as to why infection with Helicobacter pylorithe leading cause of gastric cancer may also increase the risk of colorectal cancer but.
Studies show that people who are infected with H. Pylori are also up to 8 times more likely to get a certain kind of stomach or gastric cancer. But this bacterium is only one possible cause of.
