Gram negative coverage a. Infection of orthopedic implants and the use of antibiotic-loaded bone cements.

Abstract Antibioticloaded bone cement ALBC is broadly used to treat orthopaedic infections based on the rationale that highdose local delivery is.
Antibiotic loaded cement in orthopedic surgery a review. Despite the widespread use of the antibiotic-loaded bone cement in orthopedics many issues are still unclear or controversial. Bacterial adhesion and antibiotic resistance modification of mechanical properties which follows the addition of the antibiotic factors influencing the release of the antibiotic from the cement and the role of the surface the method for mixing the cement and the antibiotic the choice. Infections in orthopaedic surgery are a serious issue.
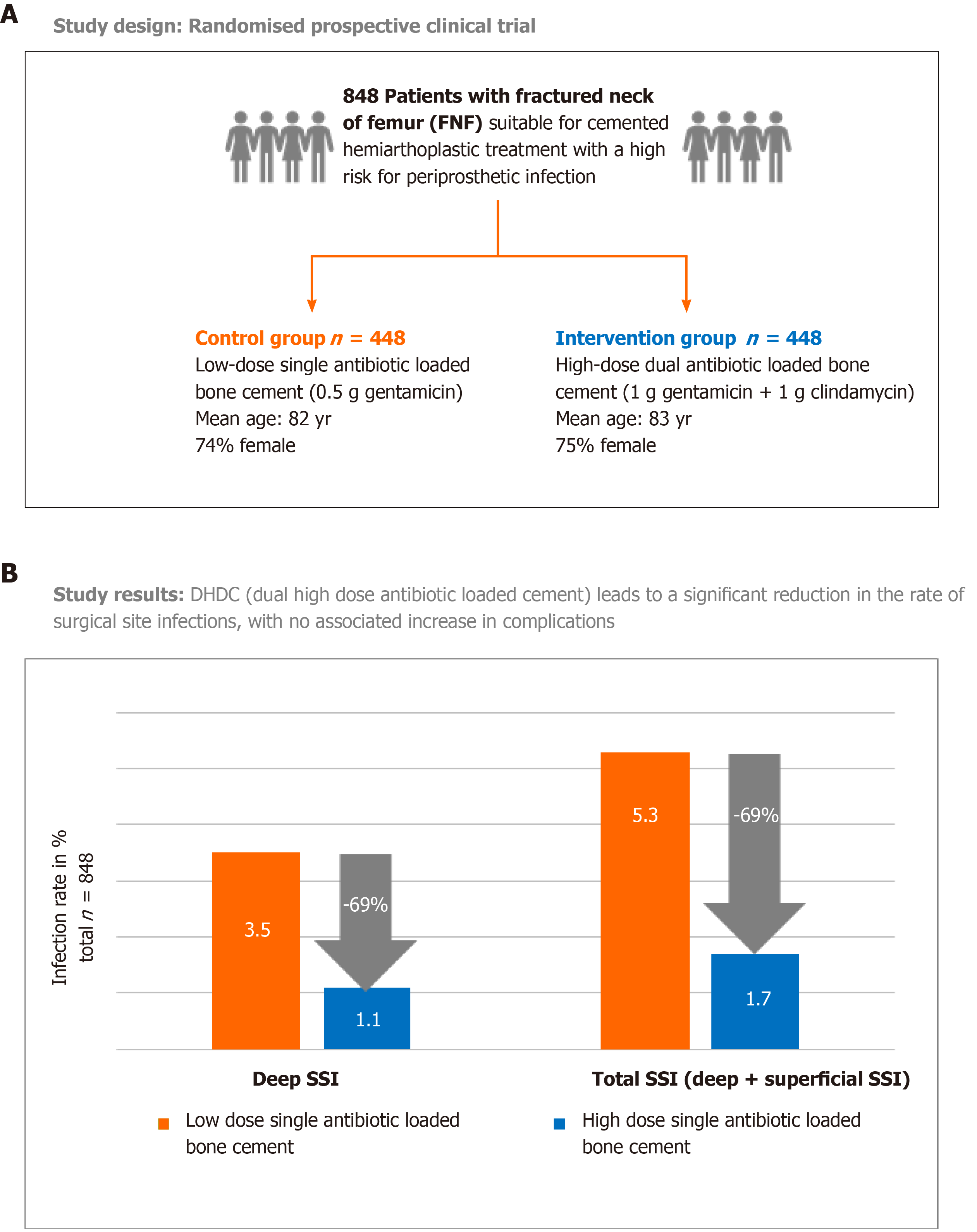
Antibiotic-loaded bone cement was developed for the treatment of infected joint arthroplasties and for prophylaxes in total joint replacement. The use of the antibiotic loaded cement in primary implants is indicated in patients with hag surgical risk in elder patients in patients with general health problems like immuno-depression diabetes history of previous prosthetic and periprosthetic infections and particular diseases such as rheumatoid arthritis and SLE or in conditions of malnutrition 33 34. In a study of 684 patients with total hip arthroplasty infection they obtained a 71 success rate after one-step prosthesis replacement with gentamicin-loaded cement but no systemic antibiotic treatment.
