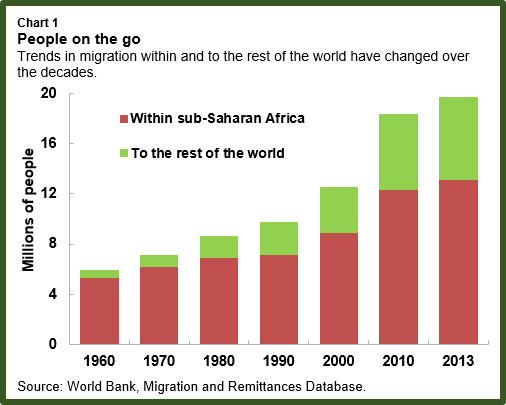
Migration contributes to the regional integration process in West Africa by enhancing trade commerce and enabling people-to-people contact from different societies. Conflict and violence also lead to internal and cross-border displacement.
An insoluble question as it is inadequate 32 The paradigm of autonomy.
Causes of migration in west africa. West Africa has experienced a variety of migrations caused by population pressure poverty poor economic performances and endemic conflicts. Gular migration from Sub-Saharan Africa SSA to Europe originates in West Africa. It is of the economic variety rooted in decades of policies which have impoverished rural economies and dis-possessed small-scale producers to make room for exported-oriented monocultures.
In the first half of 2018 the number of migrants entering through Spain has risen dramatically. Irregular African migration to Europe demands closer attention for several key reasons. First the movement of young and educated workers creates a brain drain in an already vulnerable region.
Root Causes and Regulatory Dynamics AMIREG There are an estimated 1 billion migrants in the world today and demographic imbalances economic inequality increased globalization political instability and climatic changes all forecast further episodes of large-scale migration in the coming decades. Migration contributes to the regional integration process in West Africa by enhancing trade commerce and enabling people-to-people contact from different societies. It strengthens the Economic Community of West African States ECOWAS established in 1975 which covers 51 million km² in comparison to 44 million square kilometres covered by the EU.
Request PDF Getting to the root causes of migration in West Africa whose history framing and agency counts. Todays irregular migration from Sub-Saharan Africa has its roots. Mobility within and out of the region takes place through temporary circular and more permanent movements principally for the purpose of labor but also for other reasons including personal or family reasons.
Conflict and violence also lead to internal and cross-border displacement. Transport sector by the Colonial government stimulated and altered large-scale. Population m ovements which gave rise to the m ale dom inated seasona l and cross -.
Border migration which later. Causes of migration The causes of migration may be numerous and these may range from natural calamities climatic change epidemics and draught to social economic cultural and political. The over population and heavy pressure on resources may be the cause of permanent or temporary and long distance or short distance migration.
The causes of migration may be numerous and these may range from natural calamities climatic change epidemics and drought to social economic cultural and political. The overpopulation and heavy pressure on resources may be the cause of permanent or temporary and long distance or short distance migration. Many a time the differences between groups in.
Conflicts inevitably cause population displacement. As intraregional mobility is limited by dense vegetation and the lack of interconnecting roads the majority of migrants move to Europe or other African. Migration is a well-entrenched tradition in West Africa and is mainly shaped by kinship and religious networks operating beyond the boundaries of national borders.
31 The causes of irregular migration. An insoluble question as it is inadequate 32 The paradigm of autonomy. A reversal of perspective looking at migrations through a new lens.
West and Central Africa face some of the worlds greatest challengesclimate change and desertification displacement due to conflict galloping population growth and a. Level using nationally representative surveys and focus group data collected in West Africa. Respondents in six West African countries cite economic factors as the reason for migrating and those who wish to stay claim family and love of country as the ties that bind.
The root causes perspective of migration has generally focused on material conditions and life circumstances and from this migration debates have centred largely around. Conflict and violence on the Horn of Africa. Poor governance in the Democratic Republic of the Congo DRC and Somalia.
Political instability in Burkina Faso. And socio-economic inequalities and a lack of solid. Conflict-induced migration itself a prominent feature in Africa.
The movement of skilled andor wealthy Africans is also generally viewed negatively eg.