
The aim of this study was to investigate the disease characteristics in CHCC patients and compare them with those in hepatocellular carcinoma HCC or intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma ICCThe perioperative and follow-up data of CHCC patients n 15 HCC patients n 577 and ICC patients n 61 were. Image studies of combined HCCCC may vary depending on whether HCC or CC is the.
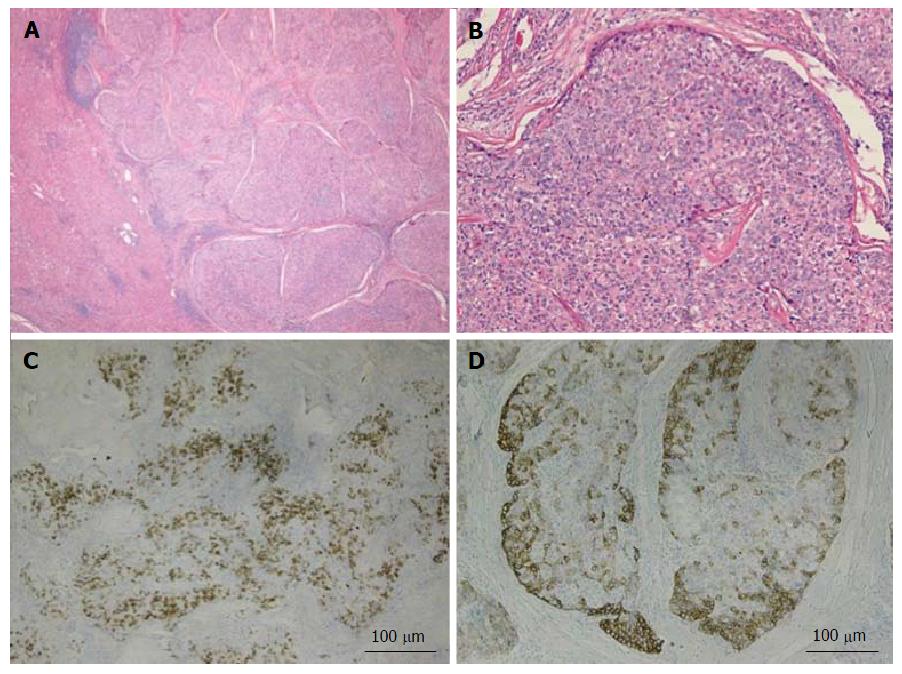
Combined hepatocellularcholangiocarcinoma HCCCC is a primary liver carcinoma with unequivocal presence of both hepatocellular and cholangiocellular biliary differentiation in the same tumor seen by the routine hematoxylin and eosin stain.
Combined hepatocellular cholangiocarcinoma pathology. Definition general. Combined hepatocellular carcinoma-cholangiocarcinoma cHCC-CC is a rare primary liver malignancy. CHCC-CC exhibits unequivocally both hepatocytic and biliary differentiation within the same tumor.
Collision tumors are excluded. Primary liver tumor composed of homogenous biphenotypic tumor cells called intermediate cell. Combined hepatocellular-cholangiocarcinoma is a rare primary neoplasm in the liver.
It has gained increasing recognition recently which in part may be due to more extensive sampling of the explants and surgical resection specimens the diagnostic challenges encountered in the clinical practice and the yet to be determined clinical outcome but partly may be attributed to its intriguing histogenesiscells of. Pathology of combined hepatocellularcholangiocarcinoma Introduction. Combined hepatocellularcholangiocarcinoma HCCCC also known as mixed HCCCC is a rare incidence.
Image studies of combined HCCCC. Image studies of combined HCCCC may vary depending on whether HCC or CC is the. Combined hepatocellularcholangiocarcinoma HCCCC is a primary liver carcinoma with unequivocal presence of both hepatocellular and cholangiocellular biliary differentiation in the same tumor seen by the routine hematoxylin and eosin stain.
Currently there is no requirement for the extent of each tumor type or confirmation by immunohistochemistry. The definition does not include. Combined hepatocellular-cholangiocarcinoma HCC-CC also known as mixed HCC-CC is a rare incidence among primary liver cancer ranges from 10 to 47 but an increasingly recog- nized primary malignant neoplasm in the liver14It shares.
