C-peptide is considered the best function marker in recipients of an islet graft. Then glucose will be elevated again because theres no insulin again from dead pancreas.

Es wird bei der Aktivierung von Insulin vom Proinsulin abgespalten und gelangt mit dem Insulin in das Blut.
C peptide insulin level. C Peptide Insulin C Peptide Blood Level C Peptide Blood Insulin C-peptide measurement Measurement of C-peptide in blood for the evaluation and treatment of disorders related to abnormal insulin levels such. Used to identify patients who secretly self-administer insulin. Die Bestimmung von C-Peptid dient der Unterscheidung zwischen einem Diabetes mellitus Typ 1 und einem Typ 2 incl.
Bei Typ 1 finden sich erniedrigte C-Peptid-Konzentrationen da die Insulinsynthese gestört ist. Bei Diabetes mellitus Typ 2 sind die Werte anfangs erhöht im Spätstadium ebenfalls erniedrigt. Hilfreich bei der Unterscheidung ist der.
Das C-Peptid connecting peptide entsteht in den Betazellen des Pankreas. Es wird bei der Aktivierung von Insulin vom Proinsulin abgespalten und gelangt mit dem Insulin in das Blut. Hier weist es eine längere Halbwertzeit als Insulin auf.
Während das C- Peptid bisher nur als labordiagnostischer Parameter angesehen wurde weisen neuere Arbeiten auf ein eigenes Wirkungsprofil dieses Peptides. Furthermore C-peptide and insulin levels are a function of plasma glucose levels which will vary from visit to visit. Since type 2 diabetes is also characterized by insulin resistance insulin and C-peptide levels may be high early in the course of the disease as a compensatory response making it difficult to interpret results.
There is not a consensus as to which therapies may be more effective at any given C-peptide. Wann bestimmt man das C-Peptid. Im Labor wird der C-Peptid-Wert hauptsächlich bestimmt um die Leistung der beta-Zellen des Pankreas zu beurteilen.
Sind die beta-Zellen in der Lage Insulin zu produzieren kann auch C-Peptid nachgewiesen werden. Eine Einschätzung der Pankreas-Leistung ist auch wichtig für die Therapieplanung bei Diabetes also bei der Entscheidung ob ein. Lower HDL-C level was found to be significantly related to higher C-peptide levels.
Similarly TGL and C-peptide levels displayed a significant positive correlation. A significant negative correlation was observed between C-peptide quantiles and sensitivity. Thus insulin resistance showed a positive correlation until the fourth quantile.
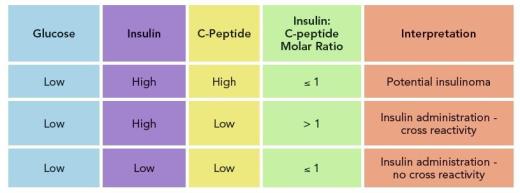
Fasting serum insulin and C-peptide levels progressively increased from the NGT to the diabetic subjects. Serum C-peptide was more strongly associated with newly diagnosed diabetes than insulin and was an independent factor associated with newly diagnosed diabetic subjects. High levels of c-peptide with a low level of blood glucose could be an indication of insulin resistance either type 2 diabetes or Cushings syndrome.
High levels of c-peptide but low blood glucose levels may be a result of insulinoma a tumour of the pancreas unless glucose lowering medication has influenced the result. High C-peptide levels indicate that your beta cells are still functioning properly and your likelihood of completely getting off of oral hypoglycemic drugs andor insulin injections is very high whereas low C-peptide levels indicate that your beta cell function has been permanently impaired and you may likely require insulin to control your blood glucose. Causes of a high C-peptide level include.
Tumors known as insulinomas insulin resistance kidney disease Cushing syndrome an endocrine disorder. Plasma glucose and serum C-peptide levels were determined before and after IV injection of 1 mg glucagon on three separate days in 21 type 2 diabetic subjects. Without pharmacological treatment and fasting plasma glucose 111 mmolL.
Fasting plasma glucose 4478 mmolL 1 h after withdrawing intravenous regular insulin infusion. And post lunch C-peptide levels are good indicators of insulin levels in the blood and pancreatic β-cell function. In contrast to this group Type II diabetes have features resembling that of metabolic syndrome and increased plasma C-peptide levels with clustering of cardiovascular risk factors.
Insulin and C-peptide are cosecreted into the. High c-peptide will cause high insulin levels and low glucose hypoglycemia until the pancreas beta cells destroy themselves. Then glucose will be elevated again because theres no insulin again from dead pancreas.
A low level of C-peptide can mean your body isnt making enough insulin. It may be a sign of one of the following conditions. Addison disease a disorder of the adrenal glands.
It may also be a sign that your diabetes treatment is not working well. A high level of C-peptide can mean your body is making too much insulin. It may be a sign of one of the following conditions.
C-peptide is considered the best function marker in recipients of an islet graft. 7 It is cosecreted with insulin in equimolar amounts but is cleared at a slower and less variable rate from the blood than insulin. 24 25 Unlike the latter C-peptide does not undergo a significant hepatic extraction which amounts to about 50 at first pass for insulin.
Peripheral C-peptide clearance occurs mainly via the kidney and. Equimolar amounts of C-peptide and insulin were found in serum of subjects with a wide range of insulin values. Thus the C-peptide level can be used as an indicator of beta cell secretory function.
This application is especially useful in diabetic patients who develop circulating insulin antibodies in response to exogenous bovine or porcine insulin therapy. Measurement of serum C-peptide.