Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress and Osteoporosis Osteoporosis OP is a common systemic metabolic disease in the elderly. ER function is indeed deteriorating with age see below.
Perturbations in the normal functions of the endoplasmic reticulum ER trigger a signaling network that coordinates adaptive and apoptotic responses.
Diseases associated with the endoplasmic reticulum. Endoplasmic reticulum ER dysfunction might have an important part to play in a range of neurological disorders including cerebral ischaemia sleep apnoea Alzheimers disease multiple sclerosis amyotrophic lateral sclerosis the prion diseases and familial encephalopathy with neuroserpin inclu. Endoplasmic reticulum ER dysfunction might have an important part to play in a range of neurological disorders including cerebral ischaemia sleep apnoea Alzheimers disease multiple sclerosis amyotrophic lateral sclerosis the prion diseases and familial encephalopathy with neuroserpin inclusion bodies. Recent progress in the understanding of neurodegenerative diseases revealed that multiple molecular mechanisms contribute to pathological changes in neurons.
A large fraction of these alterations can be linked to dysfunction in the endoplasmic reticulum ER and mitochondria affecting metabolism and secretion of lipids and proteins calcium homeostasis and energy production. Perturbations in the normal functions of the endoplasmic reticulum ER trigger a signaling network that coordinates adaptive and apoptotic responses. There is accumulating evidence implicating prolonged ER stress in the development and progression of many diseases including neurodegeneration atherosclerosis type 2 diabetes liver disease and.
Furthermore stroke or Alzheimers disease and Parkinsons disease occur more frequently with age suggesting that cellular senescence may lead to reduced tolerance of cells to conditions associated with ER stress. ER function is indeed deteriorating with age see below. Another possible common denominator contributing to ER dysfunction in acute and chronic diseases of the.
Endoplasmic reticulum ER stress has been known to be involved in the pathogenesis of various diseases particularly neurodegenerative disorders such as Parkinsons disease PD. We previously identified the human ubiquitin ligase HRD1 that is associated with protection against ER stress and its associated apoptosis. This article will review the genetic evidence implicating ERAP1 which encodes the endoplasmic reticulum-associated amino-peptidase 1 in susceptibility to rheumatic disease.
Genetic variants and haplotypes of ERAP1 are associated with AS psoriasis and Behçets disease in people of varying ancestries. Introduction The endoplasmic reticulum ER a vesicle-like structure that branches out from the nuclear membrane. 8 Zeilen Endoplasmic reticulum ER stress is induced in cells following stress caused by both internal.
Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress and Osteoporosis Osteoporosis OP is a common systemic metabolic disease in the elderly. It is characterized by bone pain decreased bone strength increased bone fragility and degeneration of bone tissue. Osteoporosis is marked by low bone mineral density BMD which is associated with endoplasmic reticulum stress.
Because of the key role of the endoplasmic reticulum ER in regulating protein homeostasis in the last decade multiple reports implicated this organelle in the progression of Parkinsons Disease PD and other neurodegenerative illnesses. In PD dopaminergic neuron loss or more broadly neurodegeneration has been improved by overexpression of genes involved in the ER. Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress and Osteoporosis Osteoporosis OP is a common systemic metabolic disease in the elderly.
It is characterized by bone pain decreased bone strength increased bone fragility and degeneration of bone tissue. Osteoporosis is marked by low bone mineral density BMD which is associated with endoplasmic reticulum stress. Metabolic disorders have become among the most serious threats to human health leading to severe chronic diseases such as obesity type 2 diabetes and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease as well as cardiovascular diseases.
Interestingly despite the fact that each of these diseases has different physiological and clinical symptoms they appear to share certain pathological traits such as. ALR Augmenter of liver regeneration. GRP75 glucoseregulated protein 75.
HBV hepatitis B virus. HBx hepatitis B virus X. HCV hepatitis C virus.
IMM inner mitochondrial membrane. Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum Alteration. Disease Bioinformatics Research of Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum Alteration has been linked to Endoplasmic Reticulum Alteration Spinal Cord Transection Injury Ulcer Spinal Cord Injuries Hypertrophy.
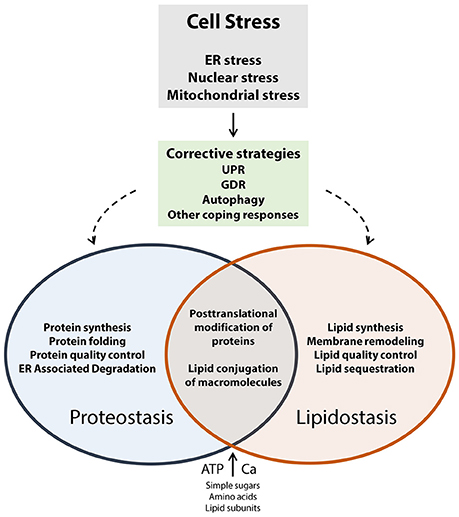
The Endoplasmic Reticulum ER has adopted a highly sophisticated stringent and conserved quality control mechanism known as ER-associated protein degradation ERAD to dispose of improperly folded secretory and membrane proteins and orphaned subunits of protein complexes Preston and Brodsky 2017. Sun and Brodsky 2019. The endoplasmic reticulum ER is a multifunctional organelle required for lipid biosynthesis calcium storage and protein folding and processing.
A number of physiological and pathological conditions as well as a variety of pharmacological agents are able to disturb proper ER function and thereby cause ER stress which severely impairs protein folding and therefore poses the risk of proteotoxicity.
