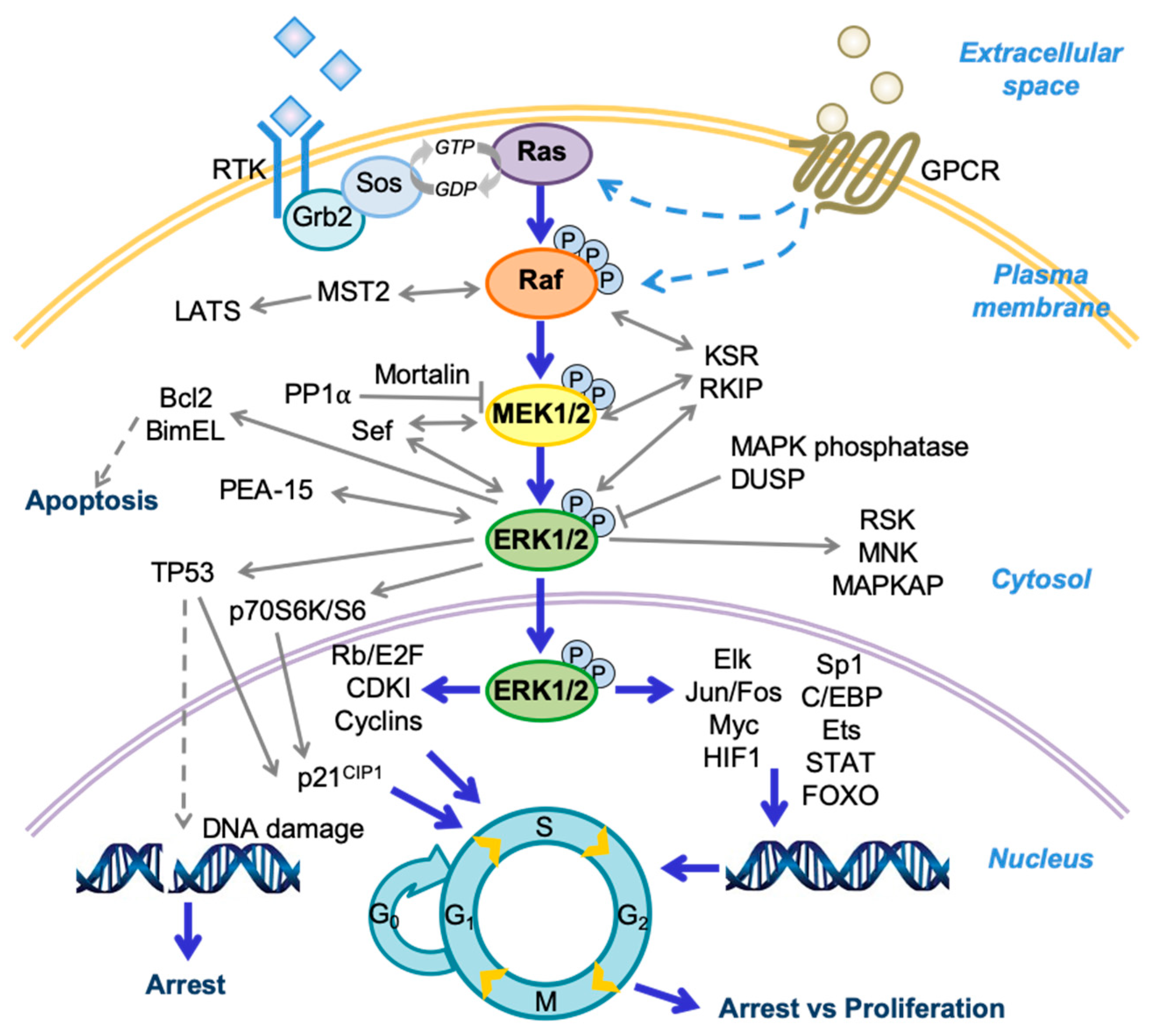
Historically ERK signalling was synonymous with cell. Since ERK1 and ERK2 are very similar the singular form of ERK is used in this review although two subtypes exist.

Overexpression and activation of this receptor are commonly detected in colorectal cancer and several lines of evidence indicate that overexpression and activation of ERK MAPK play an important.
