JupiterimagesComstockGetty Images Fungus that resides in the stomach is actually Candida yeast on most occasions. While researchers focused on how bacteria can positively or negatively affect the human gut Dr.

Viruses protists archaea and fungi.
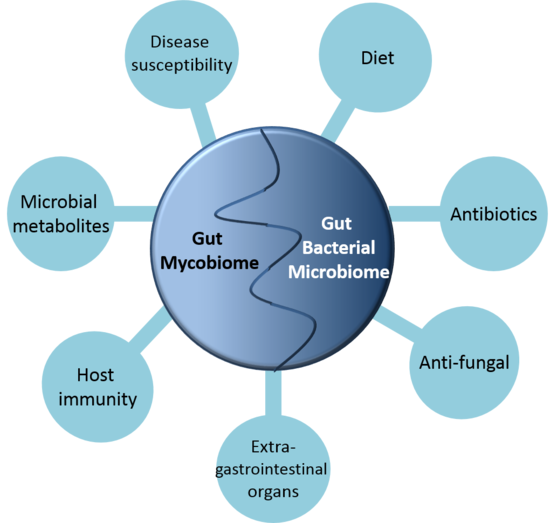
Fungus in human gut. This includes a diversity of fungal species that is collectively referred to as our mycobiome. Although research into the mycobiome is still in its infancy its potential role in human disease is increasingly recognised. Here we review the existing literature available on the human mycobiota with an emphasis on the gut mycobiome including how.
Common fungi often present in the gut teach the immune system how to respond to their more dangerous relatives according to new research from scientists at. There are 50 different species of fungi living in the gut alone. While researchers focused on how bacteria can positively or negatively affect the human gut Dr.
Ghannoum was the only one to discover the importance of fungi in the digestive system. Many types of fungi live in and on the human body including the genus of yeasts known as Candida. Candida is typically found in small amounts in the mouth and intestines and on the skin.
Malassezia is a genus found on the skin of mammalians and associated with numerous conditions from dandruff to atopic eczema or pityriasis36 Despite that Malassezia clearly belongs to the human skin microbiota species of this genus have been frequently identified in the human gut microbiota suggesting possible colonisation of the gut7 Indeed the genome of Malassezia shows the presence. JupiterimagesComstockGetty Images Fungus that resides in the stomach is actually Candida yeast on most occasions. Candida is a yeast that when you have too much in your body it is bad for you and if you have too little it is bad for you as well.
It has to remain balanced in order to do your body good. It causes white lesions that look like cottage cheese on your tongue or inner cheeks. It may also lead to soreness or burning and can spread to other parts of your mouth or throat.
Oregano Oil of oregano has many antibacterial and antifungal properties Garlic Fresh crushed garlic is a potent antimicrobial and immune booster. Citrus seed extract The phytochemicals in citrus seeds have been found to have potent antimicrobial properties. Fungi are ubiquitous transient or persistent human colonisers and form the mycobiome with shifts in niche specific mycobiomes dysbiosis being associated with various diseases.
These complex interactions of fungal species with the human host can be viewed as a spectrum of symbiotic relationships ie. Commensal parasitic mutualistic. 5 2021 Studies of the microbiome in the human gut have largely overlooked non-bacterial microbes.
Viruses protists archaea and fungi. The human body is home to a complex and diverse microbial ecosystem that plays a central role in host health. This includes a diversity of fungal species that is collectively referred to as our mycobiome.
Although research into the mycobiome is still in its infancy its potential role in human disease is increasingly recognised. The role of the gut in our overall well-being seems to grow bigger with every new study. But while attentionand research dollarshave focused on the importance of bacteria in our gut a crucial player in digestive and general health has been largely overlooked by most.
In humans fungal infections occur when an invading fungus takes over an area of the body and is too much for the immune system to handle. Fungi can live in. The complex microbial community hosted in the gastrointestinal tract GIT of humans and animals is composed of bacteria archaea fungi protozoa and viruses Qin et.
Common fungi often present in the gut teach the immune system how to respond to their more dangerous relatives according to new research from. The fungal microbiota is an important component of the human gut microbiome and may be linked to gastrointestinal disease. Albicans is the major fungal species in the human gut.
While several species of the genus Candida are generally accepted as true gut symbiotic fungi Fiers et al 2019 C. Albicans is the most frequently detected fungus in faeces of healthy humans.