
1 representing the entire mandibular bone. Specific sites of the MBS offer enough bone quantity and adequate bone quality for mini-screw insertion.
Cortical bone stress distribution in mandibles with different configurations restored with prefabricated bar-prosthesis protocol.
Cortical bone in mandible. Cortical bone stress distribution in mandibles with different configurations restored with prefabricated bar-prosthesis protocol. A three-dimensional finite-element analysis. Epub 2010 Nov 18.
The geometrical distribution of the highest mineralized areas 1250 mgcm3 representative of mandibular cortical bone was determined by 3D reconstruction of the images. The length of the mandible on each side was determined by defining a new linear measurement from the centre of the 3D reconstructed condyle to the midline of the symphysis as identified from a submental view. This is different from cortical bone found in the mandibles of humans and some monkeys where the bone has greatest stiffness in one direction much less stiffness in another direction and an intermediate amount in the third orthogonal direction.
This difference suggests a relationship between levels of orthotropy and bending stress. The comparability of these elastic moduli to those of. The distal root of the mandibular second molar showed average bone depths of 1991 mm and 165 mm respectively.
All sites showed cortical bone depth thickness greater than 2 mm. Specific sites of the MBS offer enough bone quantity and adequate bone quality for mini-screw insertion. The insertion site with the optimal anatomic characteristics is the buccal bone corresponding to the.
Mineral density of the cortical bone of the mandible was determined by single-energy QCT quantitative computed tomography for 77 menopausal women. Bone mineral densities BMD were measured in the buccal and lingual layers of the cortex distally from the foramen mentale on both sides of the mandible. All the women were edentulous in that region and the alveolar processes were far.
Clinically hip fracture most frequently occurs in the femoral neck 49 50. Moreover the bone mass of the mandible cortical bone is a crucial factor that affects the survival rate of dental implants 51 52. Therefore in the present study we used micro-CT to evaluate the effects of ovariectomy in rats on the trabecular bone microarchitecture and cortical bone morphology in the.
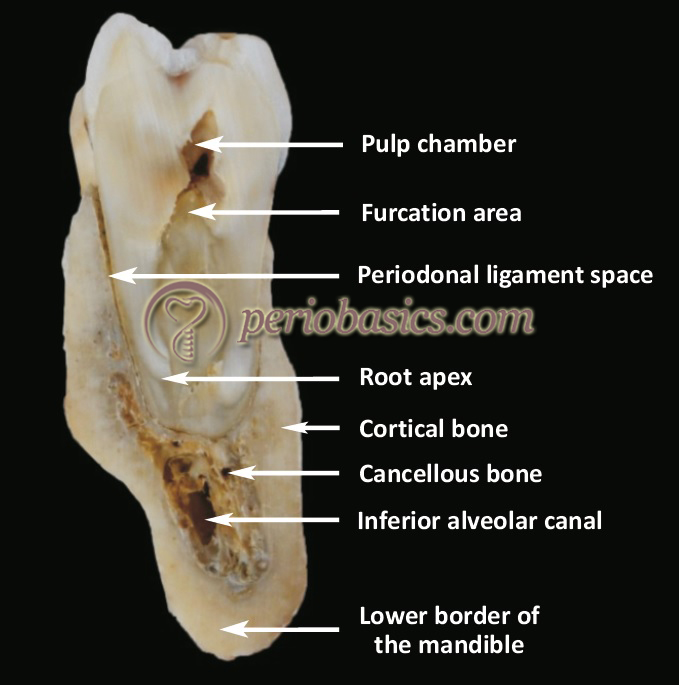
The biomechanical conditions of the mandible make this zone key to the stability of the mandibular arch and to the response to different biomechanical demands of daily functioning van Eijden 2000. The aim of this study was to quantify the cortical and cancellous bone in the mandibular symphysis and rela-te it to the teeth of the anterior area. MATERIAL AND METHOD A morphological study was.
Reconstruction of the canine mandible using bone transport distraction osteogenesis has been shown to be a suitable method for correcting segmental bone defects produced by cancer gunshots and trauma. Although the mechanical quality of the new regenerate cortical bone seems to be related to the mineralization process several questions regarding the microstructural patterns of the new bony. This study indicates that the trabecular bone in the human mandible possesses significantly higher density elastic modulus and ultimate compressive strength in the anterior region than in either the middle or distal regions.
The absence of cortical plates decreases the bone elastic modulus. These findings quantitatively confirm the need for clinical awareness in altering implant treatment. Fifty cone-beam computed tomography CBCT scans of hemi-mandibles were studied.
Linear measurements were taken from the buccal cortical plate to the tooth apex from the canine to the second premolar and from the buccal cortical plate to the tooth apex and the inferior alveolar canal in the molar area. 8 shows the distribution of the highest mineralized cortical bone within the mandible will vary among individuals. However the highest mineralized cortical bone always occupies certain regions of the mandible that include the corpus of the mandible and the anterior border of the ramus.
This pattern extends to include more regions of the mandible during growth. To test the mechanical properties of regenerate cortical bone created using mandibular bone transport MBT distraction five adult male American foxhound dogs underwent unilateral distraction of the mandible with a novel MBT device placed to linearly repair a 30-35 mm bone defect. The animals were sacrificed 12 weeks after the beginning of the consolidation period.
Distribution in the mandible. The number and distribution of the pixels were determined at three levels. 1 representing the entire mandibular bone.
2 the cortical bone at 60 above the baseline defined as the. Segmentation level around 1050 mgcm3 and representative of. In the mandible buccal cortical plate was thickest between first and second molar in all skeletal classes.
In the maxilla the highest cortical bone thickness for Class I subjects was between first and second molar for Class II subjects was between canine and first premolar and for Class III subjects was between first and second premolar. Printed in Great Britain CORTICAL BONE STRUCTURE OF THE PIG MANDIBLE KATHLEEN POWELL P. WOODHEAD Biological Research Unit and Department of Prosthetics Dental School and Hospital University of Leeds Leeds SummaryThe structure of pig mandibular bone was studied to provide base-line infor- mation for experimental implantation studies.
The density of samples of bone taken from the tooth-bearing part of the mandible provided overall information about bone. Cortical bone thickness minimum to maximum measurement ranges between the posterior teeth in the mandible at 6 mm from the CEJ on the right side41 Figure 25. Cortical bone thickness minimum to maximum measurement ranges.
To test the mechanical properties of regenerate cortical bone created using mandibular bone transport MBT distraction five adult male American foxhound dogs underwent unilateral distraction of the mandible with a novel MBT device placed to linearly repair a 3035 mm bone defect. The animals were sacrificed 12 weeks after the beginning of the consolidation period. Above and below the mental foramen the cortical bone for miniscrew anchorage was up to 3 mm thick.
At the level of the foramen the cortical plate will provide better anchorage and the insertion of miniscrews will be free of any risk of injuring the tooth roots or inferior alveolar canal.