About Your CAC Score. Less than 10 meaning minimal to no calcium was found and those with scores of 11 to 99 who have a moderate amount of calcification.
The Agatston score for each calcified lesion is a function of the CAC area and the maximal CAC density.
Aj 130 calcium score. For example if a calcified speck has a maximum attenuation value of 400 HU and occupies 8 sq mm area then its calcium score will be 32. The score of every calcified speck is summed up to give the total calcium score. Grading of coronary artery disease based on total calcium score.
The calcium volume score is referred to as a measure to quantify coronary artery calcium and is a variant to calculate coronary artery calcium 1-3. Its calculation includes all voxels with a Hounsfield attenuation 130 and this is done by multiplying the volume of each voxel determined by the area and the slice thickness with the number of voxels showing calcification 1-3. AJ 130 scoring method uses conventional AgatstonJanowitz technique with a threshold of 130 HU which is adjusted to the appropriate image slice thickness.
Volume scoring calculates volumes mm3 of calcified plaque above the 130 HU threshold. Mass scoring calculates mass mg of calcified plaque above the 130 HU threshold. Calcium volume score - The calcium volume score has proven to be the most robust and reproducible method.
It is calculated by multiplying the number of voxels with calcification by the volume of each voxel including all voxels with an attenuation 130 HU. However this method is particularly sensitive to the partial volume especially in plaques with high attenuation and subject to variability. Coronary calcium score reflects the total amount of calcium within the walls of the coronary arteries taken together to provide a single number.
Its based on density and area. Coronary calcium score tells you nothing about arterial narrowing. One can have a high calcium score without any narrowing or blockages being present.
However a patient with high calcium score is more likely to have a significant narrowing affecting blood flow than a patient with low calcium score. Understand the meaning of your Agatston score. The lower the score the lower your risk of coronary heart disease.
There are four categories of scores. Less than 10 meaning minimal to no calcium was found and those with scores of 11 to 99 who have a moderate amount of calcification. A score between 100 and 399 is classified as increased calcification and any score over 400 signifies extensive calcium deposits.
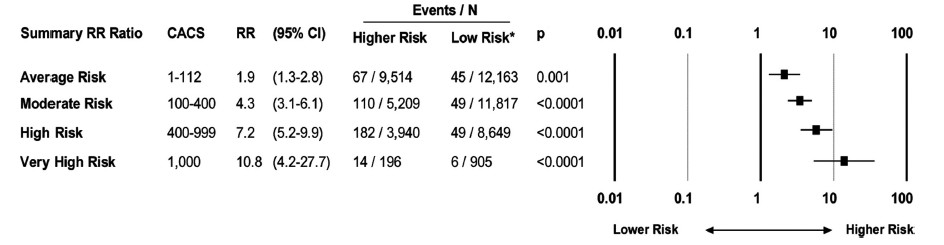
According to the American Heart Association if your Agatston score. Calcium scores from 81 to 400 identify individuals at increased risk for cardiac events and many of these individuals will be re-stratified to the intermediate-risk or high-risk groups. These individuals should be treated according to the secondary prevention guidelines of the American Heart Association with reduction of the LDL cholesterol to less than 100 mg as specified in the NCEP ATP III guidelines.
SmartScore 40 is designed to identify the presence of regional and global coronary artery calcification from a CT scan then measure and score the results. Scores can be calculated using a standard AgatstonJanowitz AJ method. When correlated with a patients personal information the score can yield an estimation of a patients risk for coronary artery disease.
A calcium score of 0-100 is still felt to be relatively low risk. With the predicted chance of an event over 10 years estimated to be around 2-6. A calcium score of 101-400 signifies intermediate risk of an event.
The predicted 10-year chance of an event is between 13-16. A calcium score of 400 signifies high risk of an event. Coronary artery calcium score distributions.
Coronary artery calcium scores ranged from 0 to 4058. The mean score standard deviation was 135 377 and the median was 4 25 th 75 th percentile. The prevalence of zero scores ranged from 80 among women younger than 50 years to 5 among men 70 years old or older.
Calcium in the coronary circulation roughly tracks the amount of plaque the higher the score the more plaque. Obviously a score of zero is optimal and a score of 300 or 400 depending upon who you listen to warrants further work-up like a treadmill test or nuclear study. A higher score does NOT correlate with the SEVERITY of any particular stenosis.
Your score is not. The 2013 ACCAHA Atherosclerotic CVD Risk Assessment Guidelines indicate that CAC score 300 or 75 percentile for age sex and ethnicity is a suitable cut-off for treatment decisions 143942 although CAC score 100 and CAC score 400 have also been published as appropriate cut-offs for predicting significant CVD risk and influencing treatment decisions 144344. Coronary artery calcium score results.
The amount of calcium detected in the coronary arteries is converted to a calcium score which correlates with the severity of the atherosclerosis. The score used is the Agatston score which is calculated from weighted density and area of the calcification identified. Scores are then used to define severity as follows.
The calcium score is of no benefit to someone who has already had a heart attack coronary bypass surgery or a coronary artery stent. These events already indicate a high risk. A calcium score cannot be used to see if any treatment is working or not.
Your doctor may decide that a second calcium score scan after a few years might be helpful to compare the results with the previous scan. The coronary calcium scan is a better predictor of coronary events than cholesterol screening or other risk factor assessments. About Your CAC Score.
A calcium score sometimes called an Agatston score is calculated based on the amount of plaque observed in the CT scan. It may be converted to a percentile rank based on your age and gender. The results from your cardiac scoring will be sent to.
The Agatston score for each calcified lesion is a function of the CAC area and the maximal CAC density. The total Agatston score is a simple sum of all CAC lesions. Contiguous voxels 130 HU are defined as a calcified lesion.