In a subsequent study by the same group a similar treatment program yielded a 77 success rate. Others reported similar success rates with one- or two-step replacement. Antibiotic loaded bone cement ALBC is used for prevention as well as treatment of orthopaedic infections.
Below is a short review of salient points and practical tips regarding antibiotic loaded cement. Antibiotics which can be used i. Gram positive coverage a.
Gram negative coverage a. Since the early 1970s the use of antibiotics in bone cement has been widespread. Antibiotic-loaded bone cement is used prophylactically in both primary and aseptic revision joint replacement surgery Buchholz et al 1984.
Espehaug et al 1997. A survey including a total of 25 controlled randomised trials published between 1966 and 1998 showed the overall rate of infection in THR surgery to be 1. Bone cement consisting of polymethyl methacrylate is a bioinert material used for prothesis fixation in joint arthroplasty.
To treat orthopedic infections such as periprosthetic joint infection antibiotic-loaded bone cement ALBC was introduced into clinical practice. 48 rows Currently polymethylmethacrylate PMMA is the most widely used bone. Antibiotic loaded bone cement can be customized intraoperatively to different shapes and forms.
In intramedullary infections antibiotic bone cement nails or antibiotic cement nails ACNs are preferable. Figure 1 presents an example of an ACN. They offer local delivery of antibiotics while filling the dead space and offering stability to the fracturenonunion site if present.
Acrylic cement is used to secure implants to bone. When mixed with antibiotics or anticancer agents acrylic cement slowly releases these agents while retaining its mechanical properties thus providing specific in situ treatment. The use of high-dose antimicrobial-loaded bone cement is generally considered safe.
Mean peak tobramycin serum levels reported in the literature range from 012 to 11µgmL. When given parenterally optimum peak serum concentration of tobramycin is between 6-10 µgmL and trough concentrations should be less than 2 µgmL. Hanssen classified antibiotic loaded bone cement into high dose 2 g antibiotic per 40 g of cement and low dose.
Abstract Antibioticloaded bone cement ALBC is broadly used to treat orthopaedic infections based on the rationale that highdose local delivery is. Polymethylmethacrylate PMMA has been extended from the ophthalmological and dental fields to orthopedics as acrylic cement used for fixation of prosthetic implants for remodeling osteoporotic neoplastic and vertebral fractures repair. The PMMA bone cement is a good carrier for sustained antibiotic release in the site of infection.
Infection of orthopedic implants and the use of antibiotic-loaded bone cements. Infections by bacteria are a serious complication following orthopedic implant surgery that can usually only be cured by removing the implant since the biofilm mode of growth of infecting bacteria on an implant surface protects the organisms from the host immune system and antibiotic therapy. Aminoglycoside-loaded bone cement ALBC implants are frequently used in orthopedic surgery.
Parenteral aminoglycosides are known to cause nephrotoxicity. Antibiotic-loaded bone cement was developed for the treatment of infected joint arthroplasties and for prophylaxes in total joint replacement in selected cases.