Click on the article title to read more. Combined hepatocellular carcinoma and cholangiocarcinoma cHCC-CC is an uncommon subtype of primary liver cancer that has rarely been reported in large-scale clinical studies. The aim of this study was to clarify the clinical features treatment modalities and prognosis of cHCC-CC.
Combined hepatocellular cholangiocarcinoma CHC accounts for 04-142 of primary liver cancer cases and possesses pathological features of both hepatocellular carcinoma and cholangiocarcinoma. Since this disease was first described and classified in 1949 the classification of CHC has continuously evolved. The latest definition and classification of CHC by the World Health.
To determine the enhanced computed tomography CT and magnetic resonance imaging MRI characteristics of combined hepatocellular carcinoma and cholangiocarcinoma cHCC-CC in Chinese patients. Patients with histopathologically proven cHCC-CC n54 were compared with hepatocellular carcinoma HCC. N41 and cholangiocellular carcinoma CCC.
Histologic type is hepatocellular carcinoma with grade G2 - G3. Moderately to poorly differentiated. The tumor is confined to the liver and biliary and vascular margins are free of tumor.
No lymph nodes submitted or found. AJCC 8th edition pathologic stage is ypT2NX combined stage II and UNOS stage is T4a. Combined hepatocellular and cholangiocarcinoma is a more aggressive malignancy with a poorer prognosis than ordinary hepatocellular carcinoma HCC.
The reported frequency of combined hepatocellular and cholangiocarcinoma combined tumors varies widely. 10-65 among patients with primary liver cancer. Statistical data indicate that combined tumors occur predominantly.
Of Pathology University of Washington School of Medicine 1959 NE Pacific Street NE140D Box 356100 Seattle WA 98195 e-mail. Combined hepatocellular carcinoma-cholangiocarcinoma cHCC-CCA is a heterogeneous primary liver tumor with many phenotypes that have common features of both hepatocytic and cholangiocytic differentiation. A rare autopsy case of combined hepatocellular and cholangiocarcinoma occurring in a 54-year-old man with liver cirrhosis is presented.
Initial laboratory data included CEA 521 ngmL DUPAN-2 1600 UmL AFP 2 ngmL and negativity for hepatitis B surface antigen hepatitis B early antigen and hepatitis B core antibody. Ultrasonography and CT scan showed a large tumor node in the liver with ringed. The purpose of this study was to clarify characteristics of combined hepatocellular and cholangiocarcinoma HCC-CC on CT and clinicopathological examinations.
Dynamic incremental CT was performed on 15 combined HCC-CC patients. CT of the early phase was started at 30 s and of the late phase at 120-140 s after the start of contrast medium injection at a rate of 3 mls. Combined hepatocellular-cholangiocarcinoma CHCC is a rare type of primary liver cancer PLC.
The aim of this study was to investigate the disease characteristics in CHCC patients and compare them with those in hepatocellular carcinoma HCC or intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma ICCThe perioperative and follow-up data of CHCC patients n 15 HCC patients n 577 and ICC patients n 61 were. To evaluate gadoxetic acid-enhanced magnetic resonance imaging MRI findings of combined hepatocellular cholangiocarcinoma cHCC-CC with special emphasis on correlation of MRI findings with histopathologic tumor characteristics and survival outcomes after curative surgery. Our Institutional Review Board approved this study with a waiver of.
In humans combined hepatocellular-cholangiocarcinoma HCC-CC a rare but increasingly recognized primary malignant neoplasm of the liver unequivocally shares features of both hepatocellular carcinoma HCC and cholangiocarcinoma CC. Combined hepatocellular and cholangiocarcinoma with sarcomatous transformation was first recognized in Ramathibodi Hospital in 2005. This variant of carcinoma has been increasingly reported particularly from Asian countries.
Dedifferentiation of the epithelial component to various sarcomatous components is likely the underlying mechanism. The causative factors of hepatocarcinogenesis in.