Erk pathway and cancer. The extracellular signal-regulated kinase ERK signaling pathway is a major determinant in the control of diverse cellular processes such as proliferation survival differentiation and motility. This pathway is often up-regulated in human tumors and as such represents an attractive target for the development of anticancer drugs. Because of its multiple roles in the acquisition of a complex.
Excessive activation of upstream proteins and kinases in the ERK pathway has been shown to induce various diseases including cancer inflammation developmental disorders and neurological disorders 18 22. Since ERK1 and ERK2 are very similar the singular form of ERK is used in this review although two subtypes exist. The importance of suppressing the ERK signaling pathway has significant influence in drug therapy for cancer treatment.
There are currently multiple inhibitors that have reached clinical trial stage including BAY 43-9006 Raf Inhibitor PD184352 PD032591 and ARRY-142886 MEK 12 inhibitors9 In tumors the ERK pathway is upregulated and controls the cells ability to burgeon differentiate and. Deregulation of the ERK pathway Deregulation of the ERK pathway occurs in up to one-third of all cancers. Due to its anti-apoptotic and proliferative affects ERK12 is a central player in the propagation of many forms of cancer.
The ERK MAPK pathway is one of the most important for cell proliferation. The MAPK pathways are located downstream of many growth-factor receptors including that for epidermal growth factor. Overexpression and activation of this receptor are commonly detected in colorectal cancer and several lines of evidence indicate that overexpression and activation of ERK MAPK play an important.
When activated in cancer signaling through the MAPK pathway contributes to tumor progression through multiple mechanisms including the maintenance of activated cyclin D1CDK4 complexes which increases cell growth the suppression of proapoptotic molecules such as BIM which increases cell survival and through direct regulation of the cytoskeleton which contributes to. Mutations in components of the ERK pathway are a common occurrence in human cancer. Several drugs that target components of the ERK signalling cascade such as RAF MEK and ERK have been approved.
Downstream ERK kinase appears to be the Achilles Heel of the MAPK pathway. Targeting ERK kinase provides potential therapeutic opportunities for a broad spectrum of cancers bearing RAS RAF and MEK mutations as well as those with acquired. The ERK pathway is the best studied of the mammalian MAPK pathways and is deregulated in approximately one-third of all human cancers.
Historically ERK signalling was synonymous with cell. MAPK activation in colorectal cancer. The RasRafMEKERK cascade is involved in the control of growth signals cell survival and invasion in cancer.
This pathway includes several proto-oncogenes and is deregulated in about 30 of all cancers. During the process of oncogenic transformation colorectal-cancer cells escape from normal growth and differentiation control and. The extracellular signal-regulated kinase ERK pathway regulates cell growth and is hyper-activated and associated with drug resistance in hepatocellular carcinoma HCC.
Metabolic pathways are profoundly dysregulated in HCC. Whether an altered metabolic state is linked to activated ERK pathway and drug response in HCC is unaddressed. Ras in situ gene amplification and abnormal activation leading to a sustained expression of Ras was found in 30 of human cancers 13.
Raf family members Raf-1 B-Raf and A-Raf are Ras effectors and upstream activators of the ERK pathway. The extracellular signal-regulated kinase ERK signaling pathway is a major determinant in the control of diverse cellular processes such as proliferation survival differentiation and motility. Phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase PI3K is the most common altered pathway in ER-positive breast cancer.
It is unknown whether changes in the PI3K pathway result in a different composition of the breast tumor microenvironment. Here we present the retrospective analysis of a prospective randomized trial in ER-positive breast cancer on the prognostic and predictive value of specific tumor. The RB-pathway consisting of inhibitors and activators of cyclin-dependent kinases the retinoblastoma tumor suppressor RB and the E2F-family of transcription factors plays critical roles in the regulation of cell cycle progression and cell death.
Components of this pathway particularly p16Ink4a cyclin D1 and RB are frequently altered in sporadic human cancers to promote. While RAS mutations are the most common alterations can also occur at different or multiple stages of the pathway. Approximately 60 of non-small cell lung cancer have alterations in driver oncogenes including EGFR BRAF and KRAS.
18 Meanwhile 90 of pancreatic cancers are associated with KRAS mutations 19 and the majority of thyroid cancers are RAS or BRAF mutant.