End walls may be truss-framed with field-assembled stud infill prefabricated in. The gable end frame is designed to transfer vertical loads from the roof to the continuous bearing wall below.

Vierendeel trusses are usually more expensive than conventional trusses and their use limited to instances where diagonal web members are either obtrusive or undesirable.
Frame with shear truss. Shear wall trusses used in post-frame buildings the truss in figure 1 is a parallel chord truss aka. Flat truss placed against the inside of exterior girts with its chords attached to adjacent posts. Note that the bottom truss web member has been.
Calculate the reactions at the supports of Frame and Truss - statically determinate and statically indeterminate automatically calculate bending moment and shear force of Frame and Truss. Variation of slope deflection method whereby all deformations of combined system of rigid frames and vertical shear trusses or walls are approximated by power series. Their arbitrary constants will.
A truss-frame consists of a roof truss and a floor truss joined by exterior wall studs. The wide variety of possible roof and floor truss designs and combinations is illustrated by figure 1. End walls may be truss-framed with field-assembled stud infill prefabricated in.
Shear wall-frame interaction for lateral load resistance is complex because shear walls deflect primarily in bending mode while frames deflect in shear mode. However the interaction between shear walls and frames is beneficial for high-rise buildings since the linkage and stiffness of the floor slab diaphragm and the stabilising elements give better lateral load resistance. Fazlur Khans structural systems classification Type 1 Shear Frames.
Semi-rigid and rigid Type 2 Interacting Systems. Frame with shear truss frame with shear belt outrigger trusses Type 3 Partial Tubular Systems. End channel frame with interior shear trusses Type 4 Tubular Systems.
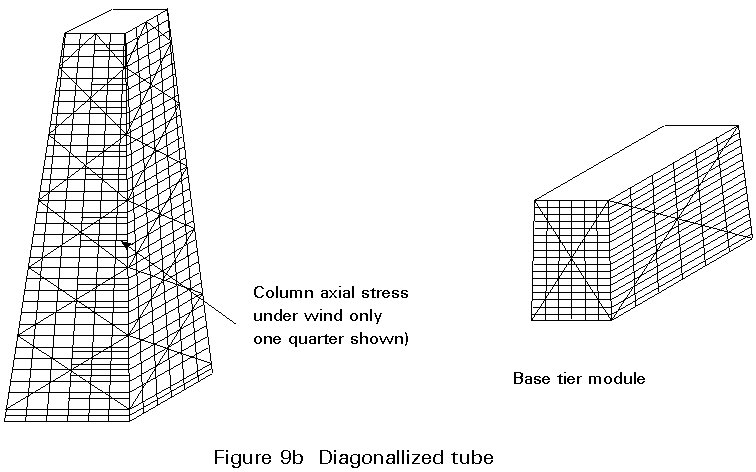
Exterior framed tube bundled frame tube exterior diagonalized tube. For low shear demand where changing framing direction helps HVAC runs Fire BlockingDraft Stopping N-S 4x8 sheathing Roof Trusses. Diaphragm Types SDPWS Tables 42A B.
Diaphragm Aspect Ratio SDPWS Table 424. Calculating Diaphragm Forces AWC Design Aid 6 Max Shear at Ends Max Moment. Space trusses and diagrids have been used to form two-way spanning roofs but the most common arrangement of truss roof construction uses one-way spanning elements.
A common form of truss is the Pratt truss or N frame with vertical shear elements in compression and diagonal shear elements in tension. This video shows the difference between truss structure and frame structure. Structure are classified into two types based on member forces.
Frame and Truss structures are designed to transfer loads from loading points to support points. Truss In a truss the joints are of pin type where end of the members can rotate freely. Moreover individual truss members should not directly loade.
Often times roof truss designs are designed by specific truss manufacturers and called out on the roof framing plan as design by others. Therefor drag trusses are often not included unless specifically requested by the engineer. When the trusses are oriented parallel to the wall the simplest method of connecting a braced wall panel to the rooffloor system above is to frame and sheath the wall up to the rooffloor deck above and attach the rooffloor sheathing to the double top plate of the braced wall panel with 6d common 0113 x 20 nails at 6 on center as shown in Figure 3.
Truss and frame both are constructed by some triangular members and connected at joints. So truss cannot transfer moments. Members are subjected to only.
Manufactured gable ends are actually frames even though they are often referred to as trusses. The webs are studs oriented vertically and usually spaced at 12 16 or 24 in. The gable end frame is designed to transfer vertical loads from the roof to the continuous bearing wall below.
Frame Element Stiffness Matrices CEE 421L. Matrix Structural Analysis Department of Civil and Environmental Engineering Duke University Henri P. Gavin Fall 2012 Truss elements carry axial forces only.
Beam elements carry shear forces and bending moments. Frame elements carry shear forces bending moments and axial forces. 22 Shear Truss and Frame System.
Shear trusses can be provided in the vertical direction if the organisation of the core permits such an arrangement. In general building core elements including elevator banks are centralized and will permit core trusses connecting columns in at least one direction. Open frame pavilions or where a truss serves to drag a lateral force between two shear wall segments.
Ultimately truss analysis software should be viewed as a tool available for developing proper member sizing and axial loads which can be used for detailing joinery and specifying fasteners. Elements in Vierendeel trusses are subjected to bending axial force and shear unlike conventional trusses with diagonal web members where the members are primarily designed for axial loads. Vierendeel trusses are usually more expensive than conventional trusses and their use limited to instances where diagonal web members are either obtrusive or undesirable.
Properly designed drag strut trusses shear walls or roof diaphragms and their connections will transfer lateral loads to the foundation and then safely into the ground.